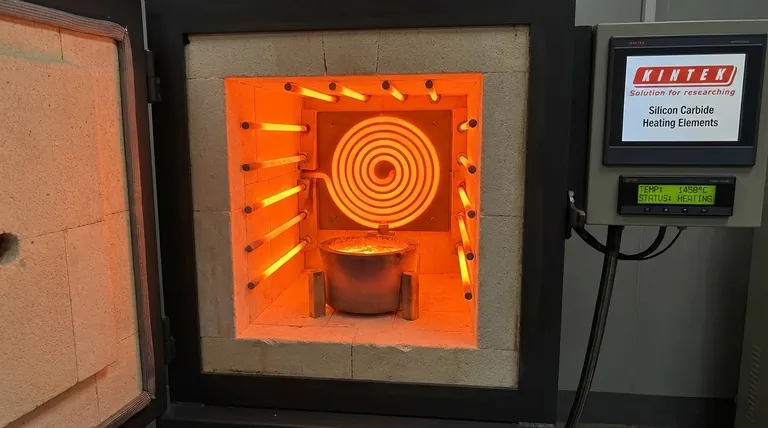
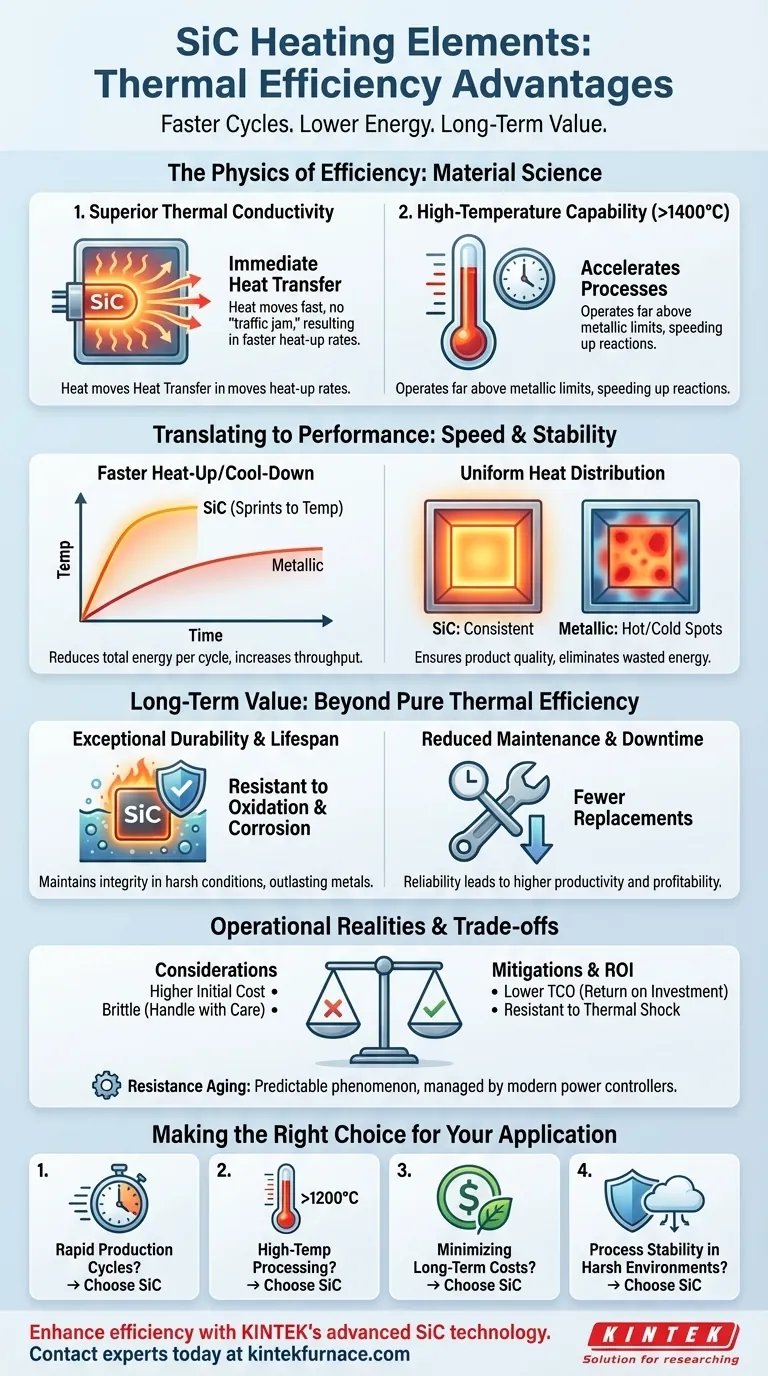
At its core, the thermal efficiency of Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements comes from two fundamental material properties: their ability to operate at extremely high temperatures and their excellent thermal conductivity. These characteristics allow them to transfer heat to a workload faster and more effectively than traditional metallic elements, directly reducing energy waste and shortening process cycle times.
The key advantage isn't just that SiC elements get hotter, but that they deliver that heat with superior speed and uniformity. This translates directly into lower energy consumption, faster production throughput, and ultimately, reduced operational costs.

The Physics Behind SiC's Efficiency
To understand the practical benefits of SiC, we must first look at the material science that drives its performance. Its advantages are not arbitrary; they are the direct result of its physical makeup.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
SiC possesses excellent thermal conductivity. This means heat generated within the element moves through it and radiates into your furnace or process chamber with minimal delay.
Unlike materials with lower conductivity that can create a "traffic jam" of thermal energy, SiC ensures the energy you pay for is put to work immediately. This results in faster heat-up rates and more uniform temperature distribution.
High-Temperature Capability
SiC elements can operate at process temperatures far exceeding the limits of most metallic alloys, often well above 1400°C (2550°F).
Operating at a higher temperature can dramatically accelerate many chemical reactions and physical processes. This means a given task can be completed in less time, which is a primary form of process efficiency, saving both time and energy.
Translating Properties into Performance
These physical properties create tangible advantages in an industrial or laboratory setting. The efficiency of SiC is most apparent in its speed and stability.
Faster Heat-Up and Cool-Down Cycles
Because SiC transfers heat so well, furnaces equipped with these elements reach their target temperature significantly faster.
This ability to "sprint" to temperature reduces the total energy consumed per cycle. For operations involving frequent heating and cooling, this leads to major improvements in throughput and substantial energy savings.
Uniform Heat Distribution
The high conductivity of SiC helps to eliminate hot and cold spots within a heating chamber. The entire element radiates heat evenly across its surface.
This uniformity ensures consistent product quality and prevents energy from being wasted on overheating certain areas while under-heating others.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Realities
While SiC offers compelling advantages, a complete technical assessment requires acknowledging its specific operational characteristics and trade-offs.
Higher Initial Investment
SiC heating elements typically have a higher upfront cost compared to common metallic elements like Kanthal (FeCrAl).
This cost should be evaluated against the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). The energy savings, longer lifespan, and reduced maintenance needs of SiC often provide a clear return on the initial investment over the element's life.
Brittleness and Handling
As a ceramic material, SiC is more brittle than ductile metal elements. It is susceptible to damage from mechanical shock or impact.
Care must be taken during installation and maintenance to avoid cracking the elements. However, their low coefficient of thermal expansion makes them highly resistant to thermal shock (breakage from rapid temperature change).
Resistance Aging
A key characteristic of SiC is that its electrical resistance increases gradually with use over time, a phenomenon known as aging.
This is not a defect but a predictable property. Your power control system must be able to compensate by delivering increased voltage over the element's lifespan to maintain constant power output. Modern SCR power controllers are designed specifically for this purpose.
The Long-Term Value: Beyond Pure Thermal Efficiency
The total value of SiC extends beyond simple energy calculations and includes its remarkable durability.
Exceptional Durability and Lifespan
SiC is highly resistant to both oxidation and chemical corrosion, even in aggressive, high-temperature atmospheres.
This allows the elements to maintain their structural integrity and performance for extended periods, far outlasting metallic elements in challenging conditions.
Reduced Maintenance and Downtime
The strength, durability, and long life of SiC elements mean fewer replacements and less frequent maintenance.
For any production environment, reduced downtime is a direct contributor to profitability. The reliability of SiC ensures your heating processes remain operational and productive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a heating element requires matching its capabilities to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid production cycles: SiC is the superior choice due to its fast heat-up rates, which minimize time between batches.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (>1200°C): SiC is one of the few practical and reliable options, significantly outperforming conventional metals.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operating costs: The combined energy savings, long service life, and low maintenance of SiC will often justify its higher initial price.
- If your primary focus is process stability in harsh environments: SiC's inherent resistance to oxidation and corrosion provides unmatched reliability and longevity.
Ultimately, choosing SiC is a strategic decision to invest in long-term performance, reliability, and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Superior Thermal Conductivity | Faster heat-up rates & uniform temperature distribution |
| High-Temperature Capability (>1400°C) | Accelerated processes & high-temperature reliability |
| Faster Heat-Up/Cool-Down | Reduced cycle times & significant energy savings |
| Exceptional Durability | Long lifespan & reduced maintenance in harsh environments |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and reduce operating costs with advanced SiC heating technology?
KINTEK's expertise in high-temperature furnace solutions, including our robust SiC heating elements, is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. We provide deep customization to precisely match your unique process requirements, whether you're using Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, or CVD/PECVD systems.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can deliver faster throughput, superior uniformity, and long-term reliability for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















