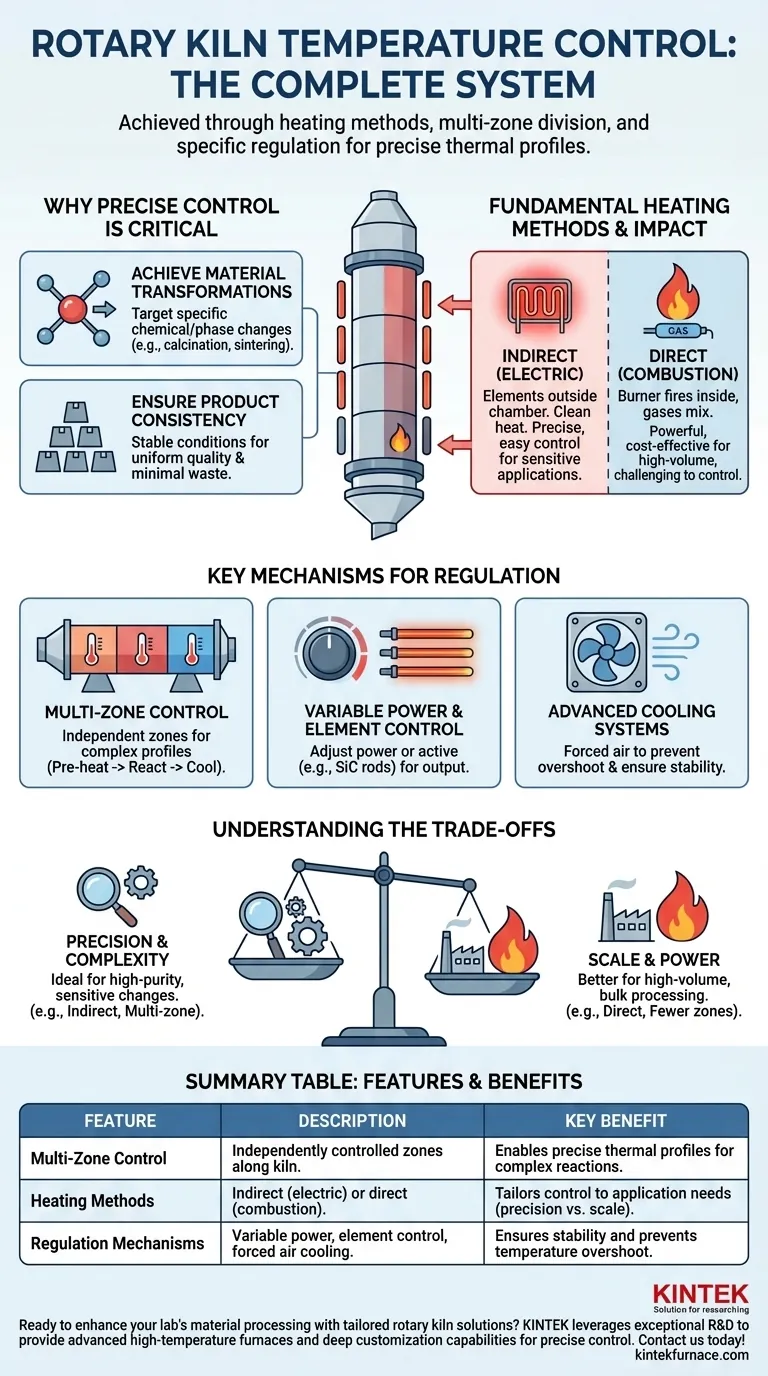
At its core, a rotary kiln's temperature is managed through a combination of its heating method, the division of the kiln into multiple, independently-controlled temperature zones, and specific regulation mechanisms. These systems can range from direct-fired burners to sophisticated multi-zone electric heaters, with temperature adjustments made by varying power to heating elements or using advanced air cooling to ensure stability.
The key to effective temperature control in a rotary kiln isn't a single feature, but a complete system design. The choice between direct or indirect heating and the number of control zones directly dictates your ability to create the precise thermal profile required for consistent, high-quality material processing.

Why Precise Temperature Control is Critical
Understanding the control features begins with understanding why temperature is the single most important variable in a kiln. The goal is not just to make something hot, but to achieve a specific material transformation.
Achieving Specific Material Transformations
At defined temperatures, materials undergo fundamental chemical reactions or phase changes. Processes like calcination (dissociating compounds), sintering (forming a solid mass without melting), or roasting (removing impurities) depend entirely on hitting and holding these exact temperature points.
Ensuring Product Consistency
Even minor temperature fluctuations can lead to inconsistent product quality, incomplete reactions, or wasted energy. Stable and precise temperature regulation ensures that every particle of material is processed under the same optimal conditions, from the first batch to the last.
Fundamental Heating Methods and Their Impact on Control
The most significant factor influencing temperature control is the kiln's primary heating method. This choice creates two distinct paths for regulation.
Indirect Heating (Electric)
In this design, electric heating elements are placed outside the rotating kiln chamber (the retort). Heat is transferred through the chamber wall to the material inside.
This method offers significantly easier and more precise temperature control. Because it doesn't involve combustion gases, the heat is clean and can be adjusted with high fidelity, making it ideal for sensitive applications.
Direct Heating (Combustion)
Here, a burner fires directly into the kiln chamber, and the hot combustion gases mix with the material. This method typically uses fuels like natural gas, propane, or oil.
Direct heating is powerful and often more cost-effective for very high-temperature or high-volume applications. However, controlling temperature with the same level of precision as an electric system can be more challenging.
Key Mechanisms for Temperature Regulation
Building on the primary heating method, several mechanisms are used to fine-tune the thermal process.
Multi-Zone Control
Modern kilns are rarely single-temperature vessels. They are divided into multiple separately controllable temperature zones along their length. For instance, a kiln might have three or four zones, each with its own thermocouple and control logic.
This allows you to create a specific heat pattern or thermal profile. Material can be pre-heated in the first zone, held at a peak reaction temperature in the middle zones, and cooled in the final zone, all within one continuous process.
Variable Power and Element Control
In electrically heated kilns, temperature is often managed by adjusting the power supplied to the heating elements. Some systems, particularly those using silicon carbide rods, work by varying the number of energized rods within a zone to increase or decrease the heat output.
Advanced Cooling Systems
Control isn't just about adding heat; it's also about removing it to prevent overshooting the target temperature. Forced air cooling systems can be used to blow ambient air over the kiln shell, providing a mechanism for rapid and stable temperature regulation, especially during cooldown phases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right temperature control system involves balancing precision, power, and complexity.
Precision vs. Scale
Indirect electric heating offers superior precision and is the clear choice for applications requiring tight temperature tolerances. However, direct-fired combustion kilns can often achieve higher throughput and reach extreme temperatures more economically, making them better for bulk material processing where pinpoint accuracy is less critical.
Flexibility vs. Complexity
A kiln with more independent heating zones provides incredible flexibility to create complex thermal profiles. However, each additional zone adds to the system's cost, control complexity, and maintenance requirements. A three-zone system might be perfect for one process, while another might require five or more.
Matching Control Features to Your Process
The ideal set of features depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity calcination or sensitive phase changes: Prioritize the precision of an indirect electric kiln with multiple, independent heating zones.
- If your primary focus is high-volume drying or bulk material reduction: The power and thermal efficiency of a direct-fired combustion kiln is likely the more practical solution.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex, multi-stage reaction: Select a kiln with the highest number of controllable zones available to give you maximum flexibility over the thermal profile.
By understanding these control principles, you can select a rotary kiln not just as a piece of equipment, but as a precise instrument for your material engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Zone Control | Independently controlled temperature zones along the kiln length | Enables precise thermal profiles for complex reactions |
| Heating Methods | Indirect (electric) for precision or direct (combustion) for high throughput | Tailors control to application needs |
| Regulation Mechanisms | Variable power, element control, and forced air cooling | Ensures stability and prevents temperature overshoot |
Ready to enhance your lab's material processing with tailored rotary kiln solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise temperature control to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















