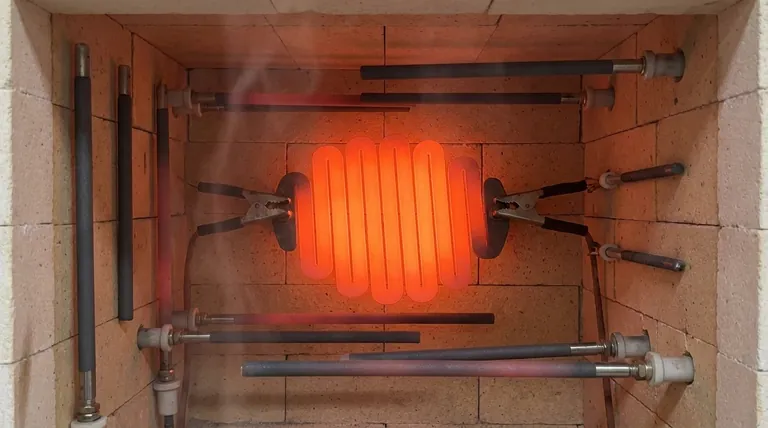
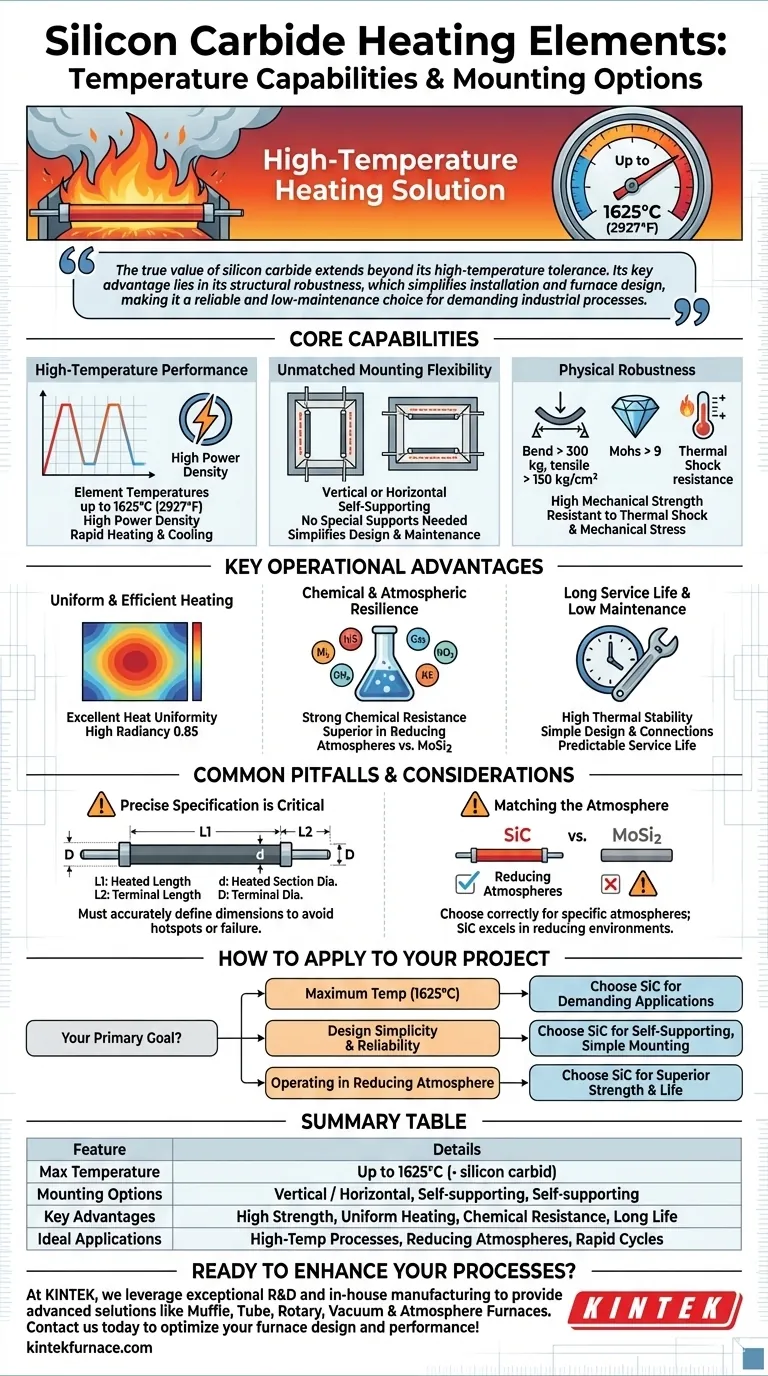
As a high-temperature heating solution, silicon carbide (SiC) elements can operate at element temperatures up to 1625°C (2927°F). Critically, their inherent physical strength allows them to be mounted either vertically or horizontally without the need for special supports, offering significant flexibility in furnace design and construction.
The true value of silicon carbide extends beyond its high-temperature tolerance. Its key advantage lies in its structural robustness, which simplifies installation and furnace design, making it a reliable and low-maintenance choice for demanding industrial processes.
Understanding the Core Capabilities
To properly evaluate SiC heating elements, you must first understand their fundamental performance and physical characteristics. These properties are the foundation of their utility in high-temperature environments.
High-Temperature Performance
Silicon carbide elements are engineered for extreme heat, capable of reaching element temperatures of 1625°C (2927°F).
This high-temperature capability is paired with a high power density, enabling rapid heating and cooling cycles that can significantly improve process throughput.
Unmatched Mounting Flexibility
A defining feature of SiC elements is their ability to be mounted both vertically and horizontally.
Unlike more fragile elements, their high mechanical strength means they are self-supporting. This eliminates the need for complex and costly ceramic hangers or supports within the furnace chamber, simplifying design and maintenance.
Physical Robustness
The installation flexibility of SiC elements is a direct result of their impressive physical properties. They possess a bend strength of over 300 kg and a tensile strength exceeding 150 kg/cm².
Furthermore, with a hardness over 9 on the Mohs scale and low thermal expansion, these elements are highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress during operation.
Key Operational Advantages
Beyond the core specifications, SiC elements offer several operational benefits that contribute to efficiency and reliability over the long term.
Uniform and Efficient Heating
SiC elements provide excellent heat uniformity due to their high thermal conductivity and a high radiancy of 0.85. This ensures consistent temperature distribution across the heated zone, which is critical for process quality.
Chemical and Atmospheric Resilience
These elements exhibit strong chemical resistance, making them suitable for a variety of process atmospheres.
Notably, they are stronger and more durable in reducing atmospheres when compared to alternatives like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements, making them a superior choice for specific chemical and metallurgical processes.
Long Service Life and Low Maintenance
The combination of high strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance results in a long, predictable service life. Their simple design and "easy connections" also contribute to low maintenance requirements.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While highly effective, the performance of SiC elements depends on correct selection and awareness of their operational context. Missteps here can undermine their benefits.
The Importance of Precise Specification
SiC elements are not one-size-fits-all. Their efficiency and lifespan are directly tied to specifying the correct physical dimensions for your equipment.
When ordering, you must accurately define the heated length (L1), terminal length (L2), heated section diameter (d), and terminal diameter (D). Any error in these critical dimensions can lead to improper power distribution, hot spots, or premature failure.
Matching the Element to the Atmosphere
While robust, the choice between SiC and other element types, like MoSi2, often comes down to the process atmosphere.
Failing to account for your specific atmosphere can lead to suboptimal performance. For example, using a less suitable element in a reducing atmosphere can cause rapid degradation, whereas SiC is specifically advantaged in this environment.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Selecting the correct heating element requires aligning its strengths with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum process temperature: SiC's capability to reach 1625°C makes it a premier choice for the most demanding thermal applications.
- If your primary focus is design simplicity and reliability: The self-supporting nature of SiC for both vertical and horizontal mounting radically simplifies furnace construction and reduces maintenance.
- If your primary focus is operating in a reducing atmosphere: SiC provides superior strength and a longer service life in these conditions compared to common alternatives.
By understanding these capabilities and considerations, you can confidently specify silicon carbide elements to achieve reliable and efficient high-temperature performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Up to 1625°C (2927°F) |
| Mounting Options | Vertical or horizontal, self-supporting |
| Key Advantages | High mechanical strength, uniform heating, chemical resistance, long service life |
| Ideal Applications | High-temperature processes, reducing atmospheres, rapid heating cycles |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable silicon carbide heating elements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your furnace design and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















