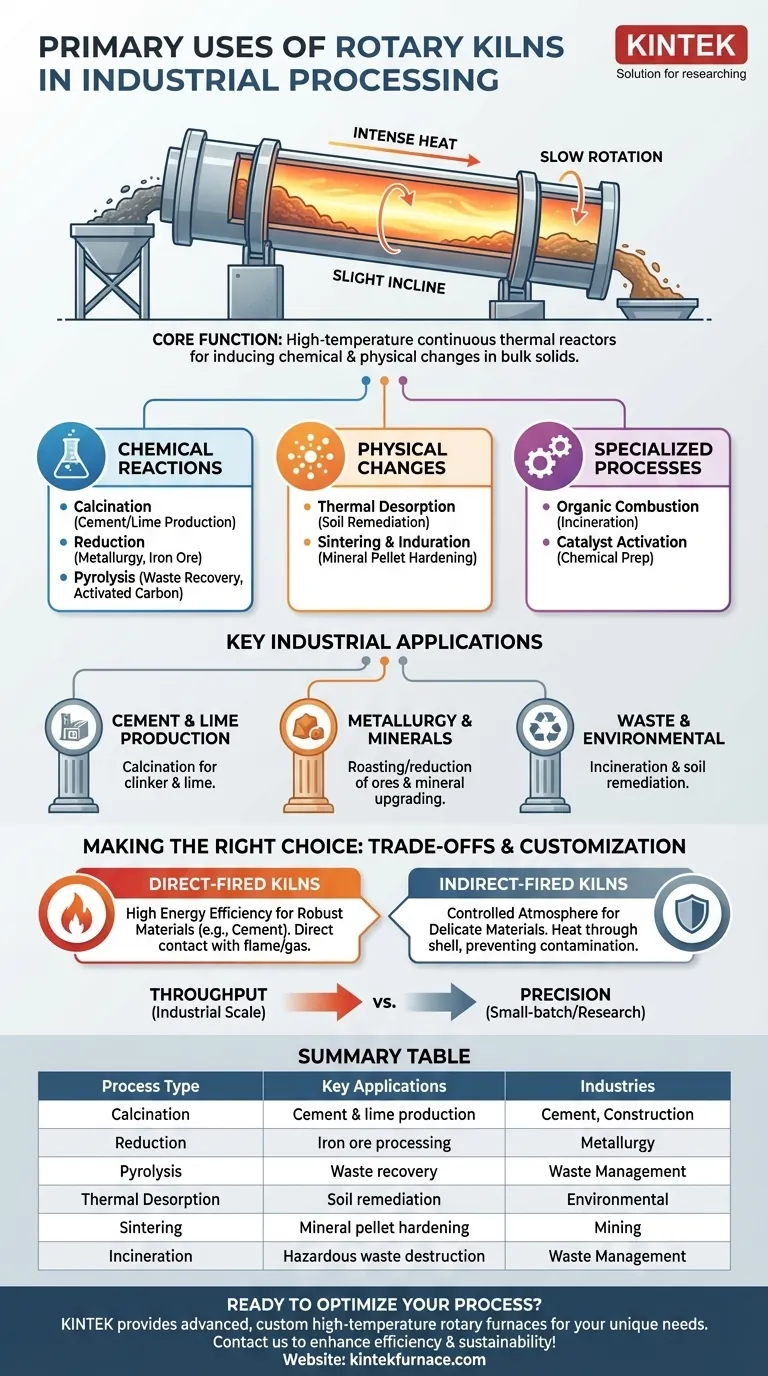
At their core, rotary kilns are the heavy-duty workhorses of high-temperature industrial processing. They are fundamental to major industries like cement and lime production, metallurgy for mineral and ore processing, and waste management. A rotary kiln uses a combination of intense heat, slow rotation, and a slight incline to induce critical chemical reactions and physical phase changes in solid materials as they flow from one end to the other.
A rotary kiln is not simply an industrial oven; it is a continuous thermal reactor. Its primary purpose is to use controlled high temperatures to transform the chemical or physical properties of bulk solid materials, making it indispensable for processes ranging from manufacturing cement to remediating contaminated soil.
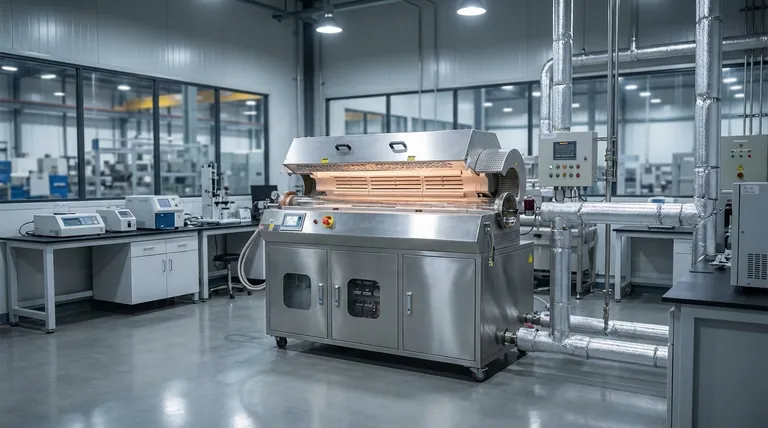

The Core Function: How Rotary Kilns Transform Materials
A rotary kiln's value comes from its ability to facilitate specific, high-temperature processes on a massive, continuous scale. It achieves this by controlling the material's residence time, temperature exposure, and atmospheric conditions inside the rotating drum.
Inducing Chemical Reactions
Many applications use the kiln to force chemical changes that would not otherwise occur.
Calcination is the most common process, where heat is used to decompose a material. This is central to producing cement from limestone and creating lime (calcium oxide) from calcium carbonate.
Reduction involves removing oxygen from a compound. In metallurgy, kilns are used for the direct reduction of iron ore, a key step in steel production.
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in an inert atmosphere (without oxygen). This is used in waste recovery and to produce substances like activated carbon.
Driving Physical Changes
Other processes focus on altering the physical state of a material rather than its chemical makeup.
Thermal Desorption uses heat to vaporize and remove volatile contaminants from a solid medium, such as cleaning up contaminated soil or industrial sludge.
Sintering and Induration involve heating granular material until the edges of its particles fuse together, creating a single, hardened mass without fully melting. This is used to strengthen mineral pellets.
Enabling Specialized Processes
The controlled environment of a kiln supports a range of highly specific industrial tasks.
Organic Combustion or incineration is used in waste management to safely and completely burn organic materials, reducing waste volume and destroying hazardous compounds.
Catalyst Activation is a critical step in the chemical industry, where a kiln's precise temperature control is used to prepare catalysts for use in manufacturing processes.
Key Industrial Applications
The principles of thermal processing are applied across a diverse range of industries, each leveraging the kiln for a specific outcome.
Cement and Lime Production
This is the quintessential application for rotary kilns. Raw materials are fed into the kiln and heated to extreme temperatures to drive the calcination process, which chemically creates the clinker that is ground to make cement.
Metallurgy and Mineral Processing
Rotary kilns are used to roast or reduce various metal ores, such as iron, to extract the desired metals. They are also used to upgrade non-metallic minerals, like processing phosphate ore for use in fertilizers.
Waste Management and Environmental Remediation
In the environmental sector, kilns are used for the thermal destruction of hazardous industrial waste through incineration. They are also deployed for soil remediation, using thermal desorption to remove pollutants like hydrocarbons from the ground.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, the choice to use a rotary kiln—and which type to use—involves key trade-offs based on the specific process requirements.
Direct-Fired vs. Indirect-Fired Kilns
A direct-fired kiln is highly energy-efficient because the flame and combustion gases make direct contact with the material. This is ideal for robust materials like cement and lime.
An indirect-fired kiln heats the material through the shell of the rotating drum, ensuring no contact with combustion byproducts. This is essential for processing delicate materials, preventing contamination, or running processes in controlled atmospheres, though it is less thermally efficient.
Throughput vs. Precision
Rotary kilns excel at processing a high-volume, continuous flow of bulk solids. Their design is built for industrial-scale throughput. This makes them less suitable for small-batch processes that require absolute temperature uniformity for every single particle.
The Value of Customization
"Rotary kiln" is a broad term. Designs are highly customized for their application. Kilns with integrated heat exchangers are chosen for energy efficiency, while smaller, modular kilns are built for research, pilot plants, and specialized, lower-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate kiln design is critical for achieving operational efficiency and desired product quality.
- If your primary focus is high-volume bulk material processing (like cement or lime): A direct-fired kiln offers the highest thermal efficiency and throughput for robust materials.
- If your primary focus is material purity or processing delicate substances: An indirect-fired kiln is necessary to prevent contamination from combustion gases and maintain a controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and sustainability: A system with integrated heat exchangers is critical for recovering and reusing waste heat from the process.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or small-scale production: A modular kiln provides the flexibility, smaller footprint, and precise control needed for pilot-scale testing and validation.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's enduring value lies in its ability to serve as a customizable, continuous thermal reactor for a vast range of industrial transformations.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Cement and lime production | Cement, Construction |
| Reduction | Iron ore processing for steel | Metallurgy |
| Pyrolysis | Waste recovery and activated carbon | Waste Management |
| Thermal Desorption | Soil remediation | Environmental |
| Sintering | Mineral pellet hardening | Mining |
| Incineration | Hazardous waste destruction | Waste Management |
Ready to optimize your industrial processing with a custom rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored for industries like cement, metallurgy, and waste management. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and sustainability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















