In modern metalworking, vacuum press technology is primarily used for shaping and forming operations that demand high precision and intricate detail. Its key applications include deep drawing, embossing, vacuum molding, and creating complex curvatures in sheet metals for industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
The core value of vacuum press technology is its use of uniform atmospheric pressure to perfectly conform a metal sheet to a mold. This method eliminates the localized stress of mechanical presses, enabling the creation of complex, detailed parts with exceptional consistency and quality.

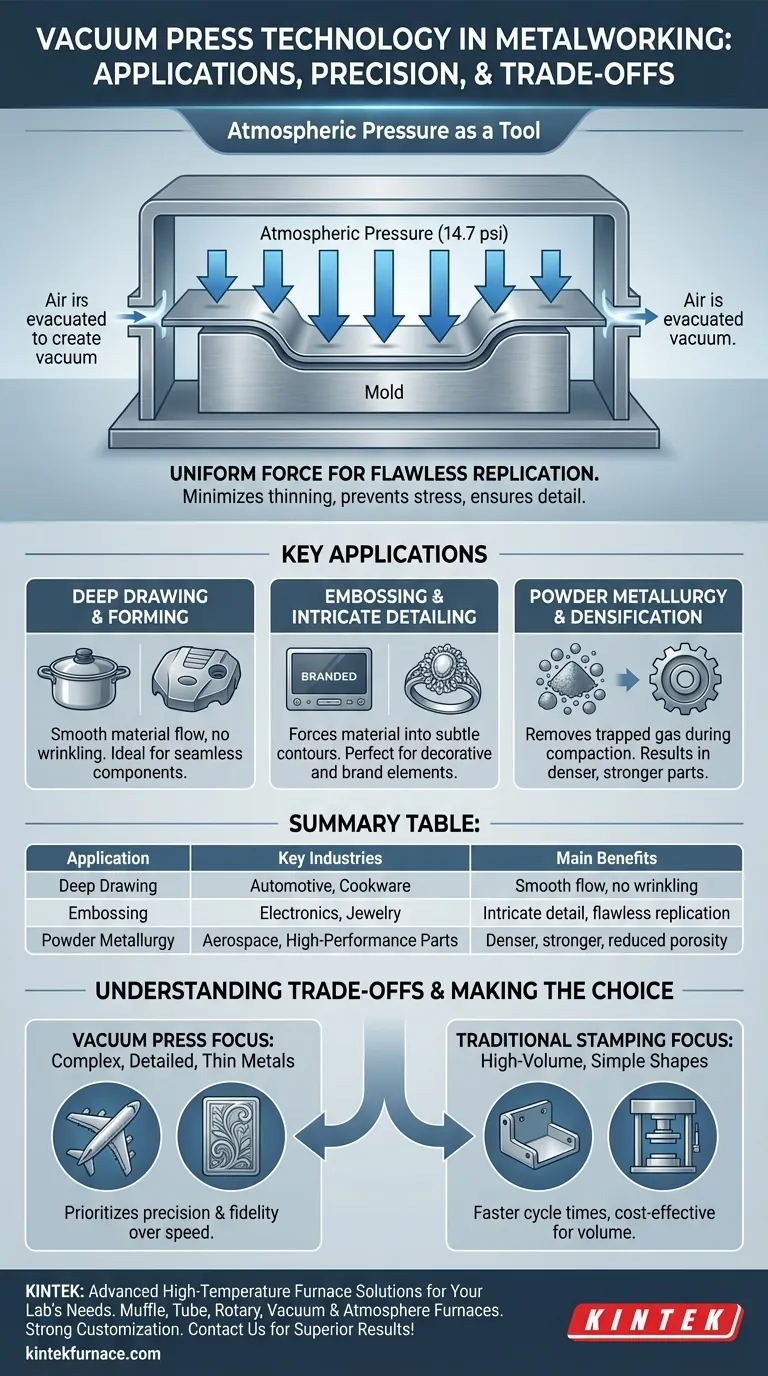
How Vacuum Pressing Achieves Precision
The Fundamental Principle: Atmospheric Pressure as a Tool
A vacuum press does not "suck" the metal into shape. Instead, it evacuates the air between the metal sheet and the mold, creating a vacuum.
The immense and perfectly uniform force of the surrounding atmosphere (approximately 14.7 psi at sea level) then presses the material onto the mold, acting as a powerful and consistent forming tool.
Uniform Force for Flawless Replication
Unlike a mechanical punch which applies force at a specific point, the atmospheric pressure exerted in a vacuum press is distributed evenly across the entire surface of the metal.
This uniformity minimizes material thinning, prevents stress concentrations, and ensures the metal perfectly captures every fine detail of the mold.
Enabling Complex Geometries
The pervasive nature of atmospheric pressure allows it to push metal into deep recesses, sharp corners, and intricate patterns that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with direct mechanical force.
This makes it the ideal technology for producing components with complex, non-linear surfaces, such as automotive interior panels or aerodynamic aerospace parts.
Key Metalworking Applications in Detail
Deep Drawing and Forming
Deep drawing is the process of forming a flat metal sheet into a hollow, three-dimensional shape like a cup or a box.
Vacuum assistance ensures the material flows smoothly into the die without wrinkling or tearing, which is critical for producing seamless components like high-end cookware or engine covers.
Embossing and Intricate Detailing
Embossing creates raised or recessed designs on a metal surface. Vacuum pressing excels at this by forcing the material into every subtle contour of the mold.
This application is common in the production of decorative panels, brand logos on electronics, and detailed components for the jewelry industry.
Powder Metallurgy and Densification
In a more advanced application, vacuum presses are used in powder metallurgy. A vacuum is applied during the compaction process to remove air and other trapped gases from between the metal powder particles.
This results in a final sintered part that is significantly denser, stronger, and free of the porosity that can compromise structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Material and Thickness Constraints
While powerful, atmospheric pressure has its limits. Vacuum forming is most effective on relatively thin sheets of malleable metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium alloys.
Forming thick metal plates still requires the immense localized force of traditional hydraulic or mechanical presses.
Cycle Time Considerations
The process of drawing a vacuum, heating the material (if required), and cooling the formed part takes more time than a simple mechanical stamping operation.
Therefore, for very high-volume production of simple parts, traditional stamping is often faster and more economical. Vacuum pressing trades raw speed for superior detail and complexity.
Tooling and Mold Investment
The final part is only as good as the mold it was formed on. Creating a precision-machined, durable mold that can withstand repeated cycles is a significant engineering task and can represent a substantial upfront investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding on a forming method, you must align the technology's strengths with your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple shapes: Traditional mechanical stamping may be more cost-effective due to its faster cycle times.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, detailed components from thin sheet metal: Vacuum press technology offers unmatched precision and fidelity to the mold.
- If your primary focus is producing dense, high-performance parts from metal powders: A vacuum press is essential for removing trapped gases and ensuring material integrity.
Ultimately, leveraging a vacuum press is a strategic decision to prioritize precision and complexity over raw production speed.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Industries | Main Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Drawing | Automotive, Cookware | Smooth material flow, no wrinkling |
| Embossing | Electronics, Jewelry | Intricate detailing, flawless replication |
| Powder Metallurgy | Aerospace, High-performance Parts | Denser, stronger parts, reduced porosity |
Need high-precision metalworking solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What role does a high-pressure press play in the preparation of zinc sample pellets? Optimize Carbothermic Reduction
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance



















