In industrial heating, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are the established workhorses for a vast range of high-temperature electric furnaces. They are essential in applications from metal heat treatment and ceramics manufacturing to advanced chemical and semiconductor processing, prized for their ability to deliver stable, high heat in demanding environments.
The core reason for SiC's widespread use is its unique combination of high-temperature capability, mechanical durability, and chemical resilience. However, understanding its operational limits, particularly in comparison to alternatives like molybdenum disilicide, is critical for proper application.
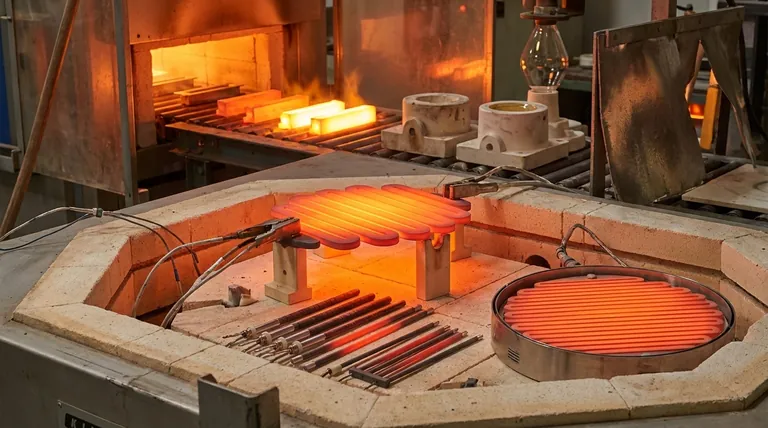

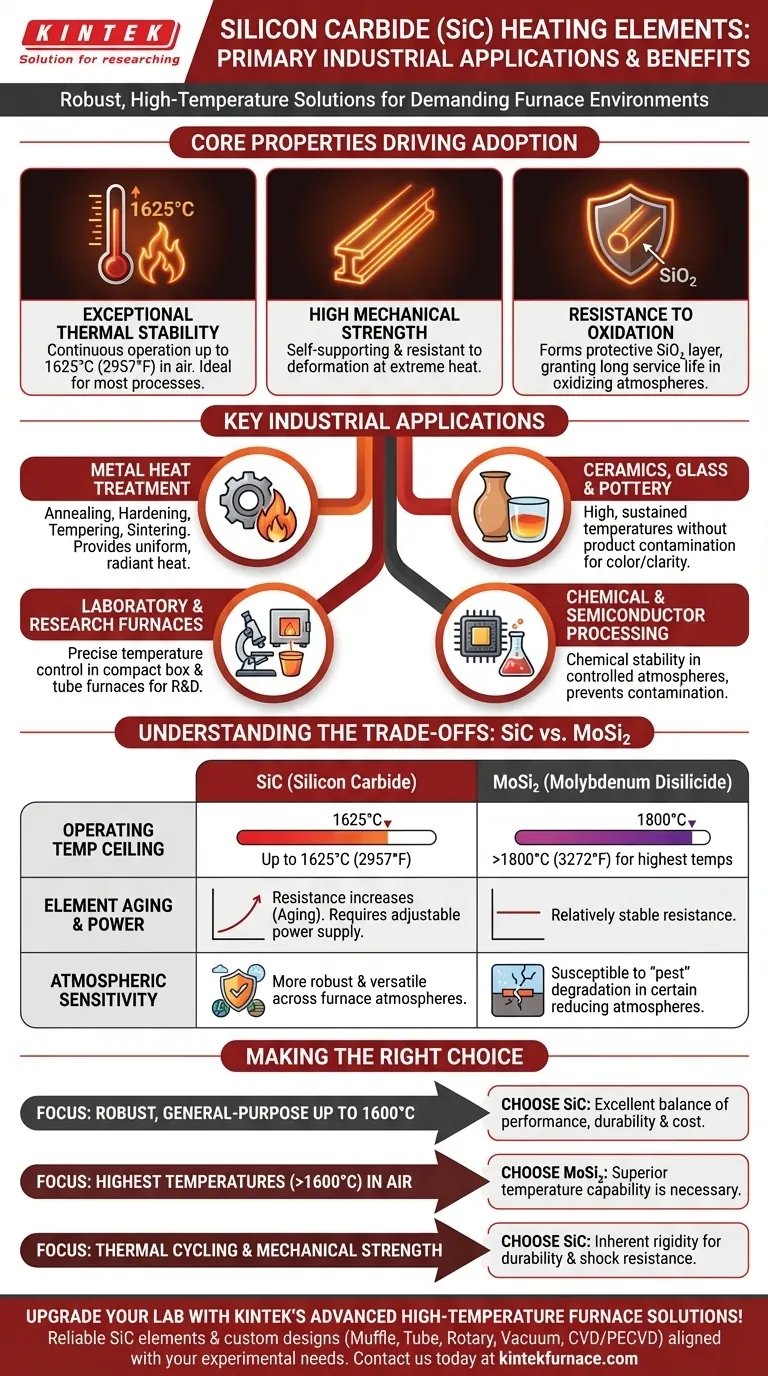
The Core Properties Driving SiC Adoption
The versatility of SiC elements stems directly from the fundamental properties of the silicon carbide material itself. These characteristics make it a reliable choice for furnace engineers and operators.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Silicon carbide elements can operate continuously at very high temperatures, typically up to 1625°C (2957°F) in an air atmosphere. This allows them to service a wide majority of industrial heat treatment and firing processes.
High Mechanical Strength
Unlike many ceramics, SiC maintains significant structural integrity and rigidity even at extreme temperatures. This self-supporting nature simplifies furnace design and makes the elements resistant to deformation.
Resistance to Oxidation
When heated, an SiC element forms a thin, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) on its surface. This layer effectively shields the underlying material from oxidation, granting it a long service life in air and other oxidizing atmospheres.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The properties of SiC translate directly into its primary applications across multiple sectors. It is chosen where reliable, clean, and precise electric heat is paramount.
Metal Heat Treatment
SiC elements are used extensively for processes like annealing, hardening, tempering, and sintering of metals and alloys. Their ability to provide uniform, radiant heat ensures consistent metallurgical properties in the final product.
Ceramics, Glass, and Pottery
The firing of ceramics, pottery, and the melting or holding of glass demand high, sustained temperatures. SiC elements provide this heat without contaminating the product, a critical factor for achieving desired colors and clarity in glazes and glass.
Laboratory and Research Furnaces
In research and development, versatility is key. SiC elements are used in laboratory box and tube furnaces for a wide variety of testing and material synthesis experiments, offering precise temperature control in a compact footprint.
Chemical and Semiconductor Processing
Many chemical and electronics manufacturing processes require controlled furnace atmospheres. The chemical stability of SiC makes it suitable for these applications, where element reactivity could otherwise compromise process integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: SiC vs. MoSi₂
Silicon carbide is not the only option for high-temperature electric heating. The other common choice is molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂), and the decision between them involves clear trade-offs.
The Operating Temperature Ceiling
The primary advantage of MoSi₂ elements is their ability to reach higher temperatures, often exceeding 1800°C (3272°F). They are the default choice for applications that operate beyond the limits of SiC.
Element Aging and Power Supply
The electrical resistance of SiC elements gradually increases over their service life. This "aging" requires a power supply system (typically using an SCR or multi-tap transformer) that can increase voltage over time to maintain constant power output. In contrast, MoSi₂ resistance is relatively stable.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
SiC elements are generally more robust and versatile across a wider range of furnace atmospheres. MoSi₂ elements, while excellent in air, can be susceptible to rapid degradation in certain reducing atmospheres at specific low-to-intermediate temperatures—a phenomenon known as "pest."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating element is a critical design decision based on your furnace's specific operational parameters and goals.
- If your primary focus is robust, general-purpose heating up to 1600°C: SiC offers an excellent balance of performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (above 1600°C) in air: MoSi₂ is the necessary choice for its superior temperature capability.
- If your furnace undergoes frequent thermal cycling or requires high mechanical strength: SiC's inherent rigidity provides an advantage in durability and resistance to thermal shock.
Ultimately, an informed choice between these technologies depends entirely on a clear understanding of your process temperature, atmosphere, and operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Metal Heat Treatment | Uniform radiant heat for annealing, hardening, and sintering |
| Ceramics and Glass | High, sustained temperatures without contamination |
| Laboratory Research | Precise temperature control in compact furnaces |
| Chemical and Semiconductor Processing | Chemical stability in controlled atmospheres |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable SiC heating elements and custom furnace designs, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for enhanced efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















