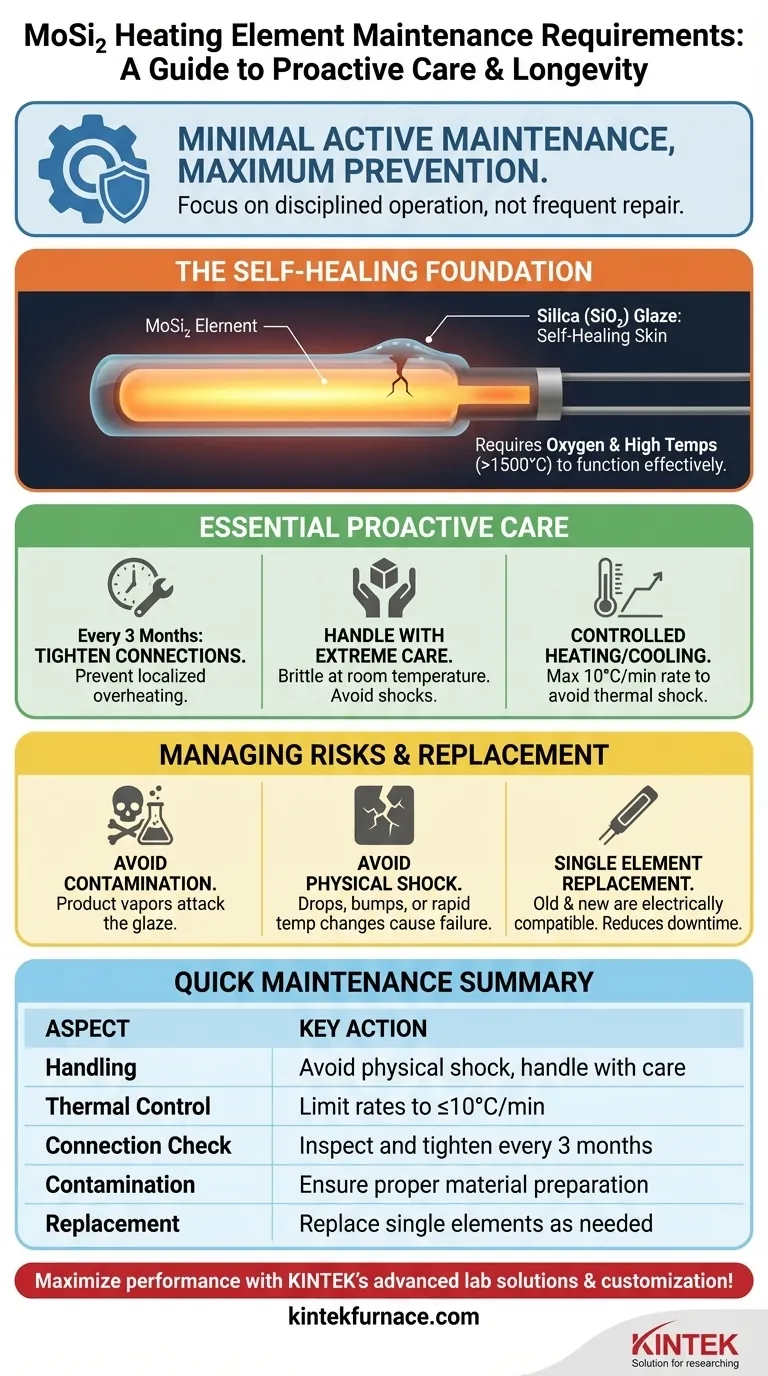
In principle, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements require very little active maintenance. Their design promotes a long operational lifespan with minimal intervention, which is a primary reason for their selection in high-temperature furnaces. However, their longevity is entirely dependent on proper operational discipline and preventative care to avoid premature failure.
The core principle of MoSi₂ maintenance is not about frequent repair, but about prevention. Your focus should be on disciplined operational procedures—specifically, controlled heating rates, careful physical handling, and avoiding contamination—rather than on a schedule of active upkeep.
The Foundation of MoSi₂ Longevity: A Self-Healing System
To understand why MoSi₂ elements are low-maintenance, you must first understand their fundamental chemistry when heated.
How the Protective Glaze Forms
When a MoSi₂ element is heated in an oxygen-rich environment, a thin, non-porous layer of silica glass (SiO₂) forms on its surface. This protective glaze is the key to the element's durability.
This glaze acts as a "self-healing skin," automatically reforming to cover any minor surface defects or oxidation that occurs during operation.
The Critical Role of Oxygen
This self-healing function is entirely dependent on the presence of oxygen. Furnaces operating with inert or reducing atmospheres will not benefit from this protective effect and will see a reduced element lifespan unless specialized elements are used.
Why They Excel at High Temperatures
This protective layer is most stable and effective at very high temperatures, typically above 1500°C. This is why MoSi₂ elements often outlast other types, like Silicon Carbide (SiC), in continuous, high-temperature applications.
Proactive Care: The "Real" Maintenance
While active repair is rare, a strict regimen of proactive care is non-negotiable for maximizing the life of your elements.
The 3-Month Connection Check
The one recurring active maintenance task is to inspect the element connections. Every three months, check that the electrical straps and clamps are secure.
Loose connections create high resistance, leading to localized overheating that can damage both the element holder and the element itself.
Careful Handling: The Brittleness Factor
MoSi₂ elements are extremely brittle and fragile at room temperature. They must be handled with immense care during shipping, storage, and installation to prevent fractures.
Controlled Heating and Cooling
The single most common cause of premature failure is thermal shock. Rapid changes in temperature cause internal stresses that will crack the element.
A maximum heating and cooling rate of 10°C per minute is a crucial rule to follow. This ensures the element can expand and contract uniformly without breaking.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
Knowing what causes these elements to fail is the best way to prevent it. MoSi₂ elements are robust, but they have specific vulnerabilities.
The Primary Risk: Contamination
The protective silica glaze is susceptible to chemical attack. Contaminants released from the product being heated are a primary cause of failure.
For example, improperly dried colored zirconia can release vapors that attack the element's surface, degrading the protective layer and leading to rapid failure. Always ensure materials are properly prepared before a firing cycle.
The Secondary Risk: Physical Shock
Dropping an element, bumping it during installation, or subjecting it to rapid temperature changes are all forms of physical shock that can cause immediate or future failure. Their high-temperature strength is contrasted by their low-temperature fragility.
Replacing Damaged Elements
A significant advantage of MoSi₂ systems is that old and new elements are electrically compatible. Unlike some other systems, you do not need to replace elements in sets.
If one element breaks, you can replace only that single element, which dramatically reduces maintenance costs and furnace downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance strategy should align directly with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: Your top priorities are preventing contamination by properly preparing all materials and enforcing strict, slow heating and cooling ramps.
- If your primary focus is minimizing furnace downtime: Implement a strict quarterly schedule for checking and tightening electrical connections and leverage the ability to replace single elements instead of entire sets.
- If you are installing new elements or moving a furnace: Treat the elements as if they are glass. Their brittleness at room temperature is their greatest weakness.
Ultimately, disciplined operation is the most effective form of maintenance for MoSi₂ heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Aspect | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Handling | Avoid physical shock and handle with care | Prevent fractures due to brittleness at room temperature |
| Thermal Control | Limit heating/cooling rates to ≤10°C per minute | Avoid thermal shock and internal stress |
| Connection Check | Inspect and tighten every 3 months | Prevent overheating from loose electrical connections |
| Contamination Prevention | Ensure materials are properly prepared | Protect the self-healing silica glaze from chemical attack |
| Replacement | Replace single elements as needed | Reduce costs and downtime, as old and new elements are compatible |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your high-temperature furnace with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable heating elements and systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, reducing maintenance issues and boosting efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's goals with tailored, high-quality equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















