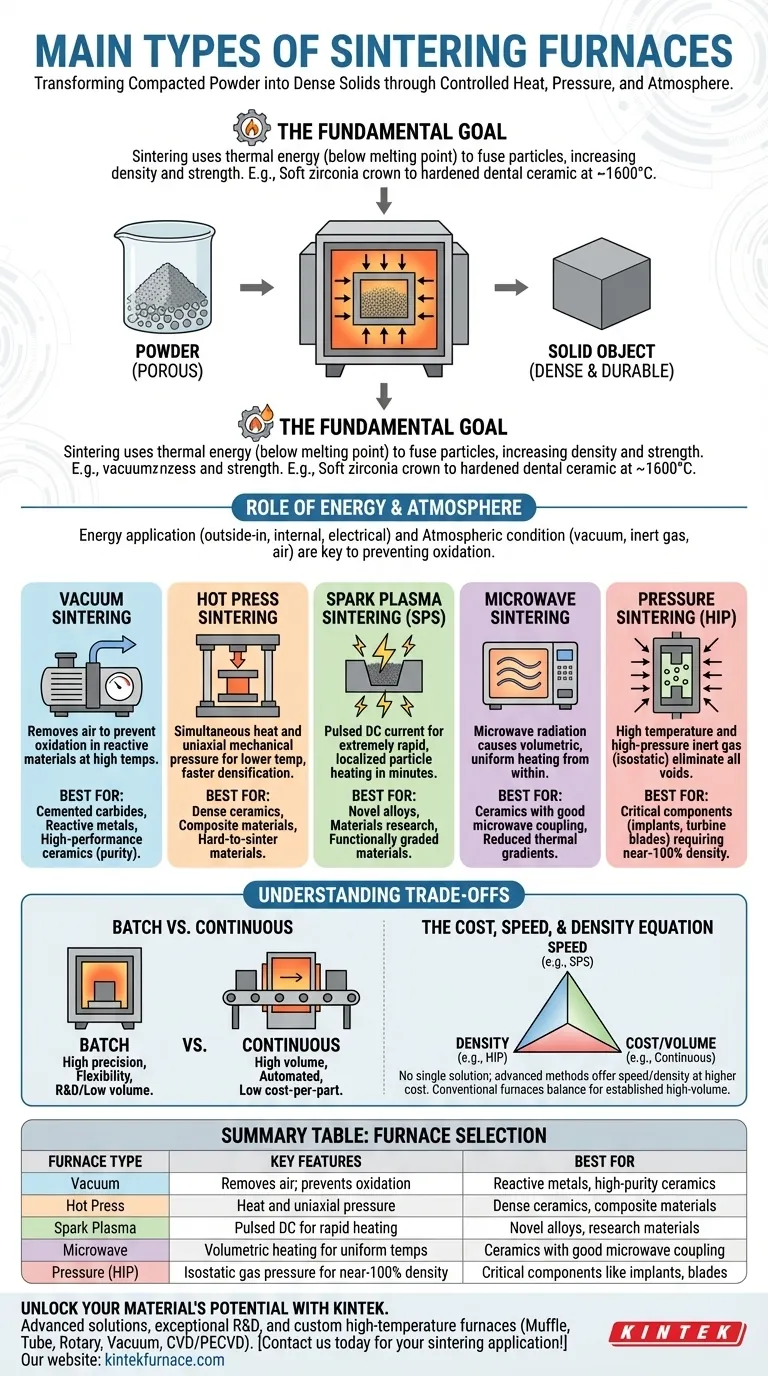
At its core, a sintering furnace is a high-temperature system designed to bond particles together, turning a compacted powder into a dense, solid object without melting it. The main types are vacuum, hot press, spark plasma, microwave, and pressure sintering furnaces. Each is distinguished by the specific energy source, pressure application, and atmospheric conditions it employs to achieve this transformation.
The choice of a sintering furnace is not about finding the "best" one, but about matching the heating mechanism and atmospheric control to your specific material, desired final density, and production goals. It is a strategic decision that balances speed, performance, and cost.
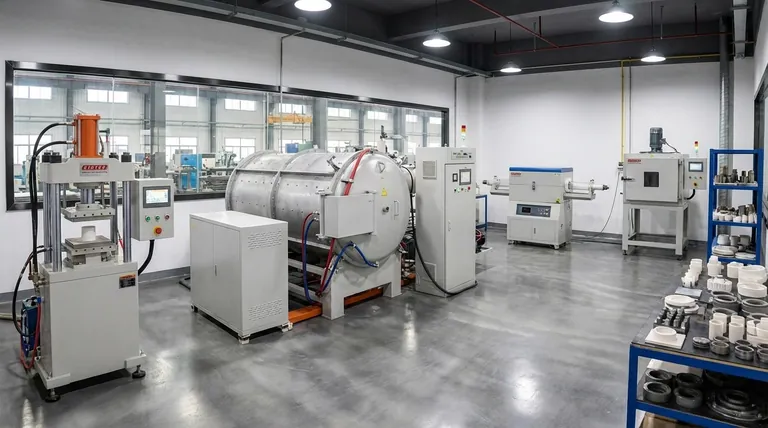

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Solid
What is Sintering?
Sintering uses thermal energy to reduce the porosity between particles in a material. As the material is heated to a high temperature—below its melting point—atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together.
The primary goal is to significantly increase the material's density, strength, and durability. For example, in dentistry, a milled zirconia crown is soft and porous until sintered at up to 1600°C, which causes it to shrink and achieve its final, hardened state.
The Role of Energy and Atmosphere
The key differences between furnace types lie in how they apply energy and what atmosphere they create.
Conventional furnaces heat from the outside in. Advanced methods may use microwaves or electrical currents to heat more rapidly or uniformly. Likewise, the atmosphere—be it a vacuum, an inert gas, or ambient air—is critical for preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.
A Breakdown of Sintering Furnace Technologies
Vacuum Sintering Furnaces
These furnaces operate by removing air from the chamber before heating. This vacuum environment is essential for processing materials that are highly reactive with oxygen or other atmospheric gases at high temperatures.
They are the standard for producing cemented carbides, processing reactive metals, and sintering certain high-performance ceramics where purity is paramount.
Hot Press Sintering Furnaces
This technology applies simultaneous heat and uniaxial mechanical pressure. A die holds the powder material, and a hydraulic press compacts it while it is being heated.
By applying direct pressure, hot pressing can achieve high densities at lower temperatures and in shorter times compared to pressureless sintering. It is ideal for fabricating dense, high-strength ceramics and composite materials that are difficult to sinter otherwise.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Also known as Field Assisted Sintering Technology (FAST), SPS is a revolutionary technique. It passes a pulsed, high-current DC electrical current directly through the powder and the graphite die containing it.
This generates extremely rapid and localized heating at the particle contact points, enabling sintering in a matter of minutes instead of hours. SPS is widely used in materials research and for producing novel alloys, composites, and functionally graded materials.
Microwave Sintering Furnaces
Unlike conventional furnaces that heat from the outside in, microwave furnaces use microwave radiation to heat the material volumetrically. The energy penetrates the material and excites its molecules, generating heat from within.
This can lead to more uniform temperature distribution, reduced thermal gradients, and significant energy savings. It is most effective for ceramics and other materials that couple well with microwave energy.
Pressure Sintering (Hot Isostatic Pressing)
Often referred to as Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), this method applies both high temperature and high-pressure inert gas (like argon) from all directions. The isostatic pressure uniformly compacts the material, closing any remaining internal voids.
HIP is used to achieve nearly 100% theoretical density, eliminating all residual porosity. This makes it indispensable for producing critical, failure-intolerant components like jet engine turbine blades and medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Batch vs. Continuous Furnaces
A fundamental operational choice is between batch and continuous processing. Batch furnaces process one load at a time, offering high precision and flexibility. They are perfect for research and development, complex parts, or low-volume production, such as dental crowns.
Continuous furnaces, on the other hand, move materials through different temperature zones on a conveyor belt. They are designed for high-volume, automated production where throughput and low cost-per-part are the primary drivers.
The Cost, Speed, and Density Equation
There is no single solution for all applications. Advanced methods like SPS offer unparalleled speed but often have higher capital costs and smaller processing volumes.
Conventional batch or continuous furnaces may be slower but are robust, reliable, and more cost-effective for established, high-volume manufacturing processes. The highest-density methods like HIP represent a significant investment reserved for the most demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal furnace is determined entirely by your project's constraints and objectives.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation in reactive materials: A vacuum furnace is the standard for creating a clean, controlled environment.
- If your primary focus is achieving high density in difficult-to-sinter materials: A hot press or Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) furnace combines heat and pressure for rapid densification.
- If your primary focus is eliminating all residual porosity for critical components: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the definitive solution for achieving near-100% theoretical density.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective production: A continuous furnace designed for your specific material offers the best throughput and lowest cost-per-part.
Ultimately, selecting a sintering furnace is a strategic decision that aligns the physics of the process with the economics of your production.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum | Operates without air; prevents oxidation | Reactive metals, high-purity ceramics |
| Hot Press | Applies heat and uniaxial pressure | Dense ceramics, composite materials |
| Spark Plasma | Uses pulsed DC current for rapid heating | Novel alloys, research materials |
| Microwave | Volumetric heating for uniform temperatures | Ceramics with good microwave coupling |
| Pressure (HIP) | Isostatic gas pressure for near-100% density | Critical components like implants, blades |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced sintering solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, boosting efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific sintering applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















