The main heat treatment processes conducted in high-temperature vacuum furnaces are vacuum annealing, vacuum brazing, vacuum sintering, and vacuum purification. These processes, along with hardening and tempering, leverage the controlled vacuum environment to prevent oxidation and remove impurities, achieving material properties unattainable in standard atmospheric furnaces.
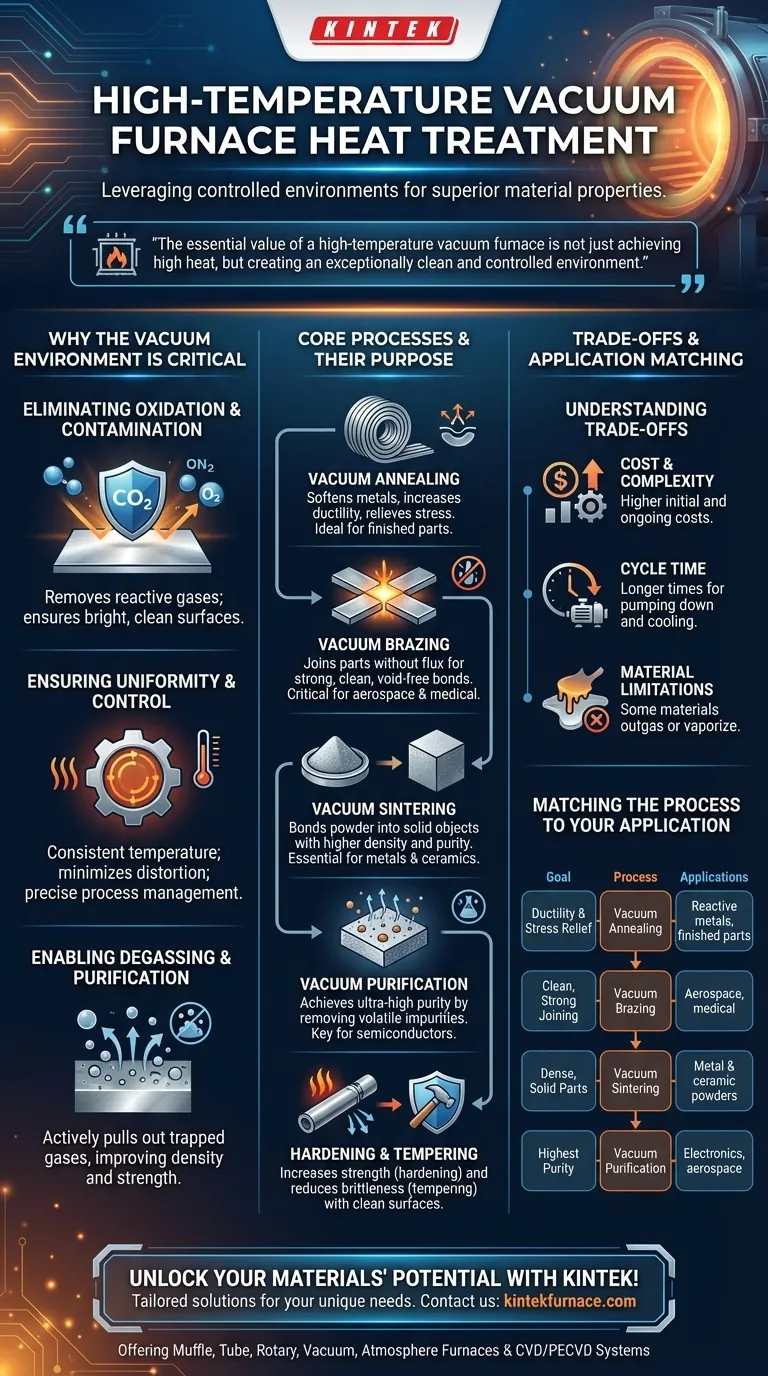
The essential value of a high-temperature vacuum furnace is not just achieving high heat, but creating an exceptionally clean and controlled environment. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, allowing for the creation of materials with superior purity, strength, and structural integrity for the most demanding applications.

Why the Vacuum Environment is Critical
Before examining specific processes, it's essential to understand why removing air is so beneficial. The vacuum environment is the foundational element that makes these advanced treatments possible.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals react readily with oxygen in the air, forming a brittle, undesirable oxide layer. A vacuum furnace removes these reactive gases, ensuring the material surface remains bright, clean, and uncontaminated throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Ensuring Uniformity and Control
Modern vacuum furnaces provide exceptionally uniform heating. The absence of air currents allows for consistent temperature across the entire part, minimizing thermal stress and distortion. Advanced control systems precisely manage heating rates, soak times, and cooling, ensuring the process is repeatable and reliable.
Enabling Degassing and Purification
Many materials contain trapped gases (like hydrogen or oxygen) that can compromise their structural integrity. The vacuum actively pulls these dissolved gases out of the material as it is heated, a process known as degassing. This significantly improves the material's density, strength, and performance.
Core Processes and Their Purpose
Each heat treatment process is designed to achieve a specific outcome. The vacuum environment enhances the effectiveness and quality of each one.
Vacuum Annealing
Annealing is a process used to soften metals, increase their ductility, and relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing. In a vacuum, annealing prevents any surface oxidation, making it ideal for finished parts or materials like titanium that are highly reactive with oxygen.
Vacuum Brazing
Brazing joins two or more metal parts by melting a filler metal between them. Vacuum brazing is superior because it requires no flux, which can be corrosive. The clean vacuum environment allows the filler metal to wet and flow perfectly, creating an extremely strong, clean, and void-free joint, critical for aerospace and medical components.
Vacuum Sintering
Sintering is the process of taking a compacted powder—often metal or ceramic—and heating it to just below its melting point. This causes the particles to bond, creating a solid, dense object. Vacuum sintering is essential for preventing oxidation and removing trapped air, resulting in higher density and superior mechanical properties.
Vacuum Purification
This is a specialized process designed to achieve ultra-high material purity. By holding a material at a high temperature in a deep vacuum, volatile impurities with a high vapor pressure can be "boiled off" and pumped away, leaving a purer base material behind. This is critical for semiconductors and high-performance alloys.
Hardening and Tempering
Hardening involves heating a metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it rapidly (quenching) to increase its strength and hardness. Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature treatment that reduces brittleness. Performing these in a vacuum ensures a clean surface, prevents decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface), and results in a higher quality, more uniform final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. It comes with specific considerations that make it more suitable for some applications than others.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. The need for robust vacuum pumps, advanced control systems, and leak-tight chambers drives up the initial and ongoing costs.
Cycle Time
Achieving a deep vacuum and executing precisely controlled cooling cycles can be time-consuming. Pumping down the chamber, heating, soaking, and then often slowly cooling under vacuum or inert gas can result in longer overall process times compared to conventional methods.
Material Limitations
Not all materials are suitable for vacuum processing. Materials with a high vapor pressure (like zinc, cadmium, or magnesium) can outgas excessively or even vaporize at high temperatures under vacuum, potentially contaminating the furnace and ruining the part.
Matching the Process to Your Application
Choosing the right process depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is improving ductility and relieving stress: Vacuum annealing is your most direct path, especially for reactive metals or finished parts.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or dissimilar materials without flux: Vacuum brazing provides the cleanest and strongest bond for critical assemblies.
- If your primary focus is creating a dense, solid part from metal or ceramic powders: Vacuum sintering is the required method for achieving superior density and purity.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material purity for sensitive applications: Vacuum purification and degassing are essential for electronics, medical, and aerospace-grade materials.
Ultimately, mastering vacuum heat treatment is about leveraging a controlled environment to achieve material properties that are otherwise unattainable.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Purpose | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Annealing | Soften metals, relieve stress, increase ductility | Reactive metals, finished parts |
| Vacuum Brazing | Join metals without flux for clean, strong bonds | Aerospace, medical components |
| Vacuum Sintering | Densify powders for solid parts with high purity | Metal and ceramic powders |
| Vacuum Purification | Remove impurities for ultra-high material purity | Semiconductors, high-performance alloys |
| Hardening & Tempering | Increase strength and hardness, reduce brittleness | High-quality, uniform products |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature vacuum furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior purity, strength, and performance for demanding applications in aerospace, medical, and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes and achieve unparalleled results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















