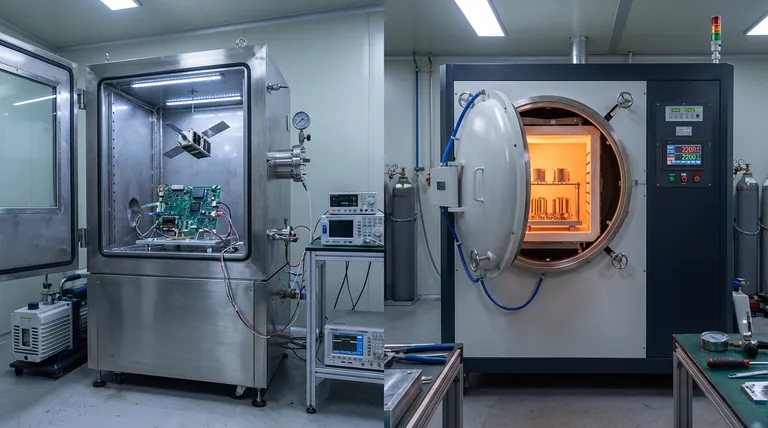
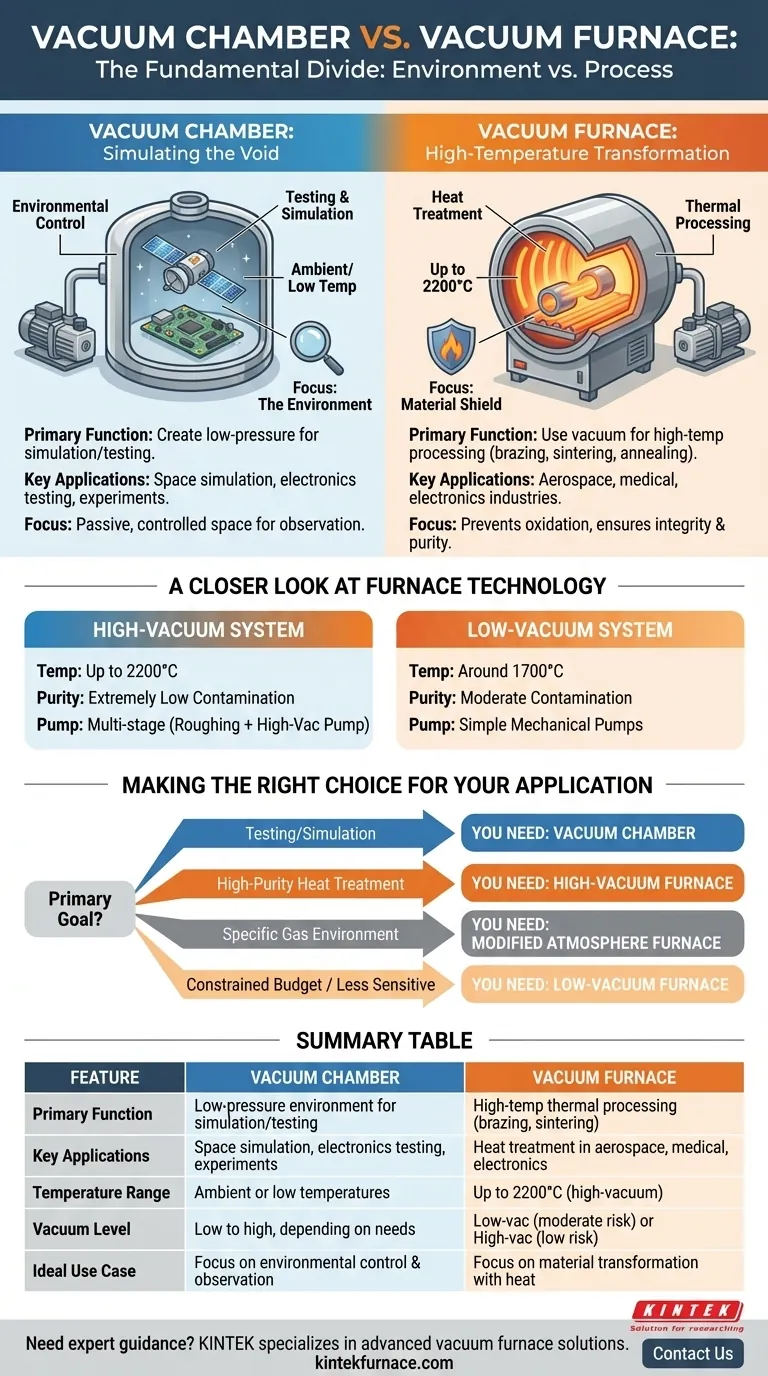
At its core, the distinction is one of purpose. A vacuum chamber is designed to create a controlled, low-pressure environment for simulation and testing, while a vacuum furnace is a specialized system that uses that vacuum to heat materials to extreme temperatures. The chamber's primary function is environmental control; the furnace's primary function is high-temperature thermal processing.
While both systems create a vacuum, their engineering goals are fundamentally different. A vacuum chamber is about creating and maintaining an empty space for testing. A vacuum furnace is about using that empty space as a protective shield for materials during intense heating.

The Fundamental Divide: Environment vs. Process
Understanding the difference begins with the intended outcome. Are you trying to observe something in a vacuum, or are you trying to change something with heat inside a vacuum?
Vacuum Chambers: Simulating the Void
A vacuum chamber is essentially a sealed container from which air and other gases are removed by a vacuum pump. Its design is optimized for creating and holding a low-pressure environment.
The primary applications are for testing and simulation. This includes simulating the conditions of outer space for satellite components, testing electronics at high altitudes, or performing experiments that would be impossible in a normal atmosphere.
The focus is on the environment itself. The chamber provides a passive, controlled space for observation or experimentation, typically at or near ambient temperature.
Vacuum Furnaces: High-Temperature Transformation
A vacuum furnace is a far more active system. While it incorporates a vacuum chamber, its main purpose is to serve as a high-temperature oven.
The vacuum is not the goal, but a critical tool. By removing oxygen and other atmospheric gases, the furnace prevents oxidation and contamination of materials during heat treatment processes like brazing, sintering, and annealing.
This ensures the structural integrity and purity of the final product, which is essential for high-performance metals and ceramics used in aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
A Closer Look at Furnace Technology
Not all vacuum furnaces are the same. The "quality" of the vacuum directly impacts the process capabilities, defining the temperature limits and purity levels that can be achieved.
The Critical Role of Vacuum Level
Vacuum furnaces are often categorized as low-vacuum or high-vacuum systems. This distinction dictates their suitability for different materials and processes.
A low-vacuum system removes most of the atmosphere, which is sufficient for many standard heat-treating applications.
A high-vacuum system removes significantly more molecules, creating a much purer environment for extremely sensitive processes where any contamination would be catastrophic.
Temperature and Purity Are Linked
The vacuum level has a direct impact on maximum temperature and final product purity.
High-vacuum furnaces can reach higher temperatures, often up to 2200°C, because the near-total lack of atmosphere minimizes heat transfer and prevents reactions at extreme temperatures. This results in an extremely low contamination risk.
Low-vacuum atmosphere furnaces have a lower maximum temperature, typically around 1700°C, and carry a moderate contamination risk due to the higher number of residual gas molecules.
The Pumping System Defines the Result
The vacuum level is a direct result of the pumping technology used.
Low-vacuum systems can achieve their targets with simpler mechanical pumps, like rotary vane pumps.
High-vacuum systems require complex, multi-stage pumping systems. These typically combine a mechanical "roughing" pump with a high-vacuum pump (like a turbomolecular or diffusion pump) to achieve much lower pressures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right system requires acknowledging that more capability is not always better. It often comes with greater complexity and cost.
Why Not Just Use a Furnace for Everything?
A vacuum furnace is overkill if you only need a low-pressure environment for testing. They are more complex, more expensive, and optimized for thermal uniformity, not necessarily for the access, instrumentation ports, or viewing windows that a test chamber might require.
When a Vacuum Isn't Enough
Sometimes, the goal is not to remove the atmosphere but to replace it. A modified atmosphere furnace allows the introduction of specific inert or reactive gases (like argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen).
This is used for processes like nitriding steel or sintering materials that require a specific, controlled gas environment during heating—a task a standard vacuum furnace is not designed for.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be driven by your specific technical goal.
- If your primary focus is testing and simulation: You need a vacuum chamber, which is designed to provide a stable, low-pressure environment for observation.
- If your primary focus is high-purity heat treatment: You need a high-vacuum furnace to prevent oxidation and contamination during processes like brazing, sintering, or annealing.
- If your process requires a specific gas environment during heating: You should investigate a modified atmosphere furnace, as a vacuum furnace's purpose is to remove gases, not introduce them.
- If your budget is constrained and the process is less sensitive to contamination: A low-vacuum atmosphere furnace may be a viable option, but be aware of its temperature and purity limitations.
Understanding this core distinction between environmental control and thermal processing empowers you to select the precise tool for your technical objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Chamber | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates a low-pressure environment for simulation and testing | Uses vacuum for high-temperature thermal processing like brazing and sintering |
| Key Applications | Space simulation, electronics testing, experiments in vacuum | Heat treatment in aerospace, medical, and electronics industries |
| Temperature Range | Typically ambient or low temperatures | Up to 2200°C in high-vacuum systems |
| Vacuum Level | Low to high, depending on testing needs | Low-vacuum (moderate contamination risk) or high-vacuum (low contamination risk) |
| Ideal Use Case | When focus is on environmental control and observation | When focus is on material transformation with heat in a protective atmosphere |
Need expert guidance for your high-temperature processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced vacuum furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing purity, efficiency, and results. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















