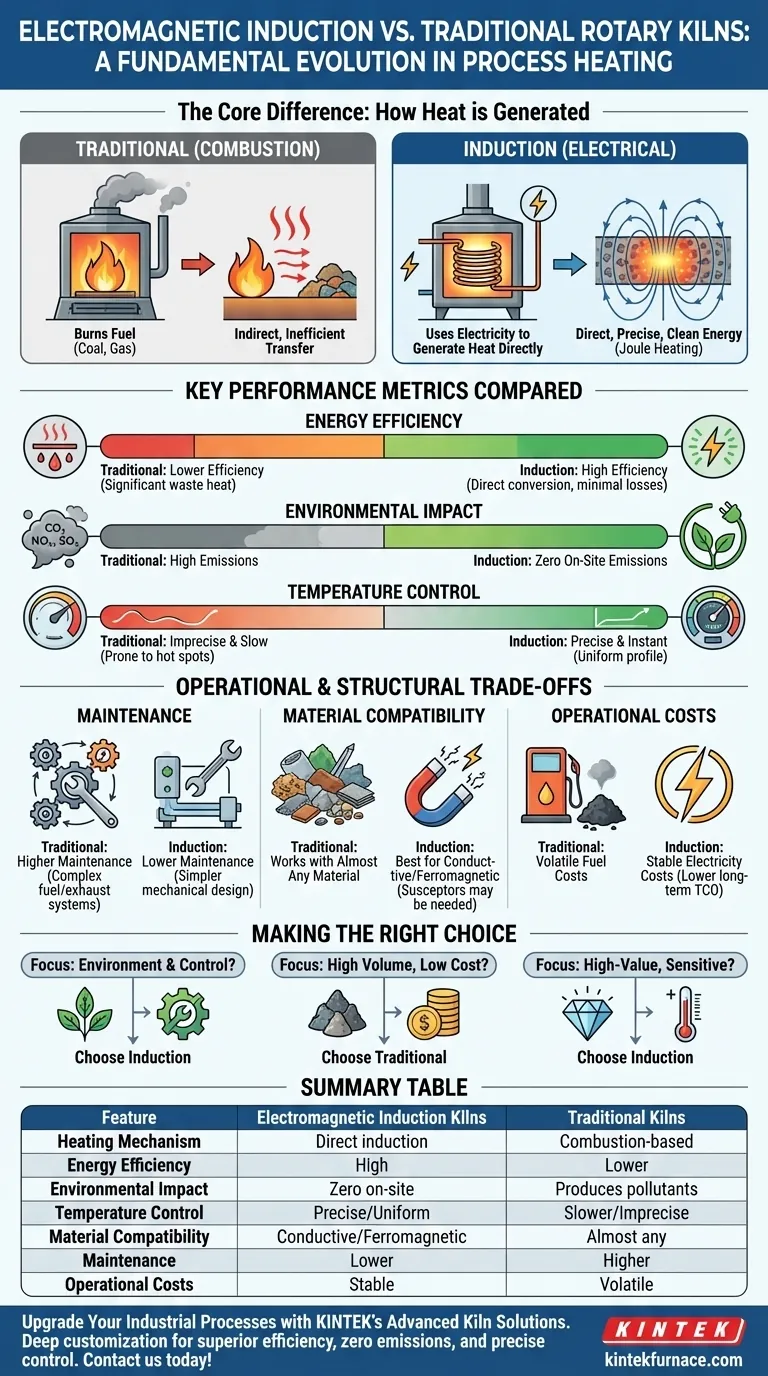
At their core, the fundamental difference is how heat is generated. Traditional rotary kilns burn a fuel source like coal or natural gas to create a hot environment, while electromagnetic induction rotary kilns use electricity to directly generate heat within the material itself, eliminating the need for combustion entirely. This single distinction leads to profound differences in efficiency, environmental impact, and operational control.
The shift from combustion to electromagnetic induction is not merely a change in fuel. It represents a fundamental evolution in process heating, moving from indirect, inefficient heat transfer to direct, precise, and clean energy application.
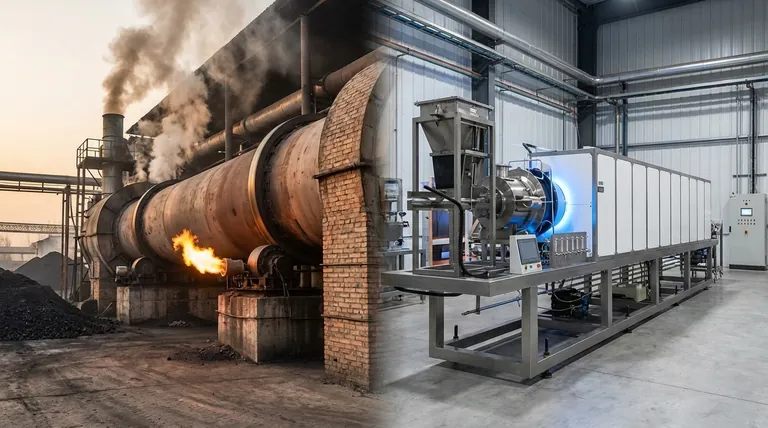

The Fundamental Difference: Heating Mechanism
Understanding how each kiln generates and applies heat is crucial to grasping its advantages and limitations.
Traditional Kilns: Combustion-Based Heating
Traditional kilns operate by burning fuel. The heat is then transferred to the material through either direct or indirect contact.
In a direct-fired kiln, the flame and hot combustion gases pass through the kiln in direct contact with the material. This is efficient but can introduce contaminants from the fuel into the product.
In an indirect-fired kiln, the kiln shell is heated from the outside. The heat then radiates and conducts through the shell to the material inside, which is kept separate from the combustion gases. This is cleaner but less energy-efficient.
Electromagnetic Induction Kilns: Direct Material Heating
Electromagnetic induction kilns bypass combustion completely. An induction coil wrapped around the kiln generates a powerful, oscillating magnetic field.
This field penetrates the kiln shell and directly induces electrical eddy currents within the conductive material being processed. The material's natural electrical resistance causes these currents to generate heat—a process known as Joule heating. The material literally heats itself from the inside out.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The difference in heating methods creates a cascade of effects across efficiency, emissions, and process control.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Transfer
Traditional kilns are inherently inefficient. A significant amount of energy is lost as waste heat through exhaust gases and the kiln shell. Heat must first be transferred from the flame to the air, and then from the air to the material.
Electromagnetic induction is far more efficient. Because heat is generated directly within the material, energy losses are drastically reduced. This direct conversion of electrical energy to thermal energy minimizes wasted heat, leading to lower overall energy consumption.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
This is the most clear-cut distinction. Traditional kilns, by their nature, produce harmful emissions. Burning coal or gas releases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter.
Electromagnetic induction kilns produce zero on-site emissions. They use electricity as their power source, eliminating the byproducts of combustion. This makes them a significantly cleaner technology, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
Temperature Control and Precision
Controlling temperature in a combustion-based system is slow and imprecise. There is significant thermal inertia, meaning it takes time to raise or lower the temperature, and hot spots can easily develop.
Induction heating offers nearly instantaneous and highly precise temperature control. By adjusting the electrical current, the heating rate can be changed in real-time, allowing for a perfectly uniform temperature profile tailored to the material's specific needs.
Understanding the Operational and Structural Trade-offs
While induction technology offers clear advantages, a complete analysis requires looking at operational realities and potential limitations.
System Complexity and Maintenance
Traditional kilns have complex support systems, including fuel storage and delivery, burners, air blowers, and exhaust gas handling. These components are frequent points of failure and require regular, intensive maintenance.
Electromagnetic induction kilns have a simpler mechanical design. They eliminate the entire combustion train, resulting in fewer moving parts and fewer failure points. This translates to higher reliability and significantly lower maintenance costs.
Material Compatibility
The primary limitation of induction heating is that it works best with materials that are electrically conductive or have ferromagnetic properties.
For materials that are not naturally receptive to induction, a secondary conductive or ferromagnetic material, known as a susceptor, can be mixed in to generate the heat. Traditional kilns do not have this limitation and can heat almost any material.
Operational Costs
The total cost of ownership depends heavily on local utility prices. Traditional kilns are subject to volatile fuel costs for coal and natural gas.
Induction kilns are dependent on the price of electricity. While their initial capital cost may be higher, this is often offset over the long term by higher energy efficiency, drastically reduced maintenance, and the elimination of fuel costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your ideal kiln technology depends on your specific production goals, material properties, and regulatory environment.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and process control: The clear choice is an electromagnetic induction kiln due to its zero-emission profile and precise, uniform heating.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes of raw, less-sensitive materials where initial cost is paramount: A traditional continuous-combustion kiln may still be a viable solution, especially if you have access to cheap fuel.
- If your primary focus is high-value or temperature-sensitive materials: The superior control and purity offered by an induction kiln are almost always worth the investment.
Ultimately, selecting the right kiln technology requires a clear assessment of your operational priorities, from product quality and environmental impact to the total cost of ownership.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electromagnetic Induction Kilns | Traditional Kilns |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Direct induction heating within material | Combustion-based heating (fuel burning) |
| Energy Efficiency | High (direct heat generation, minimal losses) | Lower (heat transfer losses, waste gases) |
| Environmental Impact | Zero on-site emissions | Produces CO2, NOx, SOx, and particulate matter |
| Temperature Control | Precise, uniform, and instantaneous | Slower, less precise, prone to hot spots |
| Material Compatibility | Best for conductive/ferromagnetic materials; susceptors may be needed for others | Works with almost any material |
| Maintenance | Lower (fewer moving parts, no combustion systems) | Higher (complex fuel and exhaust systems) |
| Operational Costs | Dependent on electricity prices; lower long-term due to efficiency and maintenance savings | Dependent on volatile fuel costs; higher maintenance expenses |
Upgrade Your Industrial Processes with KINTEK's Advanced Kiln Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior efficiency, zero emissions, and precise temperature control.
Ready to enhance your operations? Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials



















