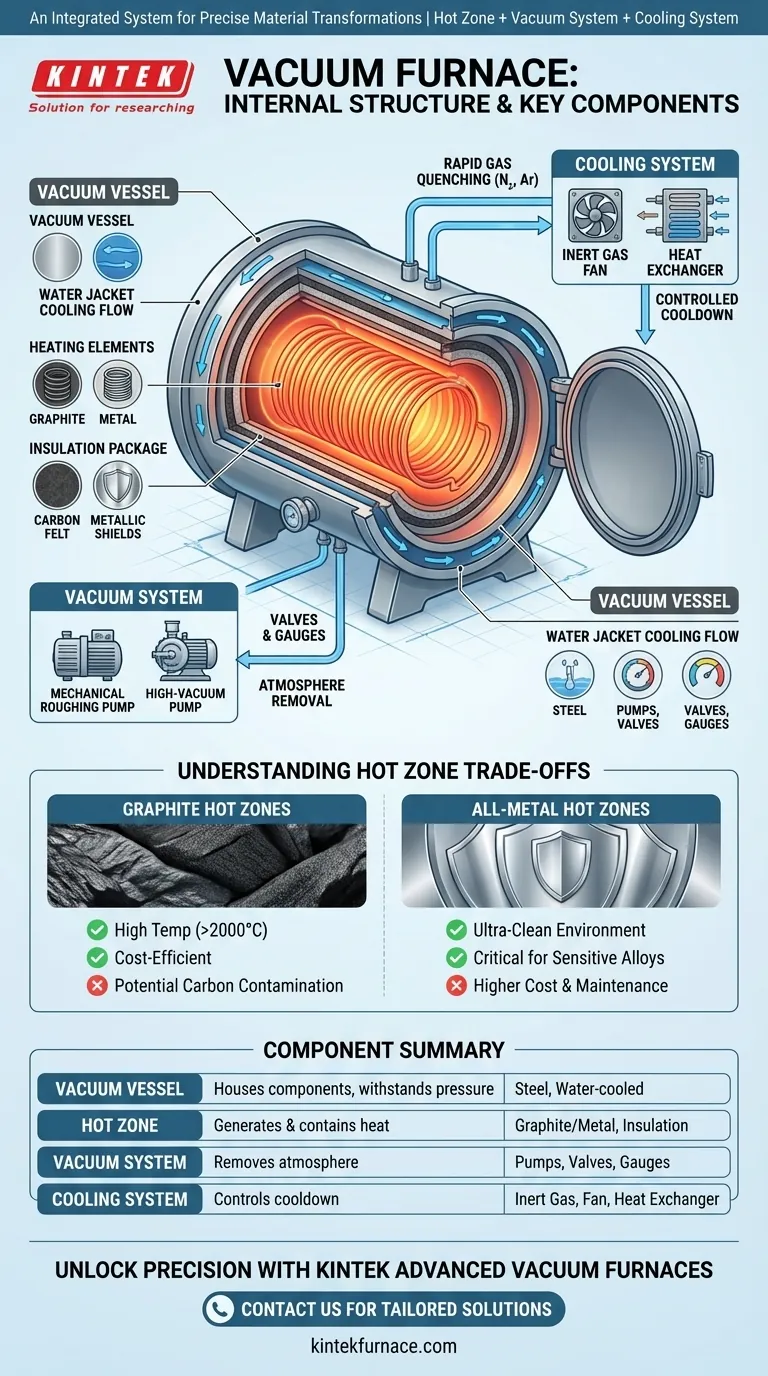
At its core, a vacuum furnace is an integrated system comprising three primary internal components: a Hot Zone to generate and contain heat, a Vacuum System to remove the atmosphere, and a Cooling System to control the final stage of the process. These components are housed within a sealed vacuum vessel and managed by a sophisticated control system to achieve precise material transformations in an environment free of contaminants.
A vacuum furnace is not simply a box that gets hot. It is a highly controlled environment where the removal of air is just as critical as the application of heat, and the internal components are designed to work in concert to manage temperature, atmosphere, and cooling with extreme precision.

The Foundation: The Vacuum Vessel
The entire internal structure is housed within the vacuum vessel, or furnace shell. This is far more than a simple container; it is a critical engineering component.
The Shell and Door
The shell is a leakproof chamber, typically constructed from high-strength steel plates. It is designed to withstand the immense external atmospheric pressure when a deep vacuum is pulled inside.
Most modern furnace vessels feature a double-wall, "water jacket" design. This means cooling water constantly circulates within the shell's walls to keep it at a safe temperature, protecting it from the intense radiant heat produced by the hot zone.
The Heart of the Furnace: The Hot Zone
The "hot zone" is the operational core where the actual heating of the workpiece takes place. Its design and materials dictate the furnace's performance, temperature capabilities, and suitability for different applications.
Heating Elements
These are the components that generate thermal energy. They are typically arranged to provide 360-degree, uniform heating around the workpiece.
Common materials include high-purity graphite, molybdenum, or specialized ceramic composites. The material choice depends on the maximum required temperature and the chemical compatibility with the materials being processed.
The Insulation Package
Surrounding the heating elements is a multi-layered insulation package. Its job is to reflect radiant heat back into the workload area and prevent it from reaching and damaging the vacuum vessel.
Insulation is typically made from high-grade carbon felt and flexible graphite paper in graphite hot zones, or layers of metallic sheets (like molybdenum and stainless steel) in all-metal hot zones.
Creating the Void: The Vacuum Pumping System
This system is responsible for evacuating air and other gases from the vessel to create the necessary processing environment. It is not a single pump but a "pumping train."
The Pump Train
Achieving a deep vacuum requires a multi-stage process. It typically starts with a mechanical "roughing" pump to remove the bulk of the air, followed by a "high-vacuum" pump (like a diffusion or turbomolecular pump) to achieve the final, low-pressure environment.
Valves and Gauges
A series of vacuum valves is used to isolate the chamber from the pumps and control the evacuation process. Precision vacuum gauges are essential sensory devices that constantly measure the pressure inside the furnace, feeding that data back to the control system.
The Controlled Cooldown: The Cooling System
Rapid and controlled cooling, or "quenching," is just as important as heating for achieving the desired material properties.
Gas Quenching System
After the heating cycle is complete, the chamber is backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon. A powerful fan circulates this gas at high velocity through the hot zone, transferring heat away from the workpiece.
Specialized cooling nozzles are often strategically placed within the hot zone to direct the gas flow for maximum cooling uniformity. The heat is then removed from the gas via an internal heat exchanger connected to a water supply.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hot Zone Materials
The choice between a graphite hot zone and an all-metal hot zone is one of the most significant decisions in furnace design, with direct impacts on performance and cost.
Graphite Hot Zones
Graphite is an excellent and robust material for heating elements and insulation. It is relatively low-cost and can operate at very high temperatures, often exceeding 2000°C.
The main drawback is the potential for carbon contamination. The high-temperature vacuum environment can cause microscopic particles of carbon to transfer to the workpiece, which is unacceptable for certain sensitive alloys.
All-Metal Hot Zones
These hot zones use refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten for both the heating elements and the insulation shields. They provide an exceptionally clean processing environment, which is critical for medical, aerospace, and nuclear applications.
The trade-off is higher cost and a generally lower maximum operating temperature compared to graphite designs. Metal shields can also become brittle over time and may require more maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the function of each internal component allows you to select the right equipment for your specific metallurgical goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (>1300°C) and cost-efficiency: A furnace with a graphite-based hot zone is often the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive alloys or ensuring maximum cleanliness: An all-metal hot zone is critical to prevent carbon contamination and ensure product purity.
- If your primary focus is rapid quenching and process repeatability: The design of the gas cooling system and the sophistication of the control system are your most important considerations.
By seeing the furnace as an integrated system, you can better control your process and achieve superior results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials/Features |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Vessel | Houses internal components, withstands pressure | High-strength steel, water-cooled double-wall |
| Hot Zone | Generates and contains heat for workpiece | Graphite, molybdenum, ceramic composites, insulation packages |
| Vacuum System | Removes atmosphere to create vacuum | Mechanical roughing pump, high-vacuum pump, valves, gauges |
| Cooling System | Controls cooldown via gas quenching | Inert gas (e.g., nitrogen), fan, heat exchanger, nozzles |
Unlock Precision in Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Furnaces
Are you striving for contaminant-free material transformations and superior heat treatment results? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs.
Whether you require high-temperature efficiency with graphite hot zones or ultra-clean processing with all-metal designs, we deliver reliable performance and rapid quenching for applications in aerospace, medical, and beyond. Don't let equipment limitations hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can enhance your process and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















