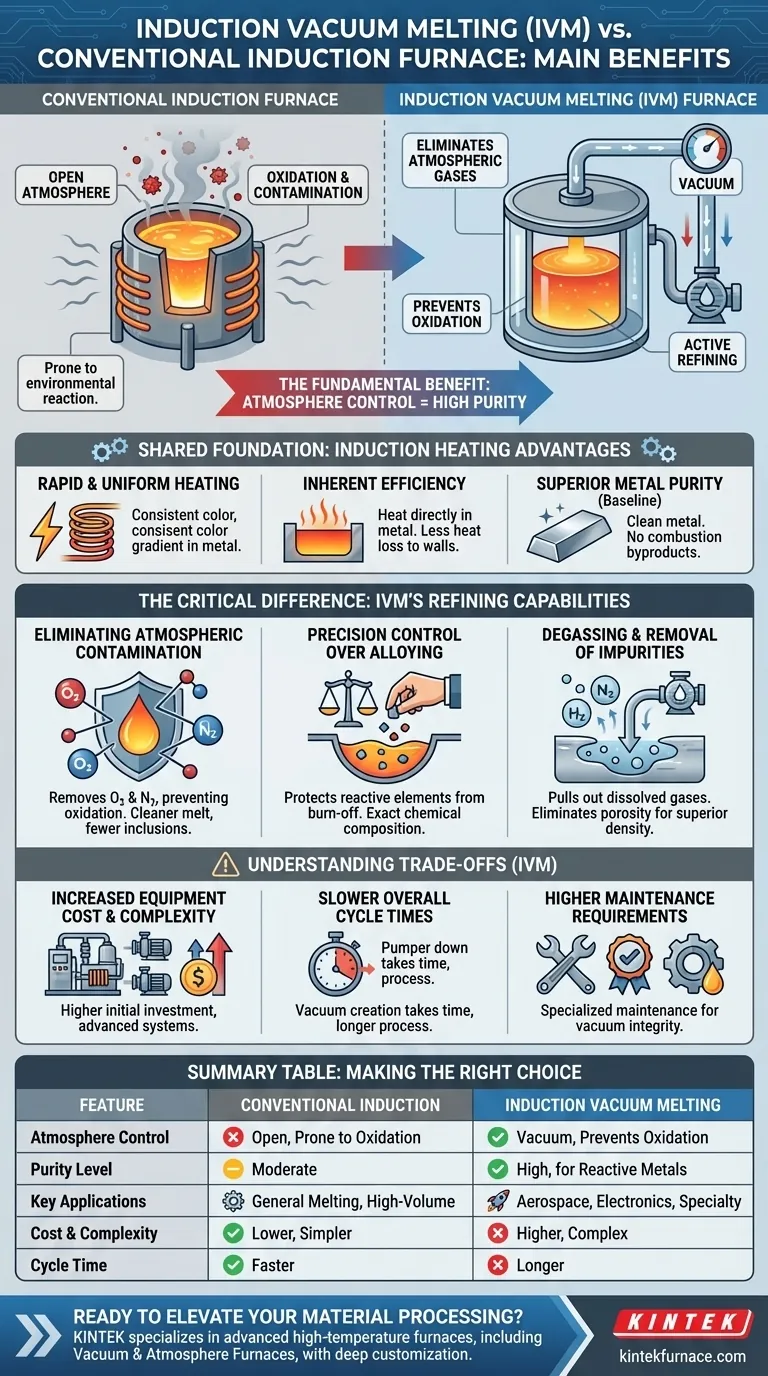
The fundamental benefit of an induction vacuum melting (IVM) furnace over a conventional induction furnace is its ability to control the furnace atmosphere. By creating a vacuum, the IVM furnace eliminates atmospheric gases that cause oxidation and contamination, resulting in significantly higher purity and enhanced properties in the final metal or alloy. This makes it indispensable for processing reactive metals and producing materials for high-specification industries like aerospace and electronics.
While both furnaces leverage the speed and efficiency of induction heating, the key difference lies in the environment. A conventional furnace simply melts the material, whereas a vacuum furnace actively refines it by removing unwanted atmospheric and dissolved elements.

The Foundation: Why Induction Heating is Effective
Before comparing the two, it's crucial to understand that both furnace types are built on the highly effective principles of induction heating. This shared foundation provides several inherent advantages over older, fuel-fired methods.
Rapid and Uniform Heating
Induction technology uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal itself. This process is incredibly fast and ensures the entire charge melts uniformly, increasing productivity and consistency.
Inherent Efficiency
By heating the material directly, induction minimizes the energy lost to heating the furnace walls or the surrounding air. This direct transfer of energy makes it a more efficient and cost-effective method for melting.
Superior Metal Purity (Baseline)
Compared to combustion furnaces, a standard induction furnace already offers a cleaner melt. There are no byproducts of combustion, like carbon or sulfur, to contaminate the metal, which is why it has become a standard for applications like melting gold.
The Critical Difference: Adding the Vacuum
The introduction of a vacuum chamber transforms the furnace from a simple melter into a sophisticated refining tool. This controlled environment is what provides the IVM furnace with its most significant advantages.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
The primary role of the vacuum is to remove oxygen and nitrogen from the chamber. This prevents oxidation of the molten metal, especially when working with highly reactive elements like titanium, aluminum, and rare-earth metals. The result is a cleaner melt free of oxide inclusions, which are a common source of mechanical failure.
Precision Control Over Alloying
In an open atmosphere, certain valuable and reactive alloying elements can burn off and be lost as oxides. In a vacuum, these elements are protected, allowing for extremely precise control over the final chemical composition of the alloy.
Degassing and Removal of Impurities
The vacuum environment actively pulls dissolved gases, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the molten metal. This degassing process is critical for eliminating porosity and internal defects, leading to materials with superior density and mechanical integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, choosing an IVM furnace involves accepting certain complexities and limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging these trade-offs.
Increased Equipment Cost and Complexity
An IVM system is inherently more complex than a conventional one. It requires a robust vacuum chamber, high-capacity vacuum pumps, sophisticated seals, and advanced control systems, all of which lead to a higher initial investment.
Slower Overall Cycle Times
Although the induction melting itself is fast, the overall process cycle for an IVM furnace can be longer. Time must be spent pumping the chamber down to the required vacuum level before melting can begin and, in some cases, backfilling with an inert gas.
Higher Maintenance Requirements
The vacuum pumps, seals, and instrumentation of an IVM furnace require more specialized maintenance than an open-air induction furnace. Maintaining vacuum integrity is an ongoing operational task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision between a conventional and a vacuum induction furnace is not about which is "better," but which is the appropriate tool for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume melting of non-reactive metals: A conventional induction furnace offers the best balance of speed, efficiency, and operational simplicity.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, reactive, or specialty alloys: An induction vacuum furnace is essential to prevent contamination, control the final composition, and meet stringent quality standards.
- If your primary focus is enhancing material properties to their theoretical maximum: The degassing and refining capabilities of a vacuum furnace are non-negotiable for creating materials free from internal defects for critical applications.
Ultimately, your choice depends on a clear understanding of your material's chemistry and the performance demands of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Vacuum Melting Furnace | Conventional Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum environment prevents oxidation and contamination | Open atmosphere, prone to oxidation |
| Purity Level | High purity, ideal for reactive metals and alloys | Moderate purity, suitable for non-reactive metals |
| Key Applications | Aerospace, electronics, specialty alloys | General melting, high-volume non-reactive metals |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher initial cost and maintenance | Lower cost and simpler operation |
| Cycle Time | Longer due to vacuum processes | Faster melting cycles |
Ready to elevate your material processing with high-purity solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's capabilities and drive innovation in your industry!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















