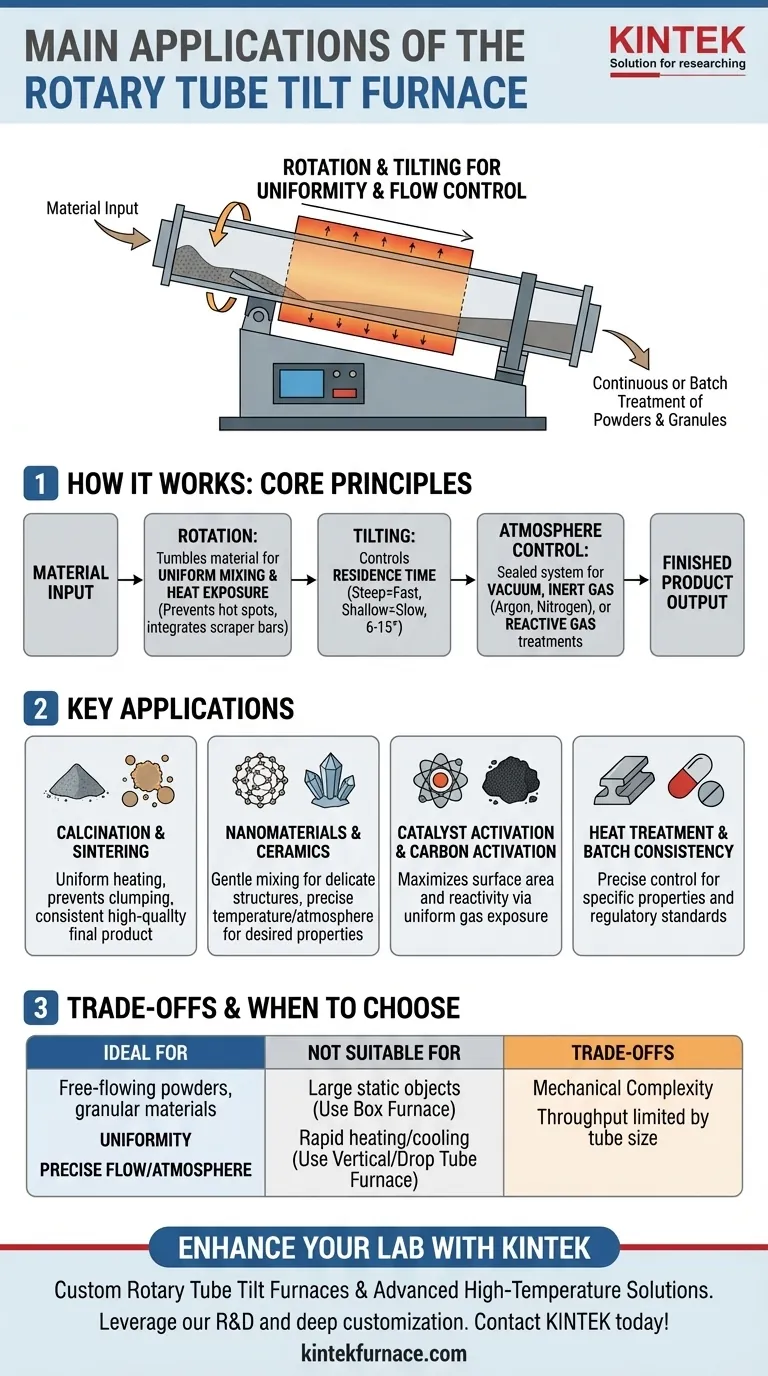
In essence, the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is a specialized tool for the continuous or batch heat treatment of powders, granules, and other free-flowing materials. Its primary applications span from powder processing like calcination and sintering to the synthesis of advanced materials like ceramics and nanomaterials, as well as chemical processing, carbon activation, and metallurgical treatments.
The furnace’s defining feature is its ability to combine rotation for uniform material mixing and heat exposure with tilting for precise control over material flow and residence time. This makes it uniquely suited for processes where every particle must be treated identically in a controlled atmosphere.

How It Works: The Core Principles
A Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace operates on a simple yet powerful mechanical concept. Material is fed into one end of a heated, rotating tube that is tilted at a slight angle, causing the material to tumble and flow towards the exit.
The Role of Rotation
The slow, constant rotation of the tube is the key to process uniformity. It gently tumbles the material, ensuring that every particle is exposed to the heat source and the controlled atmosphere inside the tube.
This tumbling action prevents hot spots and guarantees that processes like drying, calcination, or chemical reactions occur evenly throughout the entire batch. Scraper bars are often integrated inside the tube to prevent material from sticking to the walls and to enhance mixing.
The Function of Tilting
The tilt angle, typically adjustable between 6 and 15 degrees, dictates the residence time—how long the material spends inside the hot zone.
A steeper angle results in a faster flow and shorter residence time, while a shallower angle increases the time the material is processed. This adjustability provides precise control over the treatment, which is critical for achieving desired material properties. The tilt also facilitates easy and complete discharge of the finished product.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
The furnace is a sealed system, allowing for complete control over the internal environment. This is crucial for many advanced applications.
Operations can be conducted under a vacuum to remove air and prevent oxidation, or the tube can be purged with a specific gas (like argon or nitrogen) to create an inert atmosphere. This also allows for the introduction of reactive gases to perform specific chemical treatments, such as in catalyst activation.
Key Applications in Detail
The unique combination of rotation, tilt, and atmosphere control makes this furnace ideal for a range of demanding industrial and research applications.
Powder Processing (Calcination & Sintering)
For calcination (heating to drive off impurities) and sintering (heating to fuse particles together), uniform temperature is non-negotiable. The furnace's tumbling action ensures every particle reaches the target temperature, resulting in a consistent, high-quality final product without clumps or uneven processing.
Material Synthesis (Nanomaterials & Ceramics)
The gentle mixing at low RPM (1-20 RPM) is perfect for synthesizing delicate structures like nanomaterials without damaging them. For advanced ceramics, the precise temperature and controlled atmosphere are essential for achieving the desired crystalline structures and material properties.
Chemical and Carbon Processing
When activating catalysts or producing activated carbon, the goal is to maximize surface area and reactivity. The rotation constantly exposes new surfaces of the material to the reactive gases, making the process highly efficient and uniform.
Metallurgical and Pharmaceutical Powders
In metallurgy, precise heat treatment is vital for achieving specific alloy properties. In pharmaceuticals, batch consistency is a regulatory requirement. The furnace's ability to precisely control temperature, residence time, and atmosphere ensures repeatable results that meet strict quality standards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is a specialized tool. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
When Another Furnace Is a Better Fit
This furnace is designed for free-flowing powders and granular materials. It is not suitable for processing large, solid objects or static samples.
For heat-treating single, large parts, a Box Furnace is more practical. For processes requiring extremely rapid heating or cooling, such as thermal shock testing or gas quenching, a Vertical or Drop Tube Furnace is a better choice.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating seals, drive motor, and tilting mechanism add mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. This can translate to higher initial costs and more demanding maintenance requirements to ensure the seals remain intact and the motion is smooth.
Throughput and Scale
Throughput is limited by the diameter and length of the processing tube. While excellent for lab-scale and pilot production, scaling to very high-volume industrial production may require multiple units or a different technology altogether.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your material and your processing objective.
- If your primary focus is uniform processing of powders or granular materials: The Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is the superior choice due to its unmatched mixing and heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is precise control over material flow and residence time: This furnace offers unparalleled control through its adjustable tilt and rotation speed.
- If your primary focus is processing large, static objects or batches: A Box Furnace is a more practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific chemical reaction in a controlled atmosphere: The sealed tube and gas-purging capabilities make this furnace ideal for synthesizing materials and activating chemicals.
By understanding these core capabilities, you can confidently determine if this furnace is the right instrument to achieve your material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Processing | Calcination, Sintering | Uniform heating, prevents clumping |
| Material Synthesis | Nanomaterials, Ceramics | Gentle mixing, controlled atmosphere |
| Chemical Processing | Catalyst activation, Carbon activation | Efficient gas exposure, high reactivity |
| Metallurgical & Pharmaceutical | Heat treatment, Batch consistency | Precise temperature, repeatable results |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a custom Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for uniform powder processing and controlled atmosphere applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your research and production forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















