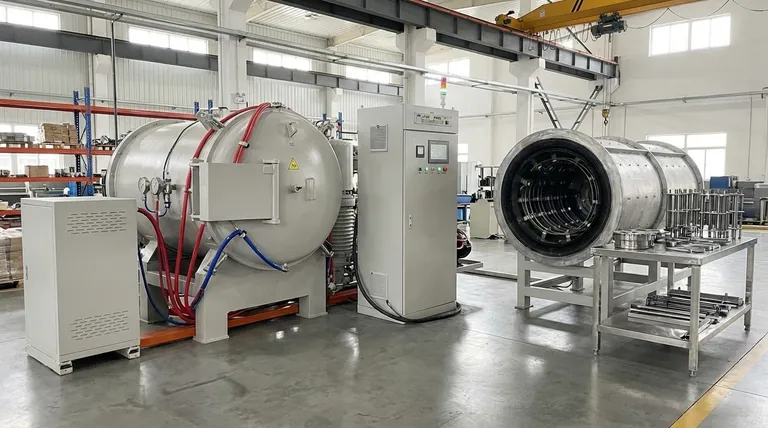
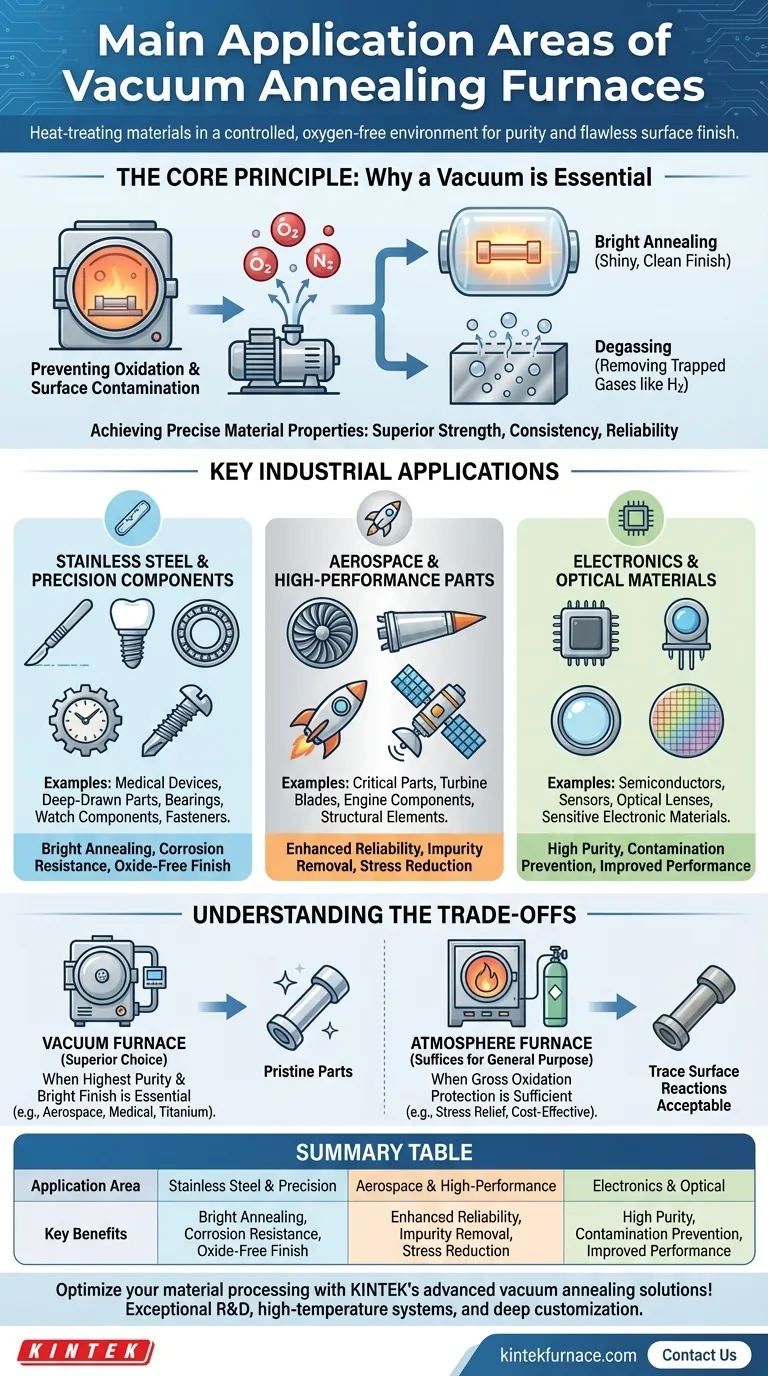
At its core, a vacuum annealing furnace is used for heat-treating materials in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. Its primary applications span industries where material purity and a flawless surface finish are critical, including the manufacturing of stainless steel components, medical devices, aerospace parts, and sensitive electronic or optical materials.
The fundamental reason to use a vacuum annealing furnace is to prevent oxidation and contamination. By removing atmospheric gases, the furnace allows for heat treatment that purifies materials and preserves their surface integrity, which is impossible to achieve in the presence of air.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum is Essential
The decision to use a vacuum furnace over other types is driven by the need for absolute control over the material's environment during heat treatment. At high temperatures, most metals readily react with oxygen and other gases in the air, forming oxides and other impurities on their surface.
Preventing Oxidation and Surface Contamination
A vacuum furnace works by pumping out the atmosphere before the heating process begins. This removal of reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen is the key to preventing discoloration and the formation of an oxide layer on the material's surface.
This process is essential for achieving a "bright annealing" finish, where the metal part exits the furnace as clean and shiny as it was when it entered. This is critical for products where aesthetics or subsequent processing, like plating, are important.
Achieving Precise Material Properties
Beyond a clean surface, the vacuum environment allows for the refinement of the material itself. Processes like degassing remove trapped gases (such as hydrogen) from within the metal, which can significantly improve its mechanical properties and reduce the risk of embrittlement.
The controlled environment also enables precise manipulation of alloy compositions and the removal of low-melting-point volatile impurities, leading to a final product with superior strength, consistency, and reliability.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique benefits of vacuum annealing make it indispensable in several high-stakes manufacturing sectors.
Stainless Steel and Precision Components
This is a primary application area. Many stainless steel products require a clean, corrosion-resistant surface that cannot be compromised by an oxide layer.
Examples include medical devices (which must be biocompatible and sterile), deep-drawn parts like plumbing fixtures, precision bearings, watch components, cutting tools, and fasteners like self-drilling screws.
Aerospace and High-Performance Parts
In the aerospace industry, material failure is not an option. Components must meet extreme performance and reliability standards.
Vacuum annealing is used to treat critical parts, ensuring they are free from internal impurities and surface defects that could become stress points and lead to catastrophic failure.
Electronics and Optical Materials
The performance of semiconductors, sensors, and optical lenses depends on extreme material purity. Even minuscule contamination can alter a material's electrical or optical properties, rendering the component useless.
Vacuum furnaces are used for annealing these sensitive materials to ensure their intended function is not compromised by atmospheric reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not always the necessary choice. The key is to understand the trade-offs compared to a simpler atmosphere furnace, which uses a controlled flow of protective gases (like nitrogen or argon) instead of a vacuum.
When to Choose Vacuum Annealing
A vacuum furnace is the superior choice when the application demands the highest possible purity. If your goal is a "bright," oxide-free finish, degassing of internal impurities, or processing highly reactive metals like titanium, a vacuum environment is essential.
When an Atmosphere Furnace Suffices
For many general-purpose heat treatments, an atmosphere furnace provides sufficient protection against gross oxidation. If trace surface reactions are acceptable and the primary goal is simply to relieve stress or alter grain structure without the stringent purity requirements of aerospace or medical applications, an atmosphere furnace can be a more cost-effective and simpler solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating environment is a critical decision based on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: Choose vacuum annealing for critical applications like aerospace components, medical implants, and high-purity electronic materials.
- If your primary focus is a "bright," oxide-free finish: Use a vacuum furnace for stainless steel products, precision bearings, and any component where surface integrity is paramount.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment: An atmosphere furnace may be a more practical and economical choice when absolute purity is not a strict requirement.
Ultimately, the choice between furnace types depends on creating the precise environment your material needs to achieve its intended properties.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel & Precision Components | Bright annealing, corrosion resistance, oxide-free finish |
| Aerospace & High-Performance Parts | Enhanced reliability, impurity removal, stress reduction |
| Electronics & Optical Materials | High purity, contamination prevention, improved performance |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced vacuum annealing solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior purity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your aerospace, medical, or electronics applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity



















