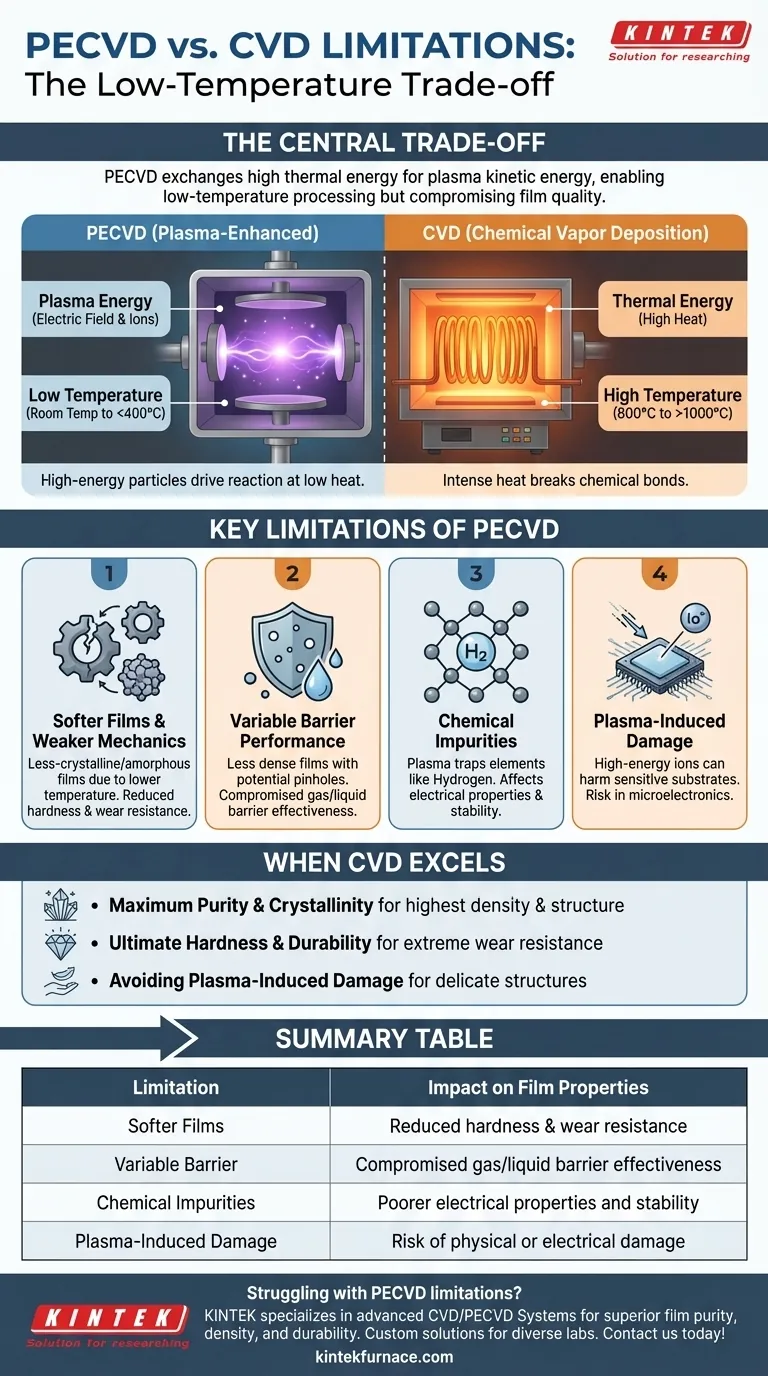
At its core, the primary limitations of Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) compared to traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) stem directly from its greatest strength: its low-temperature process. While this enables coating on sensitive materials, it can result in films with lower density, weaker mechanical properties, and the potential for chemical impurities that high-temperature CVD processes are better able to overcome.
The central trade-off is clear: PECVD exchanges the high thermal energy of CVD for the kinetic energy of plasma. This allows for versatility and speed at lower temperatures but can compromise the ultimate purity, density, and durability of the deposited film.

The Fundamental Difference: Plasma vs. Heat
To understand the limitations, you must first understand the core mechanisms. Both methods deposit a thin solid film from a gaseous state, but they use fundamentally different energy sources to drive the chemical reaction.
How Traditional CVD Works
Traditional CVD relies on thermal energy. Precursor gases are introduced into a high-temperature chamber (from several hundred to over 1000°C), and the intense heat breaks the chemical bonds, allowing the desired material to deposit onto the substrate.
This high-energy thermal environment provides atoms with significant mobility on the surface, often resulting in highly ordered, dense, and pure crystalline films.
How PECVD Works
PECVD replaces most of the thermal energy with plasma. An electric field is used to ionize the precursor gases, creating a reactive mix of ions, electrons, and free radicals.
These high-energy particles bombard the substrate surface, driving chemical reactions at much lower temperatures—often from room temperature up to a few hundred degrees Celsius.
Key Limitations of PECVD
The lower-energy nature of the PECVD process is the direct cause of its primary drawbacks when compared to high-temperature CVD.
Softer Films and Weaker Mechanics
Because the deposition occurs at lower temperatures, the atoms have less energy to arrange themselves into a perfect, dense crystal lattice.
This often results in amorphous or less-crystalline films that are softer and have lower wear resistance than their high-temperature CVD counterparts, such as silicon carbide or diamond-like carbon.
Variable Barrier Performance
While PECVD can create excellent nano-thin barrier films, their ultimate performance is highly dependent on process parameters.
The lower deposition energy can lead to films that are less dense and contain more pinholes than the highest-quality CVD films. This can compromise their effectiveness as a barrier against gases or liquids in demanding applications.
Potential for Chemical Impurities
The plasma process can incorporate unwanted elements into the film. For instance, in the deposition of silicon nitride (SiNx) or silicon dioxide (SiO2), significant amounts of hydrogen from the precursor gases can remain trapped in the film.
These impurities can negatively affect the film's electrical properties, optical transparency, and long-term stability. High-temperature CVD processes are more effective at driving off such contaminants.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When CVD Excels
Acknowledging PECVD's limitations highlights the scenarios where traditional CVD remains the superior choice, assuming the substrate can tolerate the conditions.
For Maximum Purity and Crystallinity
When the primary goal is to create a film with the highest possible density, purity, or a specific crystalline structure, the high thermal energy of CVD is often necessary. The heat provides the energy required for atoms to achieve their lowest-energy state in a near-perfect lattice.
For Ultimate Hardness and Durability
For applications requiring extreme hardness and wear resistance, such as cutting tools or industrial surfaces, high-temperature CVD is used to deposit materials like diamond, silicon carbide (SiC), or titanium nitride (TiN). PECVD typically cannot achieve the same level of hardness.
When Avoiding Plasma-Induced Damage
The high-energy ions in a plasma environment can cause physical or electrical damage to sensitive substrates, particularly in microelectronics. Traditional CVD, which lacks this ion bombardment, can be a gentler method for depositing films on delicate device structures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision between PECVD and CVD is not about which is "better" overall, but which is the correct tool for your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is the definitive choice, as it protects plastics, polymers, and complex electronic assemblies from thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity, density, and hardness: Traditional CVD is often superior, provided the substrate can withstand the intense heat required.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and lower cost for versatile coatings: PECVD frequently offers an advantage due to faster deposition rates, lower energy consumption, and the ability to tailor film properties.
Ultimately, your choice is dictated by balancing the thermal budget of your substrate against the required performance of the final film.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Description | Impact on Film Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Softer Films | Lower temperature leads to amorphous or less-crystalline structures. | Reduced hardness and wear resistance. |
| Variable Barrier Performance | Less dense films with potential pinholes. | Compromised gas/liquid barrier effectiveness. |
| Chemical Impurities | Plasma can trap elements like hydrogen in the film. | Poorer electrical properties and stability. |
| Plasma-Induced Damage | High-energy ions may harm sensitive substrates. | Risk of physical or electrical damage in microelectronics. |
Struggling with PECVD limitations in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, to help you achieve superior film purity, density, and durability. With our deep customization capabilities, we tailor solutions for diverse laboratories—whether you're working with sensitive materials or need maximum performance. Contact us today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces can meet your unique experimental needs and enhance your research outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods



















