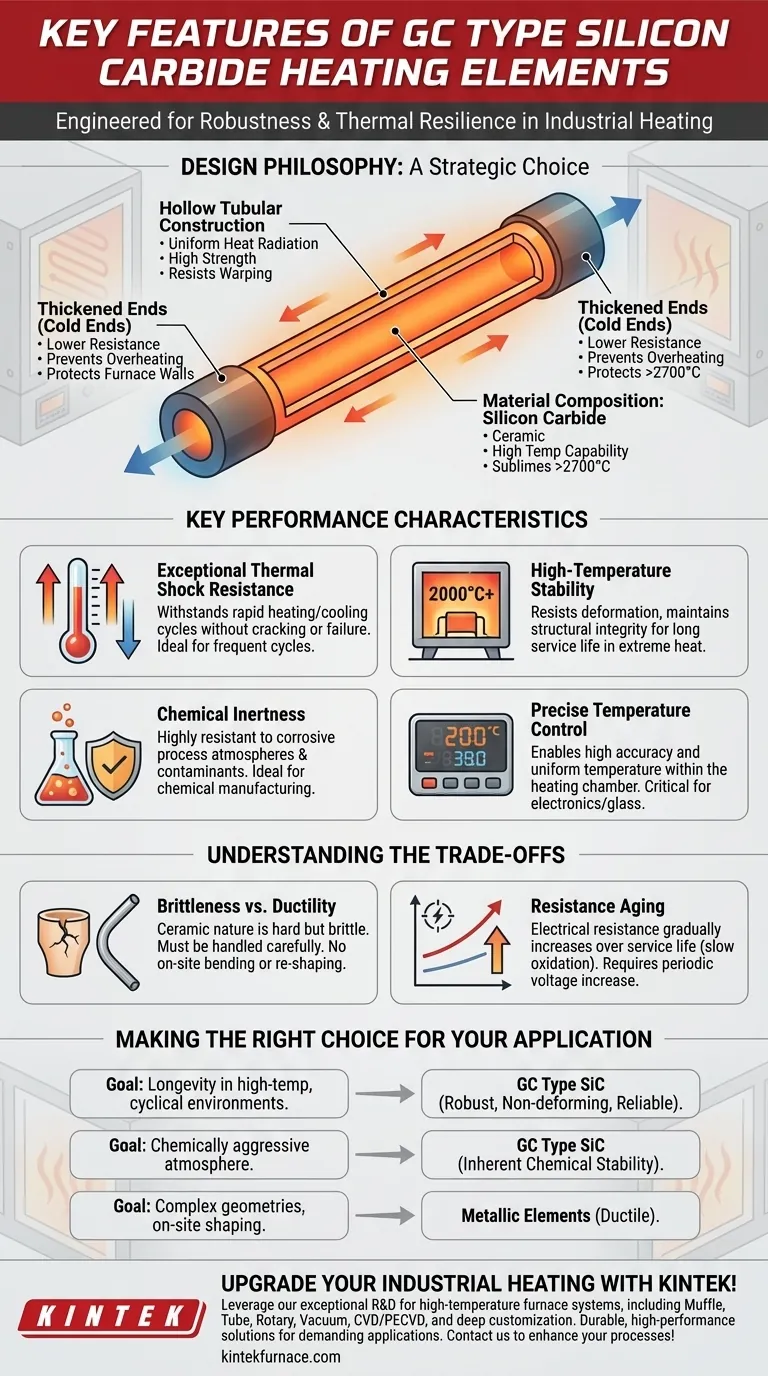
At their core, GC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are defined by a unique physical design: a hollow tubular shape with intentionally thickened ends. This specific construction is engineered to deliver exceptional robustness, allowing the element to withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles (thermal shock) without deforming, while also ensuring reliable electrical connections in high-temperature industrial settings.
The decision to use a GC Type element is a strategic choice for applications where thermal resilience and structural integrity are paramount. Its design prioritizes longevity and consistent performance in harsh chemical and high-temperature environments over the field flexibility of metallic alternatives.

The Design Philosophy of GC Type Elements
The features of a GC Type element are not arbitrary; they are direct solutions to the challenges of industrial heating. The design reflects a deep understanding of material science and thermal dynamics.
Hollow Tubular Construction
The primary body of the element is a hollow tube. This shape provides an excellent surface area for radiating heat uniformly within a furnace chamber.
This structure is inherently strong and resistant to the sagging or warping that can affect other element types at extreme temperatures.
Thickened Ends (Cold Ends)
The ends of the element are significantly thicker than the central heating section. This is a critical design feature, not just for strength.
These "cold ends" have lower electrical resistance, causing them to operate at a much lower temperature than the main body. This design prevents overheating at the connection points and protects the furnace's refractory wall from damage.
Material Composition: Silicon Carbide
The element is made from silicon carbide, a ceramic material that is exceptionally hard and strong. Unlike metals, it does not melt but sublimes at very high temperatures (above 2700°C).
This material base gives the element its fundamental characteristics: high-temperature capability and resistance to wear.
Key Performance Characteristics
The design and material choice result in a set of distinct performance advantages that make GC Type elements suitable for demanding jobs.
Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance
The most cited benefit is the ability to handle rapid temperature changes. These elements can be heated and cooled quickly without cracking or failing, which is essential for processes with frequent cycles.
High-Temperature Stability
GC Type elements are engineered to operate consistently at very high temperatures. They resist deformation and maintain their structural integrity, ensuring a long and predictable service life.
Chemical Inertness
Silicon carbide is highly resistant to chemical attack from process atmospheres and contaminants. This makes it an ideal choice for applications in chemical manufacturing and material processing where corrosive agents may be present.
Precise Temperature Control
The elements enable high-temperature control accuracy and promote a small temperature differential across the heating chamber. This uniformity is critical for producing high-quality materials in industries like electronics and glass manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No component is perfect for every situation. Being an effective technical advisor means acknowledging the limitations and operational considerations.
Brittleness vs. Ductility
Silicon carbide is a ceramic, making it hard but also brittle. Unlike ductile metallic wire elements, GC Type elements cannot be bent or re-shaped on-site. They must be handled carefully during installation to avoid fracture from impact or stress.
Resistance Aging
A fundamental characteristic of all silicon carbide elements is that their electrical resistance gradually increases over their service life. This "aging" is a result of slow oxidation.
This is not a defect but an operational reality. To maintain constant power output and temperature, the voltage supplied to the elements must be increased over time, typically requiring a tapped transformer or a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) power controller.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires matching its features to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is longevity in high-temperature, cyclical environments: The robust, non-deforming structure of the GC Type makes it a superior choice for furnace reliability.
- If your primary focus is operating within a chemically aggressive atmosphere: The inherent chemical stability of silicon carbide offers performance where metallic elements would quickly corrode and fail.
- If your primary focus is complex heating geometries or requires on-site shaping: A more ductile metallic heating element may be a better fit, as SiC elements are brittle and come in pre-formed shapes.
Ultimately, selecting a GC Type SiC element is an investment in predictable, long-term performance under the most demanding industrial conditions.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Hollow Tubular Construction | Provides uniform heat radiation and structural strength, resisting warping at high temperatures. |
| Thickened Ends (Cold Ends) | Lowers temperature at connections, preventing overheating and protecting furnace walls. |
| Material: Silicon Carbide | Offers high-temperature capability (sublimes above 2700°C), hardness, and chemical resistance. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or deformation. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains structural integrity and consistent performance in extreme heat for long service life. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from aggressive atmospheres, ideal for chemical and material processing. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Enables accurate temperature management and uniform heating for high-quality outputs. |
| Brittleness | Ceramic nature makes it fragile; requires careful handling and pre-formed shapes, no on-site bending. |
| Resistance Aging | Electrical resistance increases over time, necessitating voltage adjustments for constant power. |
Upgrade your industrial heating with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need reliable thermal resilience, chemical inertness, or precise control, KINTEK delivers durable, high-performance heating elements for demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your processes and ensure long-term efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















