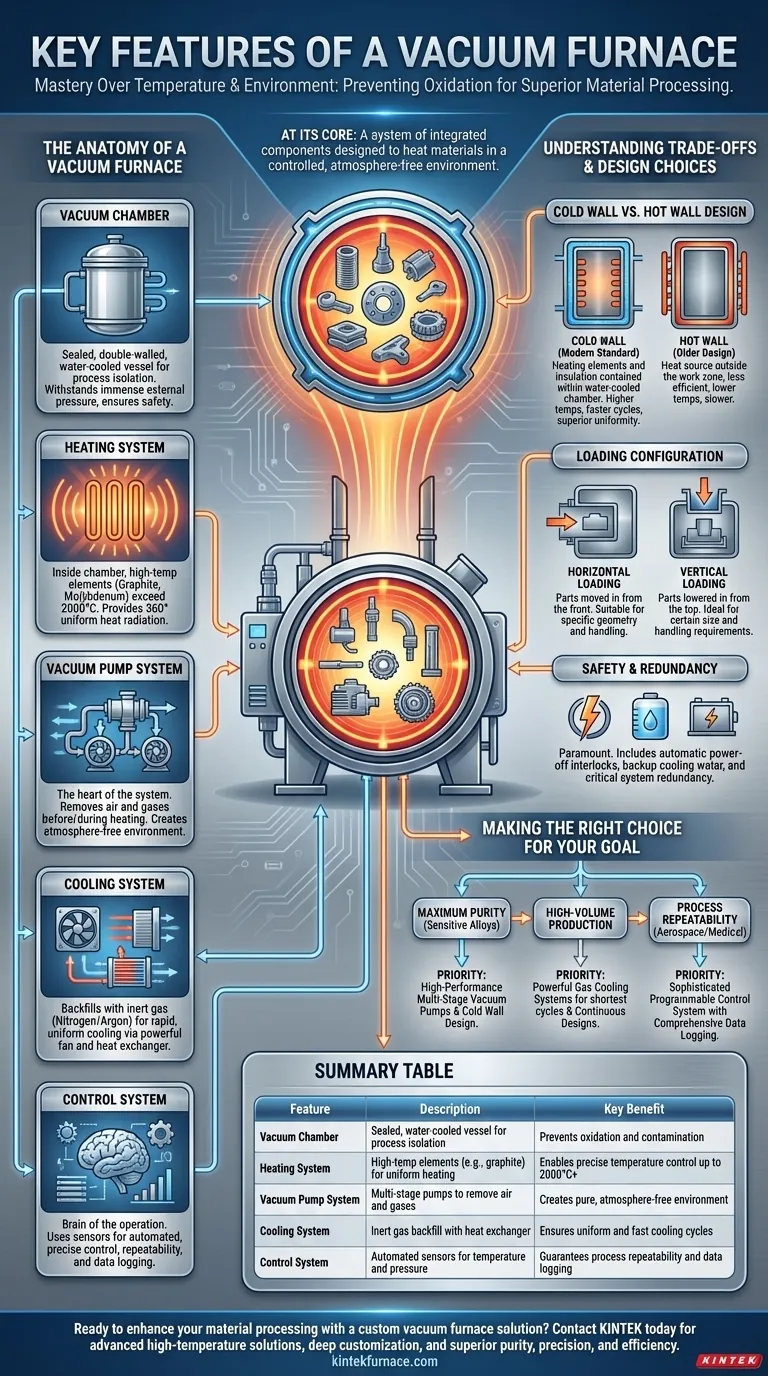
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a system of integrated components designed to heat materials in a controlled, atmosphere-free environment. The key features are the vacuum chamber that contains the process, a high-temperature heating system, a multi-stage vacuum pump system to remove air, a rapid cooling system, and a precise control system to manage the entire cycle. These elements work in concert to prevent oxidation and contamination, enabling superior material processing.
A vacuum furnace is not just a tool for applying heat; it is an instrument for creating an exceptionally pure environment. The defining feature is the vacuum itself, which allows for metallurgical processes that are impossible to achieve in the presence of air.

The Anatomy of a Vacuum Furnace
Understanding a vacuum furnace begins with its five critical systems. Each is engineered for reliability and precision under extreme conditions.
The Vacuum Chamber
The vacuum chamber is the sealed vessel where the entire process takes place. It is typically a double-walled, water-cooled structure constructed from high-strength steel.
This robust construction ensures the chamber can withstand the immense external atmospheric pressure when a deep vacuum is pulled inside, while the water jacket keeps the outer walls cool and safe.
The Heating System
Located inside the chamber, the heating system is designed for high temperatures and thermal uniformity. Heating elements are commonly made from materials like graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten, chosen for their ability to operate at temperatures often exceeding 2000°C.
These elements are often arranged to provide 360-degree heat radiation, ensuring the workload is heated evenly from all sides and eliminating hot spots. High-grade carbon felt and flexible graphite paper are used as insulation to retain heat and improve energy efficiency.
The Vacuum Pump System
This is the heart of the furnace's unique capability. The vacuum pump system removes air and other gases from the chamber before and during the heating process.
It typically consists of multiple pumps working in stages to achieve the desired vacuum level, effectively eliminating oxygen and other reactive gases that would otherwise contaminate or oxidize the material at high temperatures.
The Cooling System
After the heating cycle, materials often need to be cooled rapidly and uniformly. The cooling system accomplishes this by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon.
A powerful fan circulates this gas through the hot zone and over a water-cooled heat exchanger, quickly and controllably removing heat from the workload.
The Control System
The control system is the brain of the operation, integrating all other components. It uses precise sensors for temperature and pressure to automate the entire heating and cooling cycle.
This ensures extreme process repeatability, executes complex recipes with multiple steps, and logs all data for quality assurance and certification.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Choices
Not all vacuum furnaces are created equal. Key design decisions fundamentally alter the furnace's performance, capabilities, and suitability for a given task.
Cold Wall vs. Hot Wall Design
This is the most significant design distinction. Modern, high-performance furnaces are almost exclusively cold wall designs.
In a cold wall furnace, the heating elements and insulation are contained within the water-cooled vacuum chamber. This isolates the heat to the "hot zone," allowing for much higher operating temperatures, faster heating and cooling cycles, and superior temperature uniformity.
Loading Configuration
Furnaces can be designed for horizontal loading, where parts are moved in from the front, or vertical loading, where parts are lowered in from the top. The choice depends entirely on the geometry, size, and handling requirements of the parts being processed.
Safety and Redundancy
Because of the extreme temperatures and pressures involved, safety is paramount. Features like automatic power-off interlocks on the furnace door are standard.
Furthermore, critical support systems often have built-in redundancy. For example, a high-altitude water tank may be used to provide emergency cooling water via gravity in case of a power outage or pump failure, preventing catastrophic damage to the seals and furnace body.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a vacuum furnace requires matching its features to your specific metallurgical objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for sensitive alloys: Prioritize a furnace with a high-performance, multi-stage vacuum pump system and a proven cold wall design.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Evaluate furnaces with powerful gas cooling systems for the shortest possible cycle times and consider continuous furnace designs.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability for aerospace or medical parts: You need a sophisticated and programmable control system with comprehensive data logging and reporting capabilities.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace transforms materials by precisely controlling the two most fundamental variables: temperature and environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed, water-cooled vessel for process isolation | Prevents oxidation and contamination |
| Heating System | High-temp elements (e.g., graphite, molybdenum) for uniform heating | Enables precise temperature control up to 2000°C+ |
| Vacuum Pump System | Multi-stage pumps to remove air and gases | Creates pure, atmosphere-free environment |
| Cooling System | Inert gas backfill with heat exchanger for rapid cooling | Ensures uniform and fast cooling cycles |
| Control System | Automated sensors for temperature and pressure management | Guarantees process repeatability and data logging |
Ready to enhance your material processing with a custom vacuum furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, CVD/PECVD Systems, and more. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for superior purity, precision, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals in aerospace, medical, or production applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















