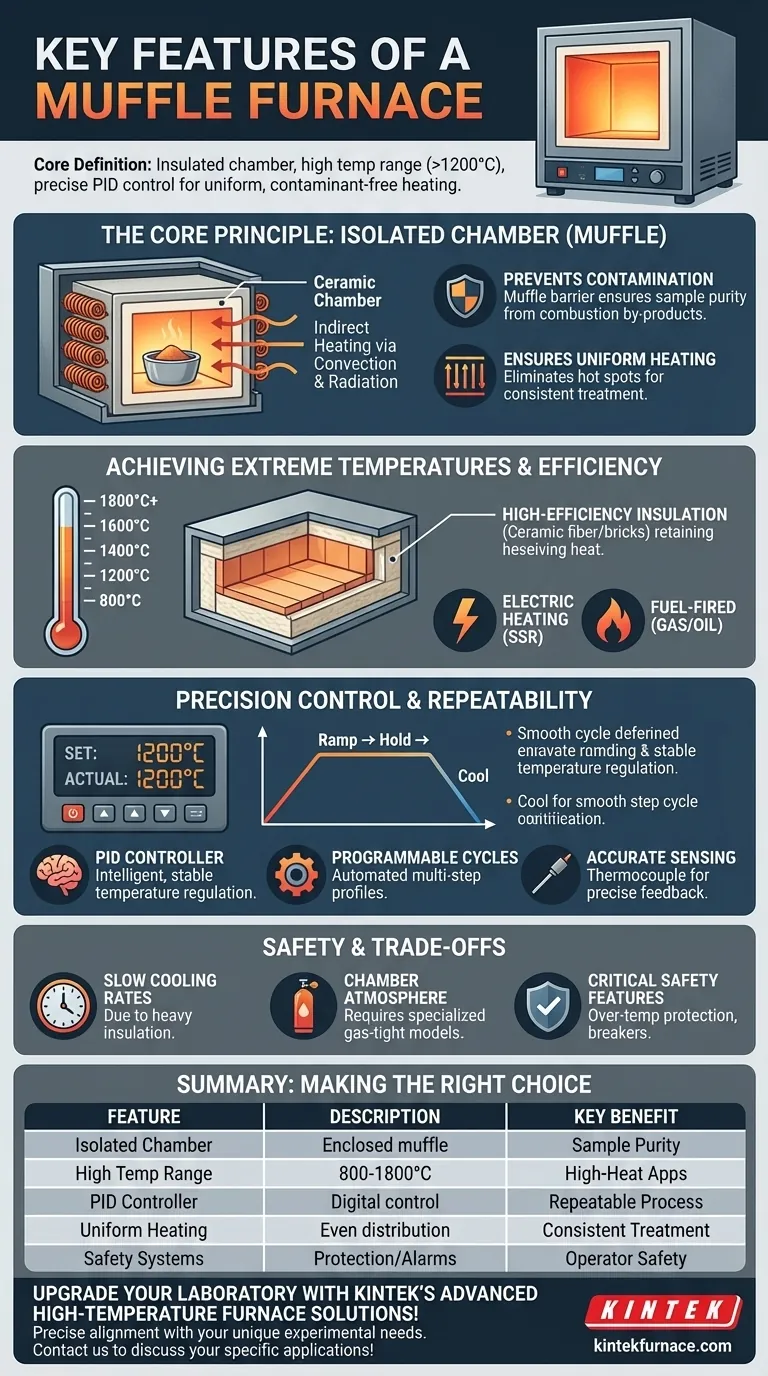
At its core, a muffle furnace is defined by several key features that work together to create a high-temperature environment. These include an insulated chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements, a high maximum temperature range (often exceeding 1200°C), and a precise digital control system, typically using a PID controller for stable and uniform heat.
The primary purpose of a muffle furnace's features is not just to get hot, but to provide an extremely uniform and controlled heating environment that is completely isolated from combustion by-products or direct radiation from electric elements. This ensures the chemical purity of the sample and the repeatability of the process.

The Core Principle: The Isolated Chamber (Muffle)
The defining feature that gives the muffle furnace its name is the "muffle" itself—the inner chamber that holds the material being heated.
What is the "Muffle"?
A muffle is a specialized, enclosed chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic or alloy. It physically separates the samples from the furnace's heating source.
This design means the material is heated indirectly. Heat transfers through the muffle's walls via convection and radiation, rather than being exposed directly to a flame or glowing electrical element.
Preventing Contamination
The primary benefit of this isolation is sample purity. In processes like ashing, chemical analysis, or creating high-purity glass, any contaminants from fuel combustion (like carbon or sulfur) could ruin the results.
The muffle acts as a barrier, ensuring the atmosphere inside the chamber remains clean and controlled, which is critical for scientific accuracy.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
By heating the entire chamber from the outside, the muffle design promotes exceptionally uniform temperature. The chamber walls absorb and radiate heat evenly, eliminating hot spots that could occur with direct heating. This uniformity is vital for consistent material treatments like annealing or tempering.
Achieving and Maintaining Extreme Temperatures
A muffle furnace is fundamentally a tool for high-heat applications. Its construction is entirely focused on reaching and holding these temperatures efficiently and safely.
High Temperature Range
Muffle furnaces are designed to operate at temperatures far beyond a standard oven, typically starting around 800°C and reaching 1200°C, 1600°C, or even 1800°C in specialized models. The required temperature range is one of the first specifications to consider when selecting a unit.
High-Efficiency Insulation
To maintain these temperatures without consuming enormous amounts of energy, furnaces use robust insulation. This is often a multi-layer system using materials like high-density ceramic fiber blankets or refractory bricks.
This insulation ensures maximum thermal efficiency by keeping heat inside the chamber and also keeps the exterior of the furnace cool to the touch for operator safety.
Heating Systems
Heating is accomplished either electrically or with fuel.
- Electric Furnaces: These are most common in laboratory settings. They use high-resistance heating elements controlled by a Solid-State Relay (SSR) for quiet and precise power delivery.
- Fuel-Fired Furnaces: Larger, industrial furnaces may be heated with natural gas, propane, or oil. Even in these models, the muffle design keeps the flame and combustion gases separate from the sample chamber.
Precision Control and Repeatability
Generating high heat is not enough; it must be precisely controlled to be useful. Modern muffle furnaces rely on sophisticated digital systems to achieve this.
The Role of PID Controllers
Nearly all modern furnaces use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. Unlike a simple thermostat that just turns the heat on or off, a PID controller intelligently anticipates heating needs to prevent overshooting the target temperature.
Many advanced models feature an auto-tuning PID, which automatically learns the thermal characteristics of the furnace to hold the set temperature with incredible stability, often within a single degree.
Programmable Cycles
For complex processes, operators can program multi-step temperature profiles. A furnace can be set to ramp up to a specific temperature, hold (or "soak") for a set duration, and then cool down, all automatically. This is essential for advanced materials science and heat treating.
Accurate Temperature Sensing
This entire control system relies on an accurate sensor. Most furnaces use a thermocouple, a simple and robust sensor made of two dissimilar metals. The specific type (e.g., J-type, K-type, S-type) depends on the maximum temperature range of the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety
While powerful, these features come with inherent operational considerations and a need for robust safety systems.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The same heavy-duty insulation that makes a furnace efficient also means it retains heat for a long time. While some models are designed for rapid heating, cool-down times can be slow. This must be factored into workflow planning.
Chamber Atmosphere
While a standard muffle furnace protects from heating contaminants, it does not inherently control the atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, argon). For processes that require an inert or reactive atmosphere, a specially designed gas-tight furnace with sealed doors and gas ports is necessary.
Critical Safety Features
Operating at extreme temperatures demands built-in safety. Key features include over-temperature protection, which automatically shuts the furnace down if it exceeds a maximum safe temperature, and electrical circuit breakers to prevent damage from power surges. Many also include alarms to alert operators to system faults.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The importance of each feature depends entirely on your intended application.
- If your primary focus is precise chemical analysis or ashing: The key feature is the isolated muffle chamber, which guarantees sample purity by preventing contamination from the heat source.
- If your primary focus is materials heat treatment (e.g., annealing): The combination of a programmable PID controller and uniform heating is most critical for achieving repeatable material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or ceramics testing: Your main concerns will be the maximum temperature rating, robust refractory insulation, and the furnace's overall durability.
Ultimately, these features work in concert to transform a simple hot box into a precise and reliable instrument for advanced scientific and industrial work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Isolated Chamber (Muffle) | Enclosed ceramic/alloy chamber separating samples from heating elements | Prevents contamination and ensures sample purity |
| High Temperature Range | Operates from 800°C to 1800°C, depending on model | Suitable for high-heat applications like sintering and ashing |
| PID Controller | Digital control system for stable, precise temperature regulation | Enables repeatable processes with minimal overshoot |
| Uniform Heating | Even heat distribution via chamber walls | Eliminates hot spots for consistent material treatment |
| Safety Systems | Includes over-temperature protection and circuit breakers | Ensures operator safety and equipment longevity |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs—enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and deliver tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















