A vacuum graphitizing furnace is defined by its integrated design, which enables the high-temperature transformation of carbon materials into crystalline graphite in a contamination-free environment. Its key features include a robust heating system capable of reaching over 2800°C, a high-performance vacuum system to ensure purity, specialized insulation to manage extreme heat, and a sophisticated control system for process precision and uniformity.
A vacuum graphitizing furnace is not just a collection of high-temperature components; it is an engineered system. Its design prioritizes the precise control of heat and atmosphere to achieve specific, high-purity crystalline structures in carbon-based materials.
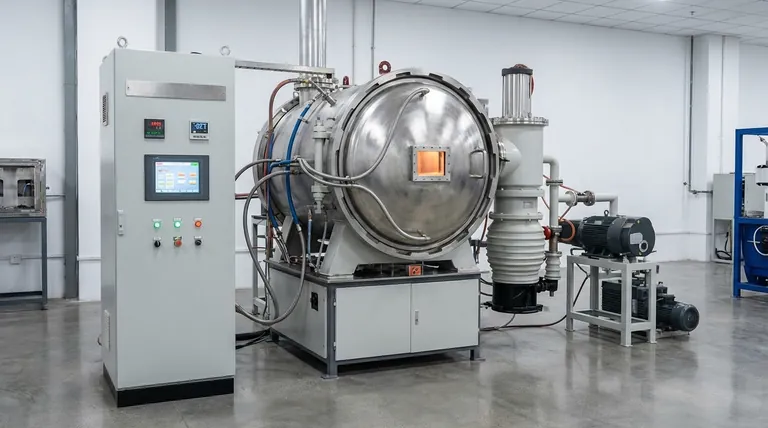

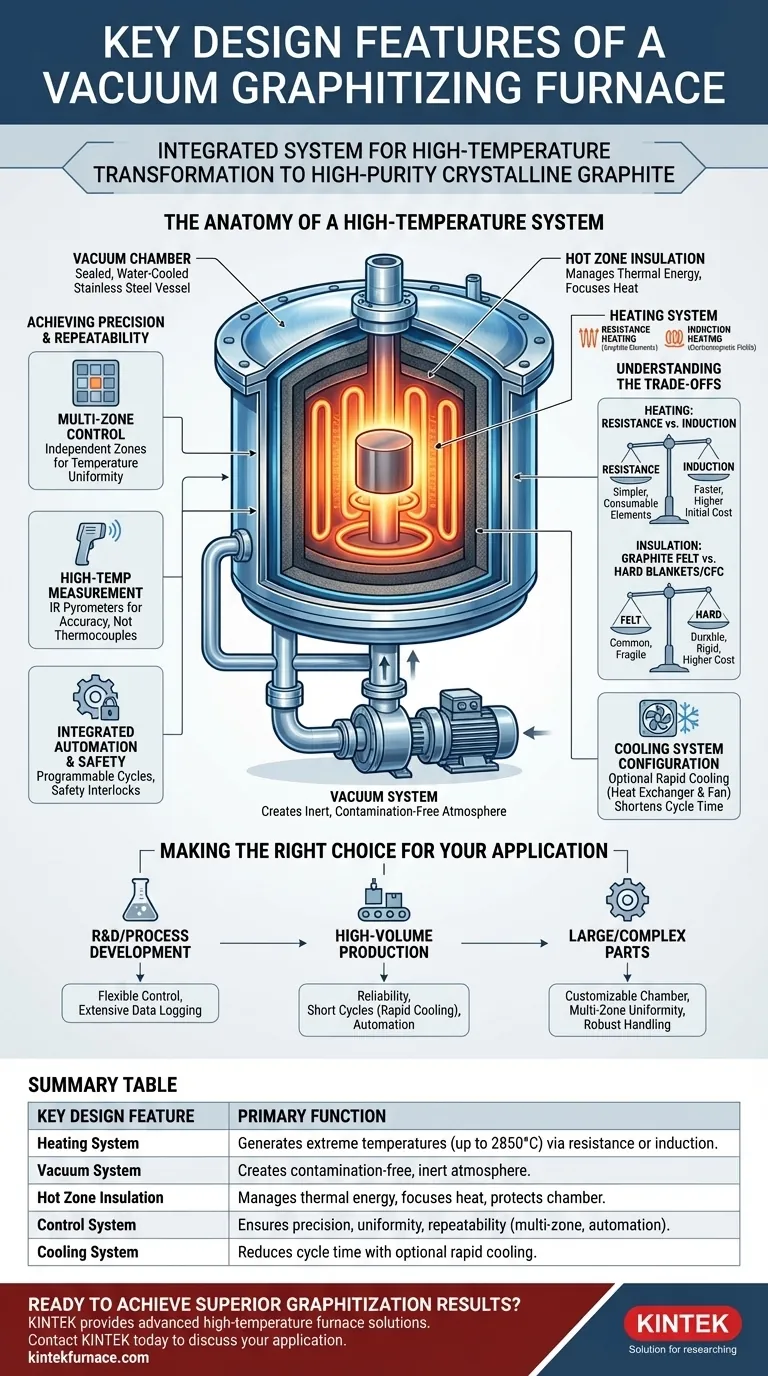
The Anatomy of a High-Temperature System
To understand a vacuum graphitizing furnace, you must see it as a set of interacting subsystems, each engineered to solve a specific challenge related to the graphitization process.
The Vacuum Chamber: The Controlled Environment
The furnace body, or vacuum chamber, is the sealed vessel where the entire process takes place. It is typically a double-walled, water-cooled structure made from stainless steel or other durable alloys.
Its primary function is to contain the vacuum and provide a stable, structurally sound enclosure that can withstand the immense thermal and pressure differentials.
The Heating System: Generating Extreme Temperatures
The heart of the furnace is its heating system, which must reliably achieve temperatures up to 2850°C. Two primary methods are used.
Resistance heating elements, often made of high-purity graphite, are common. An electric current is passed through these elements, generating intense radiant heat.
Intermediate frequency induction heating is an alternative where electromagnetic fields are used to heat a graphite susceptor, which then radiates heat to the workpiece.
The Hot Zone: Managing Thermal Energy
Surrounding the heating elements and the workpiece is the hot zone. This is a critical insulation package designed to keep the extreme heat focused on the product and protect the furnace chamber.
This insulation is typically made from layers of carbon fiber composite (CFC), graphite felt, or hard insulation blankets, all chosen for their low thermal conductivity and stability at extreme temperatures.
The Vacuum System: Ensuring Material Purity
The graphitization process requires an inert atmosphere, free from oxygen and other reactive gases that would damage the product at high temperatures. The vacuum system is responsible for creating this environment.
It is typically a multi-stage system, using mechanical pumps to achieve a rough vacuum and then molecular or diffusion pumps to reach the high vacuum levels needed for processing. This ensures that outgassing from the material is the only significant source of internal pressure.
Achieving Precision and Repeatability
The difference between a basic furnace and an advanced graphitizing system lies in the precision of its control and measurement capabilities.
Multi-Zone Control for Temperature Uniformity
To ensure the entire workpiece graphitizes evenly, the furnace is divided into multiple heating zones. Each zone has its own independent power supply and control loop.
This multi-zone control allows the system to compensate for thermal gradients and guarantee consistent temperature uniformity across even very large or complex parts.
High-Temperature Measurement for Accuracy
Standard thermocouples fail at the extreme temperatures of graphitization. Therefore, these furnaces rely on high-temperature infrared pyrometers.
These non-contact optical sensors measure the thermal radiation emitted by the workpiece or heating elements, providing accurate and reliable temperature data to the control system without being consumed by the heat.
Integrated Automation and Safety
Modern systems integrate all subsystems—heating, vacuum, and cooling—into a single automated controller. This allows for repeatable, programmable process cycles.
Crucial safety interlocks, such as automatic power cutoff when the furnace door is opened, are standard features to protect operators and the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The design of a furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and operational goals. Different choices in core components lead to different outcomes.
Resistance vs. Induction Heating
Resistance heating is generally simpler and more cost-effective for a wide range of furnace sizes. However, heating elements are consumable and will eventually require replacement.
Induction heating can offer faster heating rates and does not have consumable elements in the same way, but the initial capital cost and complexity of the power supply system can be higher.
Insulation Material Selection
The choice of insulation impacts thermal efficiency and furnace longevity. Graphite felt is a common and effective choice, but it can be fragile.
Hard insulation blankets or CFC panels offer greater structural rigidity and durability, which can be critical when processing very large or heavy loads, but they often come at a higher cost.
Cooling System Configuration
While not a part of the heating process, the cooling system is critical for cycle time. An optional rapid cooling system, which uses a heat exchanger and an internal fan to circulate inert gas like argon or nitrogen, can dramatically shorten the time needed before the furnace can be unloaded. This is a key feature for production environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal furnace design is dictated entirely by your end goal, whether it's for material research or high-volume manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is process development or research: Prioritize a furnace with a highly flexible control system, extensive data logging, and the ability to easily modify heating profiles.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Emphasize reliability, short cycle times (requiring an efficient cooling system), and advanced automation to ensure repeatability with minimal operator intervention.
- If your primary focus is processing ultra-large or complex parts: Focus on customizable chamber dimensions, proven multi-zone temperature uniformity, and a robust material handling system.
Ultimately, the right vacuum graphitizing furnace is the one whose design features directly align with the specific material properties and production goals you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Key Design Feature | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Heating System | Generates extreme temperatures (up to 2850°C) via resistance or induction heating. |
| Vacuum System | Creates a contamination-free, inert atmosphere for high-purity processing. |
| Hot Zone Insulation | Manages thermal energy, focusing heat on the workpiece and protecting the chamber. |
| Control System | Ensures precision, temperature uniformity, and repeatability with multi-zone control and automation. |
| Cooling System | Reduces cycle time with optional rapid cooling for production efficiency. |
Ready to achieve superior graphitization results?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether your focus is on R&D, high-volume production, or processing complex parts, our experts can design a vacuum graphitizing furnace tailored to your specific material and production goals. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your application and discover the right solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability



















