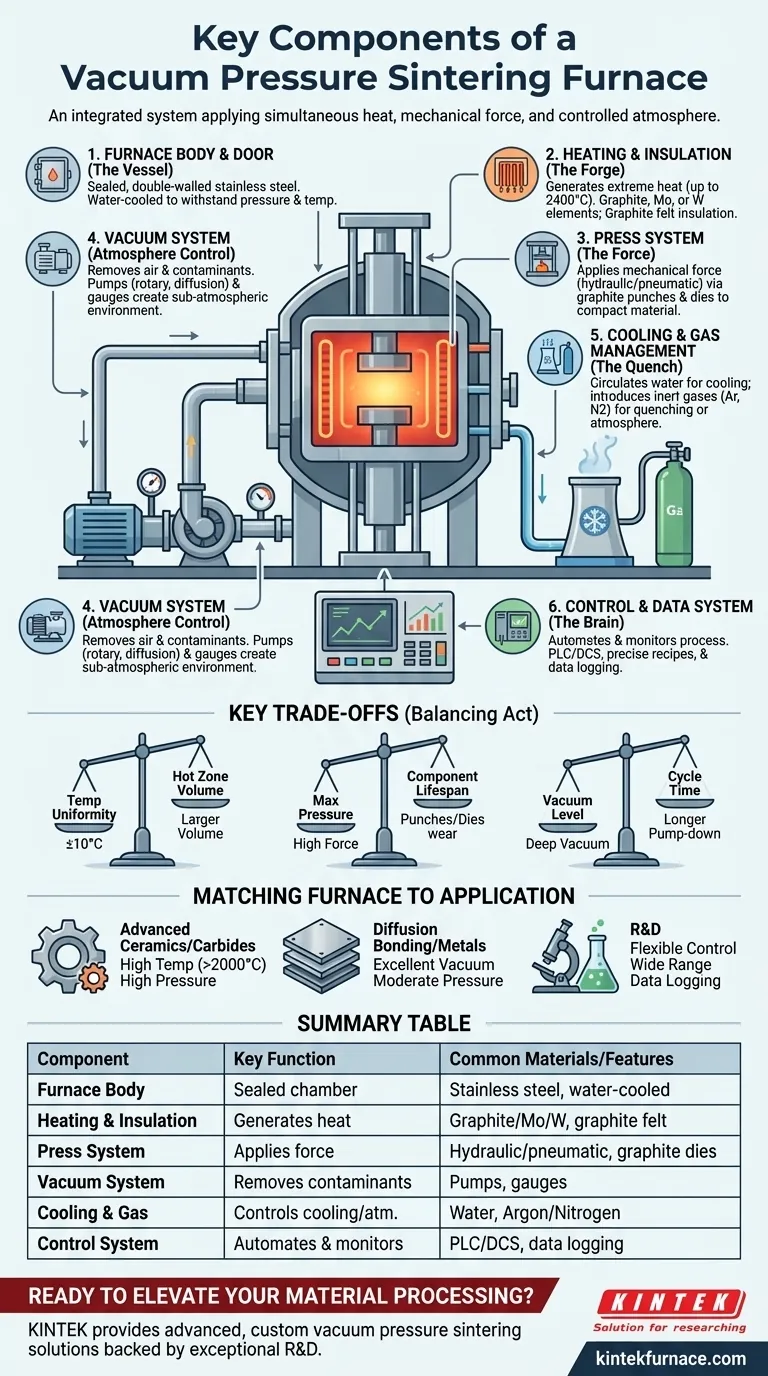
At its core, a vacuum pressure sintering furnace is an integrated system designed to simultaneously apply heat, mechanical force, and a controlled atmosphere to a material. The key components that make this possible are the furnace body itself, a heating and insulation system, a hydraulic or pneumatic press system, a vacuum system to remove atmospheric contaminants, a cooling and gas management system, and a master control system that orchestrates the entire process.
A vacuum pressure sintering furnace is not a single machine, but a collection of sophisticated subsystems. Each component must work in perfect concert to precisely manipulate temperature, pressure, and atmosphere, enabling the creation of dense, high-performance materials that are impossible to produce through conventional methods.

The Core Components: A System of Systems
To understand how the furnace functions, it's best to view it as a series of interconnected systems, each with a specific and critical job.
The Furnace Body and Door (The Vessel)
The furnace body is the central, sealed chamber where the sintering takes place. It is typically a double-walled, water-cooled structure made of stainless steel to withstand the immense internal pressure differences and prevent structural failure at high temperatures.
The furnace door provides access to the chamber for loading and unloading materials. It features robust sealing mechanisms to maintain the integrity of the vacuum or positive pressure environment during operation.
The Heating and Insulation System (The Forge)
This system generates and contains the extreme heat required for sintering.
Heating elements are responsible for raising the temperature, which can range from 1600°C to over 2400°C. These elements are made from materials that can withstand such heat, most commonly graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten.
Surrounding the heating elements is a high-performance insulation package. This is typically made of graphite felt or ceramic fiber boards and serves to contain the heat within the "hot zone," protecting the furnace body and maximizing thermal efficiency.
The Press System (The Force)
This is the component that distinguishes a pressure sintering furnace from a standard vacuum furnace. It applies mechanical force to the material during the heating cycle.
This is usually a hydraulic system, though pneumatic systems are also used. It exerts controlled pressure on the material through a set of graphite punches and dies, physically compacting the powder and accelerating the densification process.
The Vacuum System (Atmosphere Control)
The vacuum system serves a critical dual purpose. First, it removes air and other atmospheric gases from the chamber, which prevents oxidation and contamination of the material being processed.
Second, it creates the controlled, sub-atmospheric environment required for the process. This system consists of a series of pumps (e.g., rotary, diffusion, or turbomolecular pumps) and gauges to achieve and measure the desired vacuum level.
The Cooling and Gas Management System (The Quench)
Controlled cooling is just as important as heating. A water-cooling system circulates water through the double walls of the furnace body and around critical seals and electrodes, preventing them from overheating.
An inflation or gas charging system is used to introduce inert gases like Argon or Nitrogen. This can be used for rapid, controlled cooling (known as gas quenching) or to create a specific positive-pressure atmosphere for certain sintering processes.
The Control and Data System (The Brain)
This is the central nervous system of the furnace. Modern furnaces use a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a Distributed Control System (DCS) to automate and monitor every process variable.
The control system precisely manages temperature ramps, pressure application, vacuum levels, and gas flow according to a pre-programmed recipe. It also includes vital data logging features to record the entire cycle for quality assurance and process repeatability.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a furnace involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for successful operation.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Hot Zone Volume
The larger the internal volume of the furnace (the hot zone), the more challenging it is to maintain strict temperature uniformity. A specified uniformity of ±10°C is common, but achieving this in a 0.3m³ furnace is significantly more difficult than in a 0.01m³ furnace.
Maximum Pressure vs. Component Lifespan
The press system can exert enormous force, but this comes at a cost. Higher operating pressures place immense stress on the graphite punches, dies, and support structures. Running at maximum pressure frequently will reduce the lifespan of these consumable components and increase maintenance costs.
Vacuum Level vs. Cycle Time
Achieving a very deep vacuum requires more powerful and complex pumping systems. More importantly, it takes significantly longer to pump down the chamber to a high vacuum level, which extends the overall cycle time for each run.
Critical Auxiliary Systems
Some components may seem secondary but are vital for safe operation. For example, many facilities install a high-altitude water tank as a backup water supply. In the event of a power outage or pump failure, this gravity-fed system can continue to cool critical seals and prevent catastrophic failure.
Matching the Furnace to Your Application
The ideal furnace configuration depends directly on the materials you are processing and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics or cemented carbides: You need a furnace capable of very high temperatures (often >2000°C) with precise and powerful pressure control to achieve full densification.
- If your primary focus is diffusion bonding or powder metallurgy of metals: A furnace with excellent vacuum levels to prevent oxidation and moderate pressure capabilities is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize a flexible control system with advanced data logging, the ability to handle various sample sizes, and a wide operating range for both temperature and pressure.
Understanding how these components function as an integrated system is the first step toward mastering the sintering process and producing superior materials.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials/Features |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Body & Door | Sealed chamber for sintering | Stainless steel, water-cooled, robust seals |
| Heating & Insulation | Generates and contains heat | Graphite, molybdenum, tungsten elements; graphite felt insulation |
| Press System | Applies mechanical force | Hydraulic or pneumatic; graphite punches and dies |
| Vacuum System | Removes contaminants, controls atmosphere | Rotary, diffusion, turbomolecular pumps; vacuum gauges |
| Cooling & Gas Management | Controls cooling and atmosphere | Water-cooling; Argon, Nitrogen gas for quenching |
| Control & Data System | Automates and monitors process | PLC/DCS, data logging, precise recipe control |
Ready to elevate your material processing with a custom vacuum pressure sintering furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in research, ceramics, or metallurgy, we can help you achieve precise temperature control, uniform heating, and superior densification. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your laboratory's performance and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What materials can be densified using a vacuum press and what are their applications? Unlock High-Performance Material Densification
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability



















