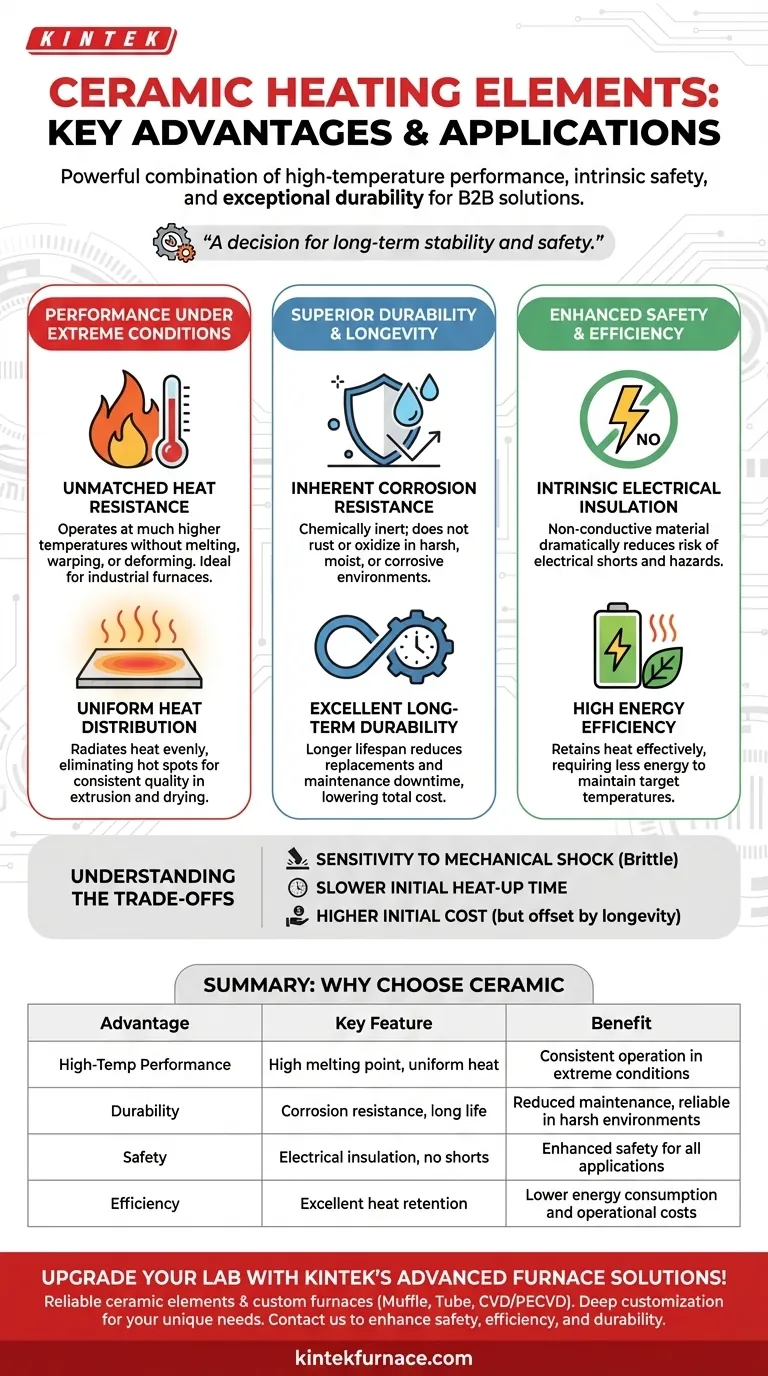
At their core, ceramic heating elements offer a powerful combination of high-temperature performance, intrinsic safety, and exceptional durability. Unlike traditional metal elements, they are highly resistant to heat, do not conduct electricity, and withstand corrosion, making them a superior choice for a wide range of demanding applications.
The decision to use a ceramic heater is a decision for long-term stability and safety. While other materials may heat up, ceramics provide reliable, controlled heat in extreme conditions without the risk of corrosion or electrical shorts that plague metallic elements.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Ceramic heaters excel where high temperatures are a constant requirement. Their material properties give them a significant advantage over metal-based alternatives.
Unmatched Heat Resistance
Ceramic materials possess exceptionally high melting points. This allows them to operate at much higher temperatures than most metals without risk of melting, warping, or deforming.
This thermal stability ensures consistent performance in applications like industrial furnaces and high-temperature material processing, where maintaining a specific heat level is critical.
Uniform Heat Distribution
Ceramic elements are known for their ability to radiate heat evenly across a surface. This eliminates hot spots, which is crucial for processes like plastic extrusion or industrial drying where uniform temperature is necessary for product quality.
Superior Durability and Longevity
The chemical inertness of ceramic materials is the foundation of their long service life and low maintenance requirements.
Inherent Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metals, ceramics do not rust or oxidize, even when exposed to moisture or corrosive chemicals. This makes them ideal for applications like water heaters or equipment used in harsh industrial environments.
This resistance means the heater's performance does not degrade over time, leading to a much longer and more reliable operational lifespan.
Excellent Long-Term Durability
The combination of heat and corrosion resistance results in a component that lasts significantly longer than a metallic equivalent. This reduces the total cost of ownership through fewer replacements and less maintenance downtime.
Enhanced Safety and Efficiency
Beyond performance, ceramic heaters provide fundamental benefits in safety and energy consumption.
Intrinsic Electrical Insulation
Ceramics are natural electrical insulators. The heating element itself does not conduct electricity, which dramatically reduces the risk of electrical shorts and related hazards.
This property is a critical safety feature, especially in consumer appliances or in industrial settings where equipment failure could have severe consequences.
High Energy Efficiency
Ceramic elements are very effective at retaining heat. Once they reach the target temperature, they require less energy to maintain it compared to elements that lose heat more quickly.
This thermal retention translates directly into lower energy consumption and more efficient operation, similar to how a cast-iron skillet stays hot long after being removed from the stove.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly advantageous, ceramic heaters are not the default choice for every situation. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Sensitivity to Mechanical Shock
The primary trade-off for ceramic's hardness and heat resistance is its brittleness. While extremely durable against thermal and chemical stress, ceramic elements can crack or shatter if subjected to a significant physical impact or drop.
Slower Initial Heat-Up Time
Due to their excellent heat retention, ceramic elements can sometimes take longer to reach their target temperature from a cold start compared to some thin metallic elements. This is a factor to consider in applications requiring very rapid heating cycles.
Higher Initial Cost
The manufacturing process for high-quality ceramic components is often more complex than for simple metallic coils. This can result in a higher upfront cost, though it is frequently offset by a longer lifespan and lower energy use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element depends entirely on your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is safety and high-temperature operation: Choose ceramic for its unmatched electrical insulation and thermal stability in furnaces, soldering, or industrial processing.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability in a harsh environment: Choose ceramic for its superior corrosion resistance, especially for applications involving moisture or chemicals.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible initial cost for a simple application: A standard metallic element might be sufficient, provided you can accept the trade-offs in longevity and potential corrosion.
Ultimately, investing in ceramic heating technology is an investment in predictable, safe, and enduring performance.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Performance | High melting point, uniform heat distribution | Consistent operation in extreme conditions, ideal for industrial furnaces |
| Durability | Corrosion resistance, long service life | Reduced maintenance and cost, reliable in harsh environments |
| Safety | Electrical insulation, no risk of shorts | Enhanced safety for consumer and industrial applications |
| Efficiency | Excellent heat retention | Lower energy consumption and operational costs |
Upgrade your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable ceramic heating elements and custom furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise performance for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance safety, efficiency, and durability in your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















