At their core, flexible heaters are specialized thermal components designed to provide precise and efficient heating on surfaces where traditional, rigid heaters cannot. Their defining features are a thin, conformable profile and a construction that embeds a heating circuit within a flexible substrate material, allowing them to wrap around complex geometries for direct, uniform heat transfer.
The most critical feature of a flexible heater is not just its shape, but its construction. The choice of heating element and, most importantly, the substrate material (like Polyimide or Silicone) dictates its temperature range, durability, and cost, making it a highly engineered solution rather than a simple component.

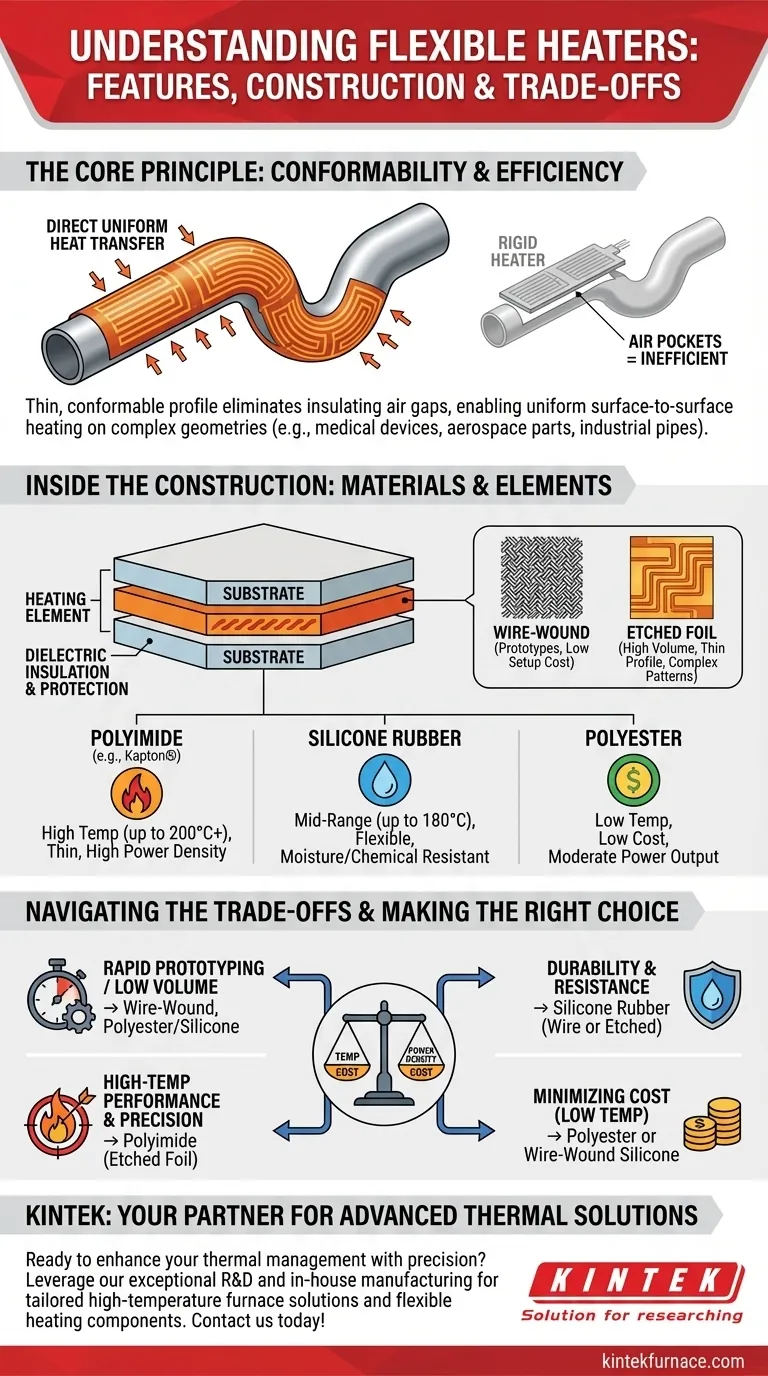
The Core Principle: Conforming to the Surface
The primary advantage of a flexible heater is its ability to match the contour of an object. This physical adaptability is the foundation of its performance.
How Conformability Improves Heat Transfer
Unlike rigid heaters that can create air gaps, flexible heaters provide direct surface-to-surface contact. This intimate contact eliminates insulating air pockets, resulting in significantly more efficient and uniform heat transfer to the target object.
Applications in Complex Geometries
This feature makes them indispensable for applications with non-flat surfaces. Common examples include heating pipes and vessels in industrial settings, maintaining temperature in medical diagnostic equipment, or preventing ice formation on aerospace components and outdoor cameras.
Inside the Heater: Construction and Materials
A flexible heater is a layered system. Understanding its internal components is key to selecting the right one for your application.
The Heating Element: Wire-Wound vs. Etched Foil
The "engine" of the heater is its resistive circuit. The two most common types are wire-wound and etched foil.
Wire-wound elements involve weaving a fine resistance wire into a specific pattern. This method is excellent for prototypes and low-volume production due to its low setup cost.
Etched foil elements are created by chemically etching a circuit pattern from a thin sheet of metal foil. This process allows for very thin profiles, complex heat distribution patterns, and higher power density, making it ideal for high-performance and high-volume applications.
The Substrate: Choosing Your Foundation
The heating element is laminated or embedded within a dielectric substrate material. This material provides physical structure, electrical insulation, and chemical protection. The choice of substrate is the single most important factor determining the heater's performance characteristics.
Common materials include:
- Polyimide (e.g., Kapton®): Offers excellent thermal stability for high-temperature applications (up to 200°C+), thin profiles, and high power density.
- Silicone Rubber: Provides outstanding flexibility, durability, and moisture resistance for mid-range temperatures (typically up to 180°C).
- Polyester: A low-cost option suitable for applications requiring lower temperatures and moderate power output.
Dielectric Strength and Chemical Resistance
The substrate material provides robust electrical insulation, measured as dielectric strength. This is critical for safety, preventing short circuits between the heating element and the component it is attached to.
Furthermore, materials like silicone and polyimide offer good resistance to many chemicals, moisture, and fungi, ensuring reliability in harsh operating environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, flexible heaters are not a universal solution. Their design involves inherent trade-offs that you must consider.
Temperature vs. Cost
Higher operating temperatures demand more advanced substrate materials, which directly increases cost. A Polyimide heater will be more expensive than a Polyester one, but it is necessary for high-temperature work.
Power Density Limitations
Every flexible heater has a maximum power density (watts per square inch) it can safely handle. Exceeding this limit can cause the heater to delaminate or burn out, potentially damaging the component it is heating. This limit is dictated by the substrate material and the efficiency of the heat transfer to the part.
Customization and Tooling Costs
While wire-wound heaters have minimal setup costs, etched foil heaters require a one-time tooling charge to create the chemical etching pattern. This makes etched foil more cost-effective for mass production but more expensive for one-off prototypes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct flexible heater requires matching its features to your specific project goals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance and precision: A Polyimide (Kapton®) etched foil heater provides the best thermal stability and heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is durability and moisture resistance: A Silicone rubber heater, either wire-wound or etched foil, is the most robust choice for challenging environments.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost for a low-temperature task: A Polyester or wire-wound silicone heater offers a practical and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or unique shapes in small batches: A wire-wound heater avoids the tooling costs associated with etched foil designs.
By understanding these core features and trade-offs, you can specify a flexible heating solution perfectly tailored to your technical requirements and budget.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Materials | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conformability | Wraps around complex shapes for direct, uniform heat transfer | Polyimide, Silicone, Polyester | Pipes, medical equipment, aerospace components |
| Construction | Heating element embedded in flexible substrate | Wire-wound, Etched foil | Prototypes, high-volume production |
| Temperature Range | Varies by substrate, up to 200°C+ for high-performance | Polyimide (high-temp), Silicone (mid-temp), Polyester (low-cost) | Industrial heating, diagnostic tools |
| Durability & Resistance | Provides electrical insulation and chemical protection | Silicone (moisture-resistant), Polyimide (chemical-resistant) | Harsh environments, outdoor use |
| Customization | Options for prototypes or mass production with trade-offs in cost | Wire-wound (low setup), Etched foil (high tooling) | Custom shapes, specific power needs |
Ready to enhance your thermal management with precision? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need flexible heaters or other thermal solutions, we ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can bring value to your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer












