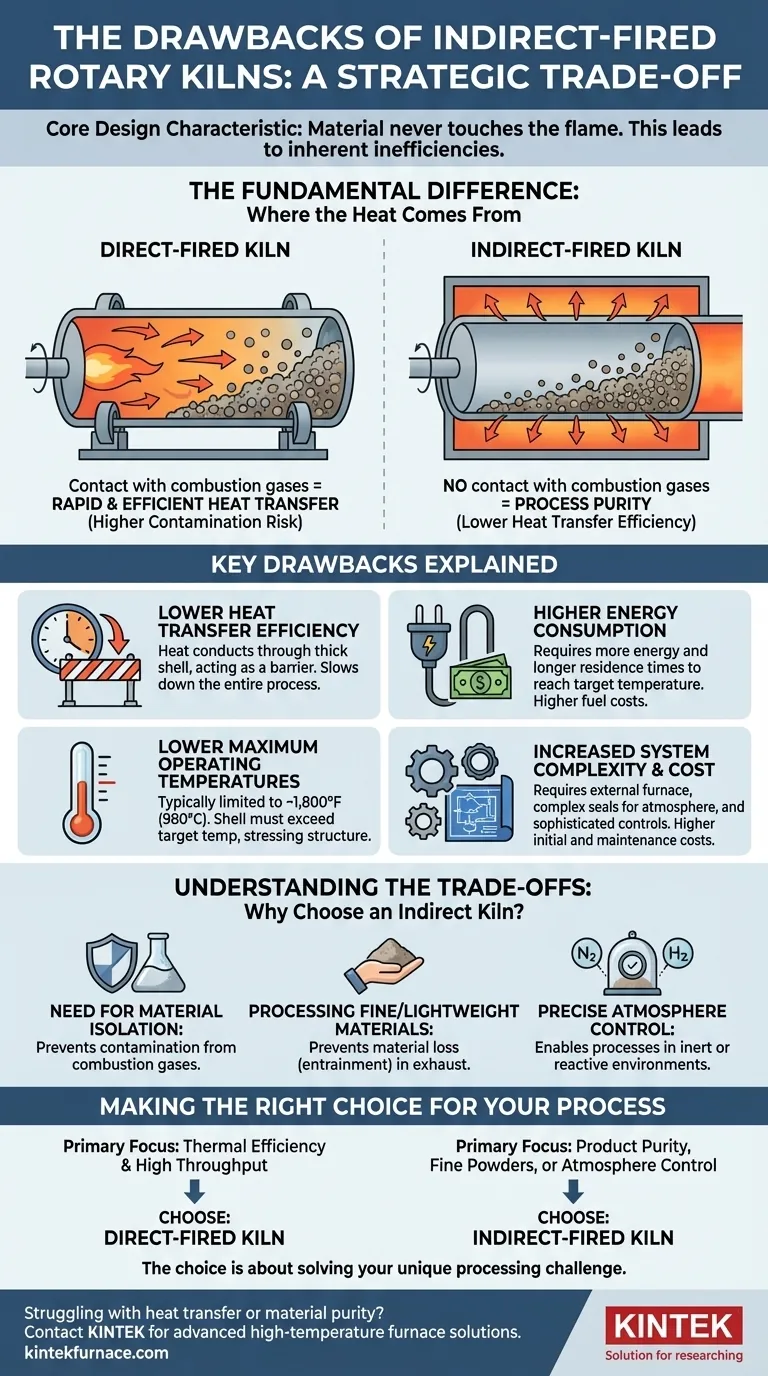
At their core, the drawbacks of indirect-fired rotary kilns stem from a single design characteristic: the material inside never touches the flame. While this provides unique benefits, it introduces inherent inefficiencies, resulting in lower heat transfer rates, higher energy consumption, longer processing times, and increased operational complexity compared to their direct-fired counterparts.
The decision to use an indirect-fired kiln is a strategic trade-off. You accept its inherent thermal inefficiencies and higher costs as the necessary price for achieving absolute material purity, processing fine particles, or maintaining a controlled internal atmosphere.
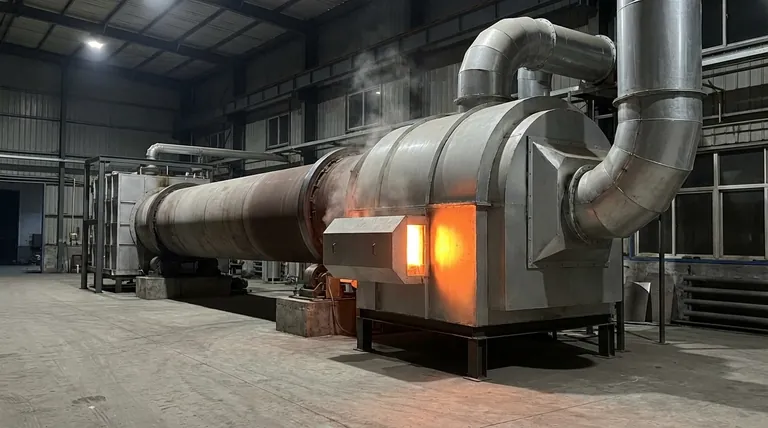

The Fundamental Difference: Where the Heat Comes From
To understand the drawbacks, you must first understand the core mechanical difference between the two primary types of rotary kilns. This distinction is the source of every advantage and disadvantage.
How Direct-Fired Kilns Work
In a direct-fired kiln, a burner flame and hot combustion gases are introduced directly into the kiln cylinder. The process material comes into direct contact with these hot gases, allowing for rapid and efficient heat transfer.
This method is thermally efficient but exposes the material to the byproducts of combustion, which can cause contamination or unwanted chemical reactions.
How Indirect-Fired Kilns Work
In an indirect-fired kiln, the rotating drum is enclosed within an external furnace or equipped with a heating jacket. The heat source warms the outside of the kiln shell, and that heat is then transferred through the metal shell to the material tumbling inside.
There is no contact between the material and the combustion gases, ensuring process purity.
Key Drawbacks of Indirect Kilns Explained
The external heating method is directly responsible for several operational and economic disadvantages.
Lower Heat Transfer Efficiency
Heating a material by conducting energy through a thick, rotating steel shell is fundamentally less efficient than showering it directly with hot gas. The shell itself acts as a barrier to heat transfer, slowing down the entire process.
Higher Energy Consumption
Because heat transfer is less efficient, an indirect kiln requires more energy and longer residence times to bring the material up to the target temperature. This directly translates to higher fuel costs over the operational life of the equipment.
Lower Maximum Operating Temperatures
Direct-fired kilns can achieve process temperatures upwards of 2,300°F (1260°C). Indirect kilns are typically limited to around 1,800°F (980°C) because the kiln's shell material must be heated to a temperature higher than the target for the material inside, placing significant stress on its structural integrity.
Increased System Complexity and Cost
An indirect kiln system is more than just the rotating drum; it requires an external furnace, a complex seal system to maintain atmosphere integrity, and often a more sophisticated control system. This increases the initial capital investment as well as potential maintenance points.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Choose an Indirect Kiln?
Despite these clear drawbacks, indirect kilns are the only viable solution for many critical industrial processes. The choice to use one is made when the process requirements make its disadvantages acceptable.
The Need for Material Isolation
This is the primary reason to select an indirect kiln. If the material cannot be exposed to combustion gases due to risk of contamination, unwanted side-reactions, or discoloration, direct firing is not an option.
Processing Fine or Lightweight Materials
In a direct-fired kiln, the high velocity of combustion gases can carry fine powders or lightweight materials out of the drum and into the exhaust system, a phenomenon known as entrainment. The gentle heating and controlled atmosphere of an indirect kiln prevent this material loss.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Because the drum is sealed from the heating source, you can maintain a specific atmosphere inside it. This allows for processes that require an inert (e.g., nitrogen) or reactive (e.g., hydrogen) environment, which is impossible in a direct-fired system filled with combustion gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision must be guided by the non-negotiable requirements of your material and process goals.
- If your primary focus is thermal efficiency and high throughput for robust materials: A direct-fired kiln is almost always the more economical and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is product purity, preventing contamination, or processing fine powders: The drawbacks of an indirect-fired kiln are a necessary cost to ensure product quality.
- If your primary focus is executing a chemical reaction in a controlled or inert atmosphere: An indirect-fired kiln is the only technology that can meet this requirement.
Ultimately, the choice is not about which kiln is universally "better," but which is specifically engineered to solve your unique processing challenge.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Description |
|---|---|
| Lower Heat Transfer Efficiency | Slower heating due to heat conduction through the kiln shell, reducing process speed. |
| Higher Energy Consumption | Increased fuel costs from longer residence times and inefficient heat transfer. |
| Lower Maximum Operating Temperatures | Limited to around 1,800°F (980°C) due to structural stress on the kiln shell. |
| Increased System Complexity and Cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance from external furnaces and seals. |
Struggling with heat transfer inefficiencies or material purity in your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Whether you're dealing with fine powders, need precise atmosphere control, or require robust thermal processing, our solutions ensure optimal performance and purity. Don't let equipment limitations hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some common processes carried out in rotary kilns? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation Solutions
- What types of physical and chemical transformations occur in a rotary kiln? Master Material Processing for Superior Results
- What data is necessary to design a rotary kiln? Essential Factors for Efficient Thermal Processing
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What role does gas flow and combustion play in a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer for Efficiency and Quality



















