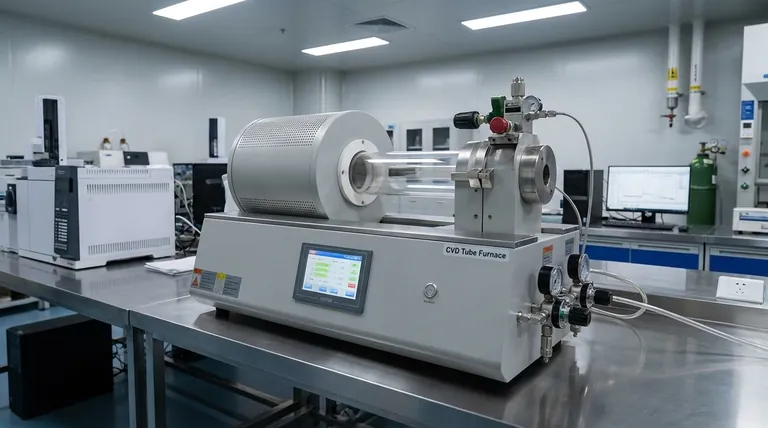
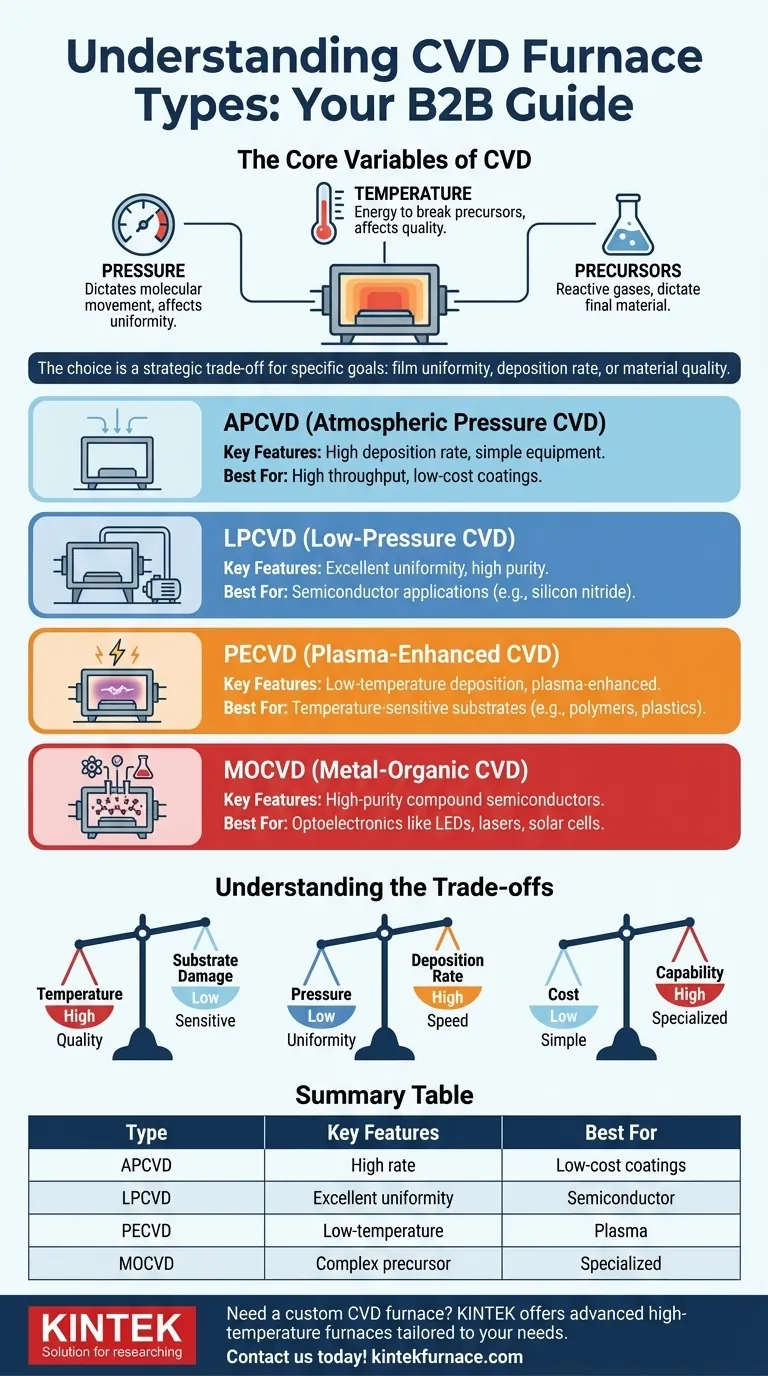
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnace is defined by its operating pressure, temperature, and the chemical precursors it uses. The primary types are Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD), Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), and Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD). Each is designed to create a specific set of conditions to optimize the deposition of thin films for different materials and applications.
The choice between CVD furnace types is not about finding the "best" one overall. It is about making a strategic trade-off between deposition temperature, operating pressure, and chemical precursors to achieve your specific goal, whether that's film uniformity, deposition rate, or material quality.

The Core Variables of CVD
Before comparing specific furnace types, it's critical to understand the three fundamental parameters that define any CVD process. Your choice of furnace is simply a choice of how you want to control these variables.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure inside the reaction chamber dictates how gas molecules move and interact. It directly influences the uniformity and conformity of the deposited film.
Lower pressure increases the mean free path of gas molecules, allowing them to travel further without colliding. This leads to a more uniform coating, especially on complex, three-dimensional surfaces.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature provides the energy needed to break down the precursor gases and initiate the chemical reaction on the substrate surface.
Higher temperatures generally result in denser, more crystalline, and higher-quality films. However, high temperatures can damage sensitive substrates or cause unwanted diffusion within the material.
The Role of Precursors
Precursors are the reactive gases that contain the elements you want to deposit. The choice of precursor chemistry dictates the final material (e.g., oxides, nitrides, carbides) and the temperature required for the reaction.
Some precursors, like metal-organics, are highly specialized and require a specific type of CVD system (MOCVD) to handle them effectively.
The Primary Types of CVD Furnaces Explained
Each type of CVD furnace offers a different method of controlling the core variables of pressure and temperature to suit different applications.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD)
APCVD operates at standard atmospheric pressure. This makes the equipment relatively simple and inexpensive, as it doesn't require a complex vacuum system.
Because of the high pressure, gas phase reactions can occur, potentially leading to particle formation. Its primary advantage is a high deposition rate, making it suitable for applications where thick films are needed and perfect uniformity is not the main priority.
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD)
LPCVD operates at a reduced pressure (a partial vacuum). This is the workhorse of the semiconductor industry for a reason.
By lowering the pressure, LPCVD significantly improves film uniformity and conformality (the ability to coat complex shapes evenly). The trade-off is a slower deposition rate and the higher cost of vacuum equipment.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
PECVD uses an electric field to generate plasma (an ionized gas) inside the chamber. This plasma provides the energy to break down precursor gases, rather than relying solely on high temperatures.
This is the key advantage of PECVD: it allows for deposition at much lower temperatures. This makes it ideal for depositing films on substrates that cannot withstand the high heat of LPCVD or APCVD, such as plastics or fully processed semiconductor wafers.
Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD)
MOCVD is a specialized form of CVD that uses metal-organic compounds as precursors. These precursors are essential for creating very high-purity, crystalline compound semiconductor films.
This technique is the gold standard for manufacturing high-performance optoelectronics, such as LEDs, laser diodes, and high-efficiency solar cells. The equipment is complex and expensive, reflecting its highly specialized purpose.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a CVD process always involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
The Temperature vs. Quality Dilemma
High process temperatures (as in LPCVD) generally produce higher-quality, more stable films. However, this heat can damage your substrate or previously fabricated device layers. PECVD solves this by using plasma to enable low-temperature deposition, but the resulting film quality may be different than a high-temperature equivalent.
The Pressure vs. Uniformity Balance
Low pressure (LPCVD) is superior for achieving uniform films over large areas and complex topographies. High pressure (APCVD) offers faster deposition rates and simpler equipment but at the cost of this uniformity.
The Cost vs. Capability Equation
An APCVD system is the simplest and most cost-effective. Adding vacuum capabilities for LPCVD increases cost and complexity. Incorporating plasma for PECVD or specialized gas handling for MOCVD further raises the investment, but unlocks capabilities that are impossible with simpler systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of furnace should be driven entirely by the material you need to create and the substrate you are using.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and low cost for simple coatings: APCVD is often the most practical choice due to its high deposition rate and simpler hardware.
- If your primary focus is exceptional film uniformity and purity for semiconductor applications: LPCVD is the industry standard for depositing flawless layers of silicon nitride or polysilicon.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is the essential technology for applications involving polymers, plastics, or fully fabricated integrated circuits.
- If your primary focus is creating high-quality compound semiconductors for optoelectronics: MOCVD is the specialized, non-negotiable tool for manufacturing modern LEDs and lasers.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the precise CVD technology that aligns with your specific material synthesis goals.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| APCVD | High deposition rate, simple equipment | High throughput, low-cost coatings |
| LPCVD | Excellent uniformity, high purity | Semiconductor applications |
| PECVD | Low-temperature deposition, plasma-enhanced | Temperature-sensitive substrates |
| MOCVD | High-purity compound semiconductors | Optoelectronics like LEDs and lasers |
Need a custom CVD furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including CVD/PECVD systems, tailored to your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis



















