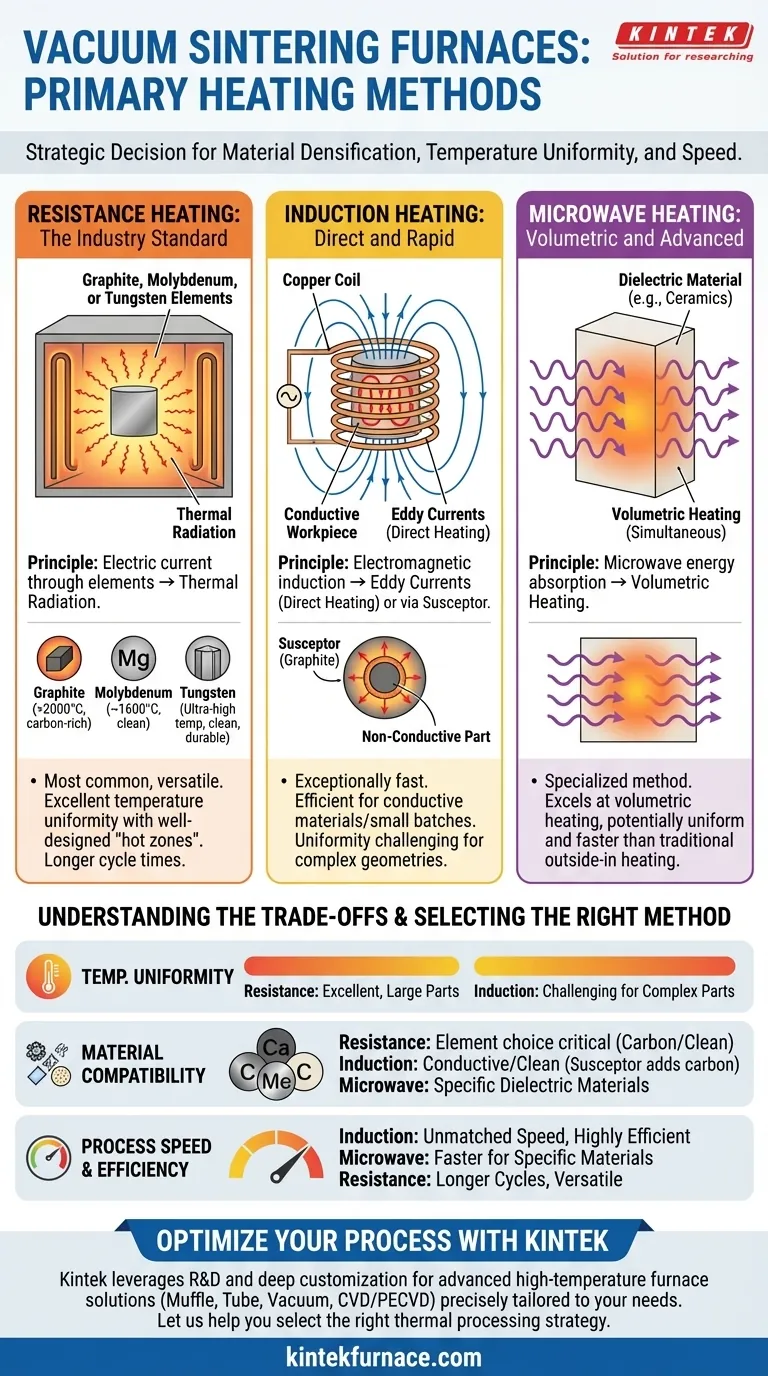
In vacuum sintering furnaces, the primary heating methods are resistance heating, induction heating, and microwave heating. Each method leverages a different physical principle to generate the high temperatures required for densifying materials in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. The choice of method is critical, as it directly impacts temperature uniformity, heating speed, and compatibility with the material being processed.
The selection of a furnace heating method is a strategic decision dictated by your material, required temperature, and process goals. While resistance heating is the most common and versatile, induction and microwave methods offer distinct advantages for specific, targeted applications.
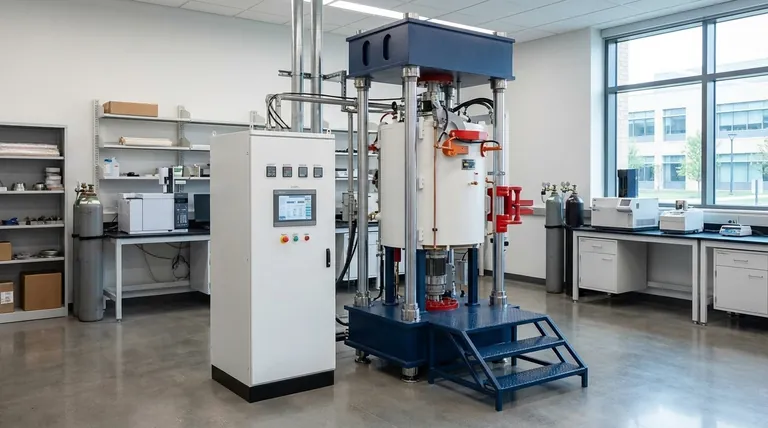

A Breakdown of Primary Heating Methods
Understanding the core principles of each heating technology is the first step toward selecting the right tool for your application. The method of heat generation and transfer defines the furnace's capabilities and limitations.
Resistance Heating: The Industry Standard
Resistance heating is the most prevalent method used in vacuum furnaces. The principle is straightforward: an electric current is passed through heating elements with high electrical resistance, causing them to become extremely hot.
In a vacuum environment where convection is negligible, these hot elements transfer their energy to the workpiece almost entirely through thermal radiation. This is why the method is sometimes referred to as radiation heating.
The material of the heating element itself is a critical design choice:
- Graphite: Cost-effective and suitable for very high temperatures (over 2000°C), but can introduce carbon into the furnace atmosphere, which may be undesirable for some materials.
- Molybdenum: A common choice for clean processing up to around 1600°C. It is more brittle than tungsten but less expensive.
- Tungsten: Used for the highest temperature applications in ultra-high vacuum where a clean environment is paramount. It is durable but also the most expensive option.
Induction Heating: Direct and Rapid
Induction heating uses electromagnetic induction to generate heat. A high-frequency alternating current is passed through a copper coil, creating a powerful magnetic field.
This magnetic field induces electrical eddy currents directly within the conductive workpiece, causing it to heat up rapidly from the inside out. If the material itself is not electrically conductive, a conductive "susceptor" (often made of graphite) is used to absorb the energy and radiate it to the part. This is often referred to as medium frequency heating.
Microwave Heating: Volumetric and Advanced
Microwave heating is a more specialized method that uses microwave energy to heat materials. It functions similarly to a household microwave oven but on an industrial scale with much higher power.
This method excels at volumetric heating, where the entire volume of a suitable material (typically ceramics) heats up simultaneously. This can lead to more uniform temperatures and significantly faster processing times compared to traditional methods where heat must conduct from the outside in.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single heating method is universally superior. The optimal choice depends on a careful balance of technical requirements, material properties, and budget.
Temperature Range and Uniformity
Resistance heating systems, with well-designed "hot zones," can provide excellent temperature uniformity across large and complex parts. The maximum temperature is determined by the element material chosen.
Induction heating is exceptionally fast but achieving temperature uniformity can be challenging for complex geometries, as heating is concentrated where the magnetic field is strongest.
Material Compatibility
This is a critical consideration. Graphite resistance elements are ideal for processing cemented carbides where a carbon-rich atmosphere is beneficial. However, they are unsuitable for materials that react with carbon.
For carbon-sensitive materials like certain specialty steels or medical alloys, molybdenum or tungsten resistance elements are necessary to ensure a clean process. Induction heating is inherently clean as long as the material itself is conductive; if a graphite susceptor is needed, carbon compatibility again becomes a factor.
Process Speed and Efficiency
Induction heating is the undisputed leader in speed, as it heats the part directly. This makes it highly efficient for processing individual parts or small batches of conductive materials.
Resistance furnaces typically have longer cycle times due to the need to heat the entire hot zone and allow thermal energy to radiate and soak into the parts.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by your end goal. By weighing the different attributes of each heating method against your specific needs, you can make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is versatility and proven performance across many materials: Resistance heating is the most flexible and widely understood technology.
- If your primary focus is the rapid processing of conductive materials: Induction heating offers unmatched speed and energy efficiency.
- If your primary focus is processing specific dielectric materials like ceramics: Microwave heating can provide unique benefits in speed and thermal uniformity.
Understanding these fundamental heating principles empowers you to select not just a furnace, but the correct thermal processing strategy for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Principle | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Electric current through elements | Up to 2000°C+ | Excellent uniformity, versatile | Most materials, general sintering |
| Induction | Electromagnetic induction | Varies with material | Rapid heating, high efficiency | Conductive materials, fast cycles |
| Microwave | Microwave energy absorption | Varies with material | Volumetric heating, fast processing | Dielectric materials like ceramics |
Struggling to select the right heating method for your vacuum sintering furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need versatile resistance heating, rapid induction, or specialized microwave methods, we can help optimize your process for superior results. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing



















