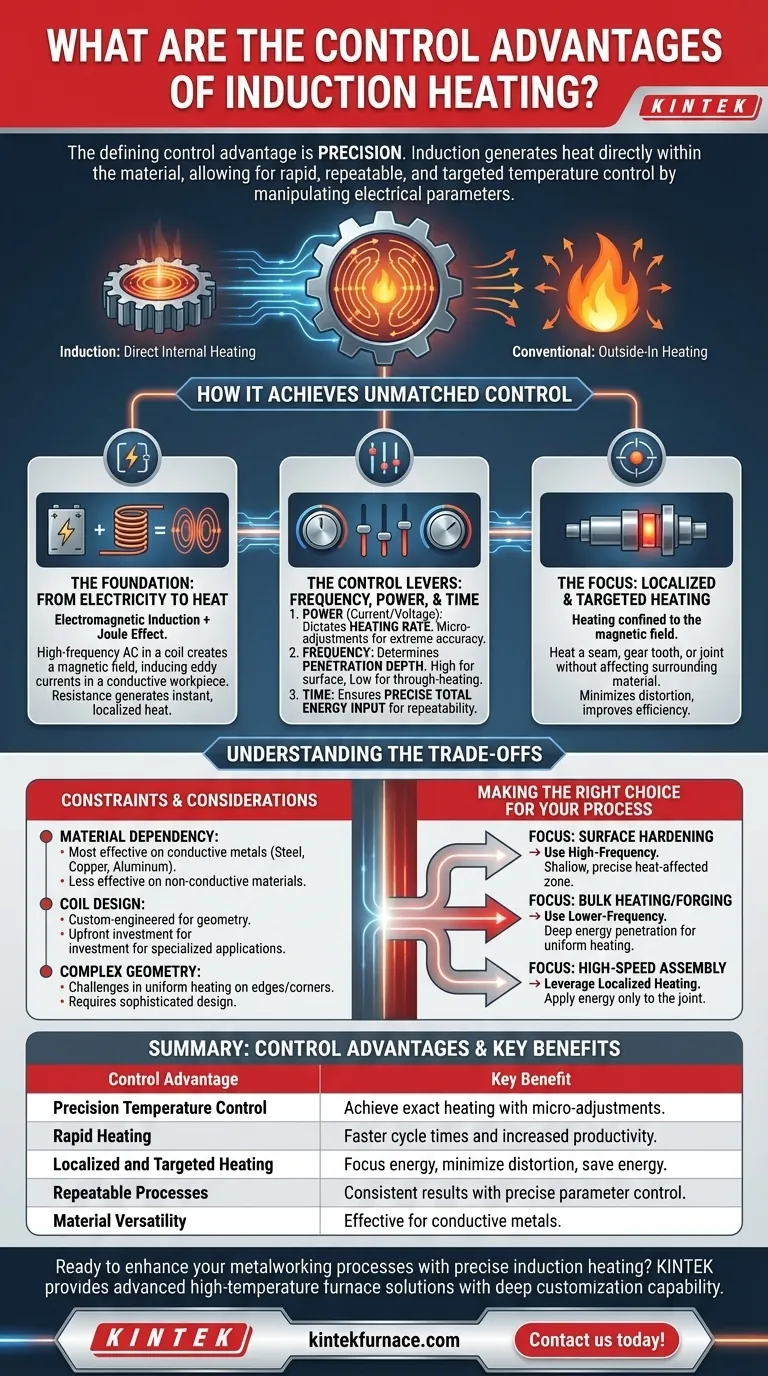
The defining control advantage of induction heating is its precision. Unlike conventional methods that heat a component from the outside-in using convection or radiation, induction generates heat directly within the material itself. This allows for exceptionally rapid, repeatable, and targeted temperature control by precisely manipulating electrical parameters like frequency, voltage, and current.
The core principle to understand is that induction heating treats thermal energy as a direct output of electrical engineering. This transforms heating from a blunt, ambient process into a controllable, targeted application of energy, giving you command over not just how hot something gets, but where and how fast.
How Induction Achieves Unmatched Control
The control advantages of induction are not a single feature but a result of its fundamental physics and modern power electronics working in tandem.
The Foundation: From Electricity to Heat
The process is built on two physical principles: electromagnetic induction and the Joule effect. A high-frequency alternating current in a copper coil creates a powerful, oscillating magnetic field. When a conductive workpiece is placed in this field, it induces small, circulating electrical currents within the material, known as eddy currents.
The material's natural electrical resistance then impedes the flow of these eddy currents, which instantly generates highly localized heat. This direct conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy is instantaneous and contact-free.
The Control Levers: Frequency, Power, and Time
Because the heat is a direct product of electrical currents, we can control it using three primary electrical levers:
- Power (Current/Voltage): Adjusting the power supplied to the coil directly dictates the rate of heating. Modern systems using IGBT technology can switch power on and off thousands of times per second, allowing for micro-adjustments that maintain a target temperature with extreme accuracy.
- Frequency: The frequency of the alternating current determines the depth of heat penetration. Higher frequencies keep the eddy currents concentrated near the surface, ideal for surface hardening. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper, which is better for through-heating or melting thicker materials.
- Time: The duration that power is applied provides the most basic level of control, ensuring a precise and repeatable total energy input for every cycle.
The Focus: Localized and Targeted Heating
Perhaps the most significant control advantage is its spatial precision. The heating effect is almost entirely confined to the portion of the material located within the magnetic field generated by the inductor coil.
This means you can heat a specific seam for welding, a single gear tooth for hardening, or a joint for brazing without affecting the surrounding material. This minimizes thermal distortion, preserves the material properties of the larger component, and dramatically improves energy efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the control of induction heating comes with specific constraints and considerations.
Material Dependency
The process is most effective on electrically conductive materials. Metals like steel, copper, and aluminum heat exceptionally well.
However, induction is far less effective for non-conductive materials like ceramics or plastics, which do not allow eddy currents to form. While magnetic materials gain an efficiency boost from hysteresis losses, non-magnetic metals can still be heated effectively.
The Cost of Precision: Coil Design
The inductor coil is not a generic part; it is a custom-engineered tool. Its shape and size must be carefully designed to match the geometry of the workpiece and produce the desired heating pattern.
This means specialized applications often require significant upfront investment in the design, engineering, and manufacturing of custom coils. The system's precision comes at the cost of "one size fits all" flexibility.
The Challenge of Complex Geometry
While highly localized, achieving a perfectly uniform heat pattern on a part with complex geometry can be challenging. Edges and corners may heat faster than flat surfaces.
Overcoming this requires sophisticated coil design and potentially multi-zone power control to ensure the entire target area reaches the desired temperature uniformly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use induction heating should be based on a clear understanding of your primary technical objective.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening: Use high-frequency induction to create a shallow, precise heat-affected zone that hardens the surface without altering the ductile core of the component.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating or forging: Use lower-frequency induction to ensure deep energy penetration, allowing for uniform heating through thick cross-sections of material.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repeatable assembly (e.g., brazing or soldering): Leverage the localized heating and rapid power control to apply energy only to the joint, minimizing thermal stress on the rest of the assembly.
Ultimately, mastering induction heating means treating thermal energy not as a blunt instrument, but as a precisely controlled electrical parameter.
Summary Table:
| Control Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Control | Achieve exact heating with micro-adjustments via power electronics |
| Rapid Heating | Instant heat generation for faster cycle times and increased productivity |
| Localized and Targeted Heating | Focus energy on specific areas to minimize distortion and save energy |
| Repeatable Processes | Ensure consistent results with precise control of power, frequency, and time |
| Material Versatility | Effective for conductive metals like steel, copper, and aluminum |
Ready to enhance your metalworking processes with precise induction heating? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your efficiency and control!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















