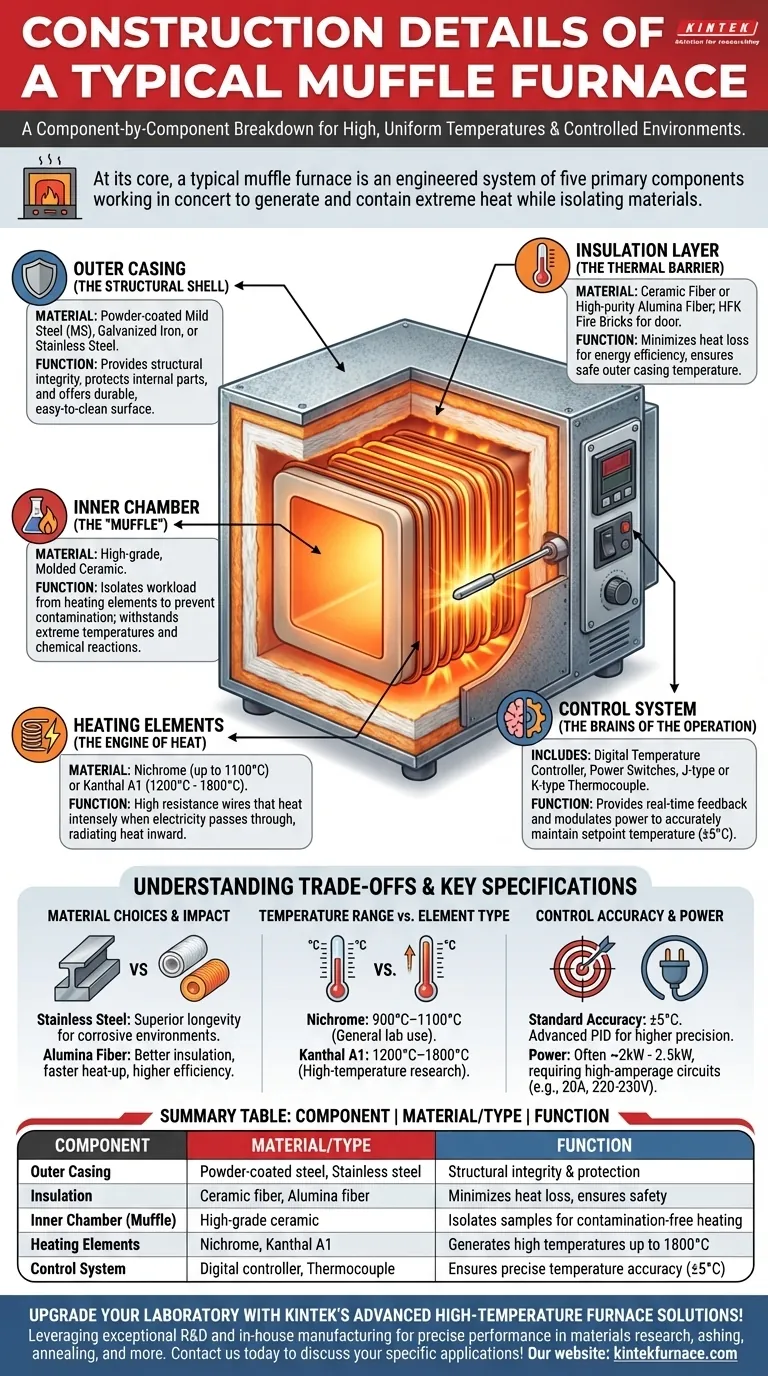
At its core, a typical muffle furnace is built from five primary components working in concert: a structural outer casing, a highly effective insulation layer, a ceramic inner chamber known as the "muffle," high-resistance heating elements, and a precise temperature control system. These parts are specifically chosen and arranged to generate extremely high, uniform temperatures while isolating the heated material from direct contact with the heating elements, ensuring a clean and controlled environment.
The construction of a muffle furnace is not just a simple assembly of parts. It is a carefully engineered system where each material—from the steel casing to the ceramic fiber insulation and Kanthal heating wires—is selected to safely contain and precisely control extreme heat for scientific and industrial applications.
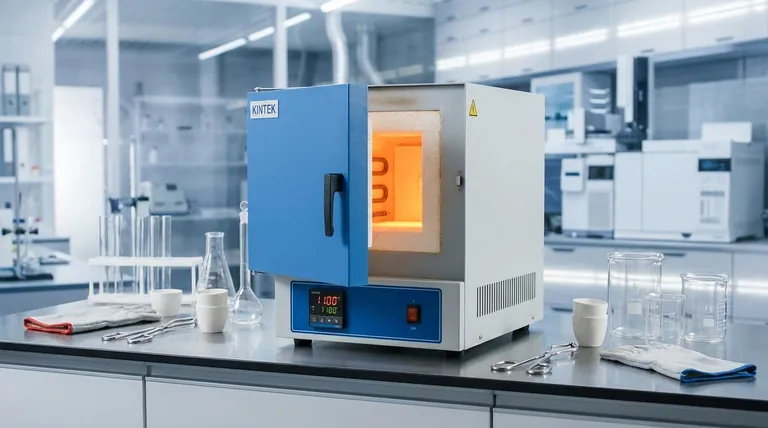

The Anatomy of a Muffle Furnace: A Component-by-Component Breakdown
To truly understand a muffle furnace, you must look at how its individual parts contribute to the overall function of generating and containing heat.
The Outer Casing: The Structural Shell
The outermost layer is typically constructed from powder-coated mild steel (MS) or a galvanized iron (G.I.) sheet. For applications requiring greater corrosion resistance, a stainless steel body is used.
This casing provides structural integrity, protects the internal components from the laboratory environment, and offers a durable, easy-to-clean surface.
The Insulation Layer: The Thermal Barrier
Between the outer casing and the inner chamber lies a thick layer of insulation. This is commonly made from ceramic fiber or high-purity alumina fiber material.
This insulation is critical for two reasons. First, it minimizes heat loss, making the furnace energy-efficient. Second, it ensures the outer casing remains at a safe temperature, protecting operators from burns. Door insulation is often made of robust HFK fire bricks.
The Inner Chamber: The Heart of the Furnace
The defining component is the inner chamber, or "muffle," which is made from a high-grade, molded ceramic material.
This ceramic chamber is the workspace where samples are placed. Its purpose is to isolate the workload from the heating elements, preventing contamination and damage from direct contact. The ceramic is chosen for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist chemical reactions from aggressive gases or vapors.
The Heating Elements: The Engine of Heat
The heat is generated by electrical heating elements, typically made from high-resistance wire like Nichrome or Kanthal (A1).
These elements are coiled and wrapped around the outside of the ceramic muffle. When electricity is passed through them, their high resistance causes them to heat up intensely, radiating that heat inward to uniformly raise the temperature of the chamber.
The Control System: The Brains of the Operation
The entire system is managed by a control panel. This includes a digital temperature controller, power switches, and indicating lamps.
A temperature sensor, typically a J-type or K-type thermocouple, is placed inside the chamber to provide real-time temperature feedback. The controller then modulates the power sent to the heating elements to accurately achieve and maintain the user's setpoint.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Specifications
The performance and cost of a muffle furnace are directly tied to the materials and specifications of its components.
Material Choices and Their Impact
A standard powder-coated steel body is cost-effective and suitable for most applications. A stainless steel body, however, offers superior longevity and is essential when working in corrosive environments.
Similarly, standard ceramic fiber is effective, but high-purity alumina fiber provides better insulation, leading to faster heat-up times and greater energy efficiency, usually at a higher price point.
Temperature Range vs. Element Type
The maximum achievable temperature is determined by the heating elements. Nichrome elements are common for furnaces operating up to 900°C–1100°C.
For higher temperatures (1200°C to 1800°C), more robust and expensive elements like Kanthal A1 or other specialized materials are required.
The Importance of Control Accuracy
Most standard furnaces offer a temperature accuracy of ±5°C. This is sufficient for general-purpose tasks like ashing, drying, or basic heat treating.
For sensitive metallurgical or materials science research, a higher degree of accuracy may be necessary, requiring a more advanced PID controller and premium thermocouple.
Chamber Size and Power Requirements
Common benchtop models feature chamber sizes like 4x4x9 or 6x6x12 inches and typically have a power rating around 2 kW to 2.5 kW.
This power draw is significant, often requiring a dedicated, high-amperage circuit (e.g., 20A) on a standard 220-230V single-phase supply.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace means matching its construction details to your specific task.
- If your primary focus is general lab use (e.g., ashing, annealing): A standard furnace with a 900°C range, Nichrome elements, and a powder-coated steel body is a reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials research (>1100°C): You must specify a furnace with Kanthal (or better) elements and high-purity alumina insulation to ensure performance and longevity.
- If your primary focus is working with corrosive vapors or materials: Prioritize a model with a high-grade ceramic muffle and a full stainless steel casing to prevent degradation over time.
By understanding how each component contributes to the furnace's function, you can confidently select a tool that is perfectly engineered for your objective.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material/Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Casing | Powder-coated steel, stainless steel | Provides structural integrity and protection |
| Insulation | Ceramic fiber, alumina fiber | Minimizes heat loss and ensures safety |
| Inner Chamber (Muffle) | High-grade ceramic | Isolates samples for contamination-free heating |
| Heating Elements | Nichrome, Kanthal A1 | Generates high temperatures up to 1800°C |
| Control System | Digital controller, thermocouple | Ensures precise temperature accuracy (±5°C) |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise performance for materials research, ashing, annealing, and more—enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















