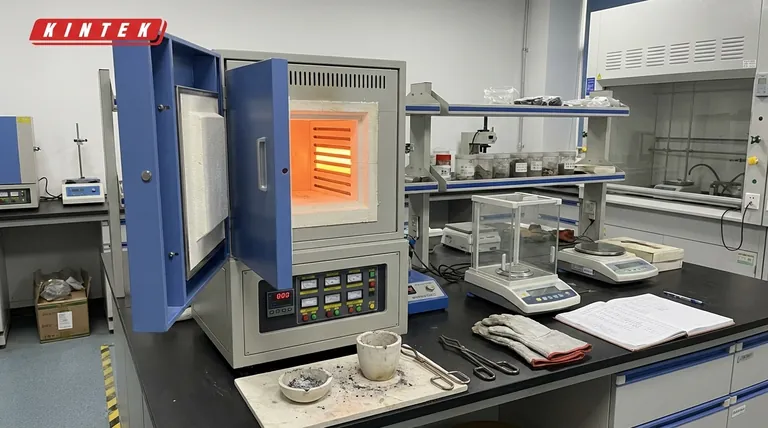
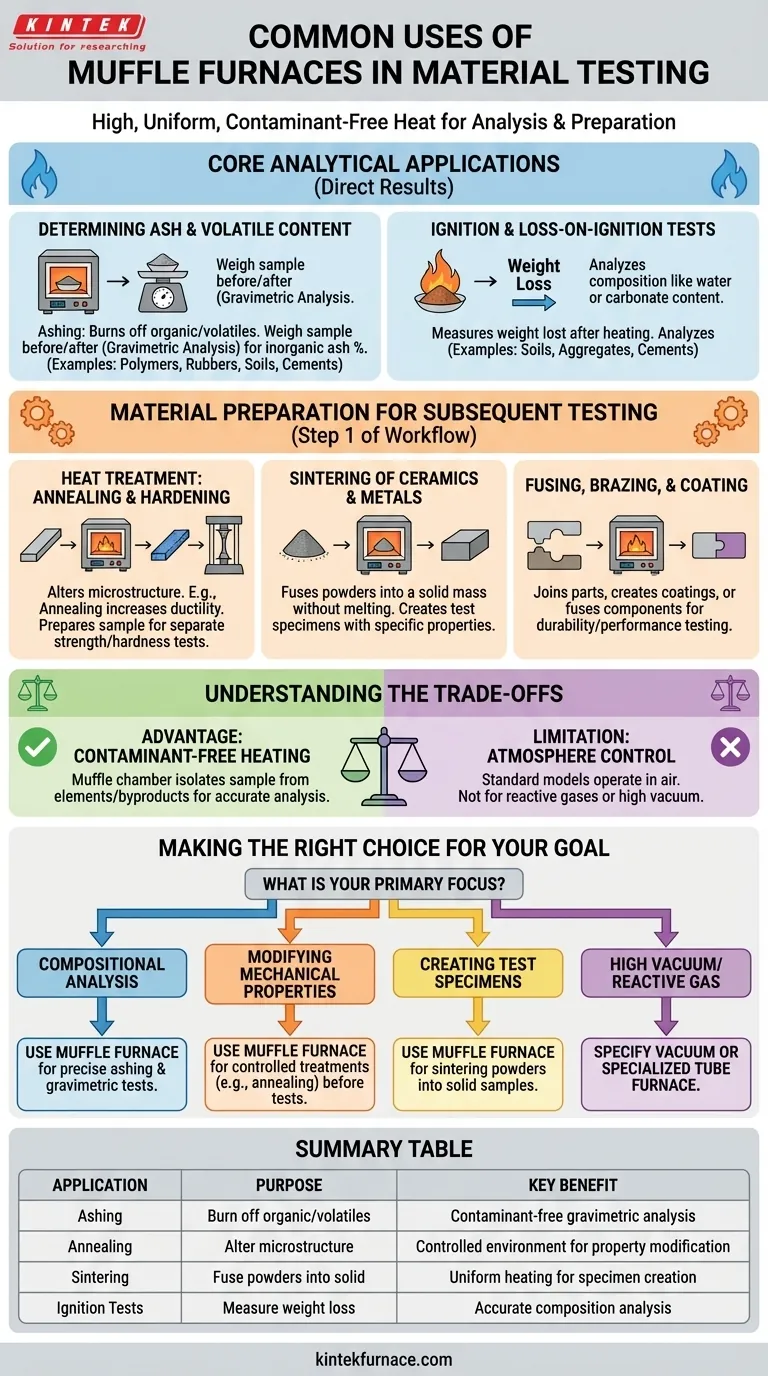
In material testing, a muffle furnace is a workhorse instrument used for processes that require high, uniform heat in a controlled environment. Its primary functions are to thermally analyze materials by burning off components (ashing), prepare samples for subsequent mechanical testing through heat treatment (annealing), and create solid specimens from powders (sintering).
A muffle furnace's core value lies in its ability to heat a material without direct contact from flames or electric heating elements. This "muffle" chamber prevents contamination, making it essential for accurately measuring compositional changes or modifying a material's structural properties under precise thermal conditions.

Core Analytical Applications
These are tests where the furnace directly provides the result, often through a change in mass.
Determining Ash and Volatile Content
Ashing is one of the most common uses for a muffle furnace. The process involves heating a sample to a high temperature to completely burn off all organic and volatile substances.
By weighing the sample before and after this process (a technique called gravimetric analysis), you can precisely determine the percentage of non-combustible inorganic residue, or ash content. This is critical for quality control in materials like polymers, rubbers, soils, and cements.
Ignition and Loss-on-Ignition Tests
Similar to ashing, these tests measure the weight lost from a material after being heated to a specific temperature. This is a standard procedure for analyzing soils, aggregates, and cements to determine their composition, such as water or carbonate content.
Material Preparation for Subsequent Testing
In many workflows, the muffle furnace is the first step in preparing a sample that will be tested using other instruments.
Heat Treatment: Annealing and Hardening
A furnace is used to precisely alter a material's microstructure. Annealing, for example, involves heating a metal and then slowly cooling it to increase its ductility and reduce hardness.
The sample is prepared in the furnace and then removed for other tests, such as tensile strength or hardness testing. The furnace doesn't measure the strength itself; it creates the specific material condition required for the test.
Sintering of Ceramics and Metals
Sintering is a process that uses heat to fuse powders into a solid, coherent mass without melting it. This is fundamental in creating test specimens from ceramics and powdered metals.
The furnace provides the controlled thermal environment needed to bond the particles together, creating a solid sample with specific density and structural properties that can then be evaluated.
Fusing, Brazing, and Coating
The furnace is also used to create enamel coatings on metals, fuse glass components, or braze (join) metallic parts with a filler metal. The resulting bond, coating, or fused object can then be subjected to durability and performance testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right heating instrument depends on understanding its core design and limitations.
The Advantage: Contaminant-Free Heating
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle"—a separating chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic. This chamber isolates the material sample from the heating elements and any potential byproducts of combustion (in fuel-fired models).
This separation is crucial for preventing contamination that could skew the results of sensitive analytical tests.
The Limitation: Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. While it provides a clean heating environment, it is not designed for processes that require a specific reactive gas (like pure nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum.
For applications demanding strict atmospheric control to prevent oxidation, a specialized tube furnace or vacuum furnace would be the appropriate choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use these guidelines to determine if a muffle furnace fits your material testing protocol.
- If your primary focus is compositional analysis: Use a muffle furnace for precise ashing and gravimetric tests to determine a material's inorganic or volatile content.
- If your primary focus is modifying mechanical properties: Use a muffle furnace for controlled heat treatments like annealing before conducting separate tensile, hardness, or ductility tests.
- If your primary focus is creating test specimens from powders: Use a muffle furnace for sintering ceramics or powdered metals to form solid samples for further evaluation.
- If your primary focus requires a high vacuum or reactive gas: A standard muffle furnace is insufficient; you should specify a vacuum furnace or a specialized tube furnace.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is a fundamental tool for thermally preparing or analyzing materials, forming a critical step in countless material science workflows.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Burn off organic/volatile substances to determine ash content | Contaminant-free heating for precise gravimetric analysis |
| Annealing | Heat treat materials to alter microstructure (e.g., increase ductility) | Controlled environment for mechanical property modification |
| Sintering | Fuse powders into solid specimens without melting | Uniform heating to create samples for density and structural tests |
| Ignition Tests | Measure weight loss to analyze composition (e.g., water content) | Accurate thermal analysis for materials like soils and cements |
Enhance your material testing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum, and atmosphere furnaces, plus CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for applications like ashing, annealing, and sintering. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your lab's efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















