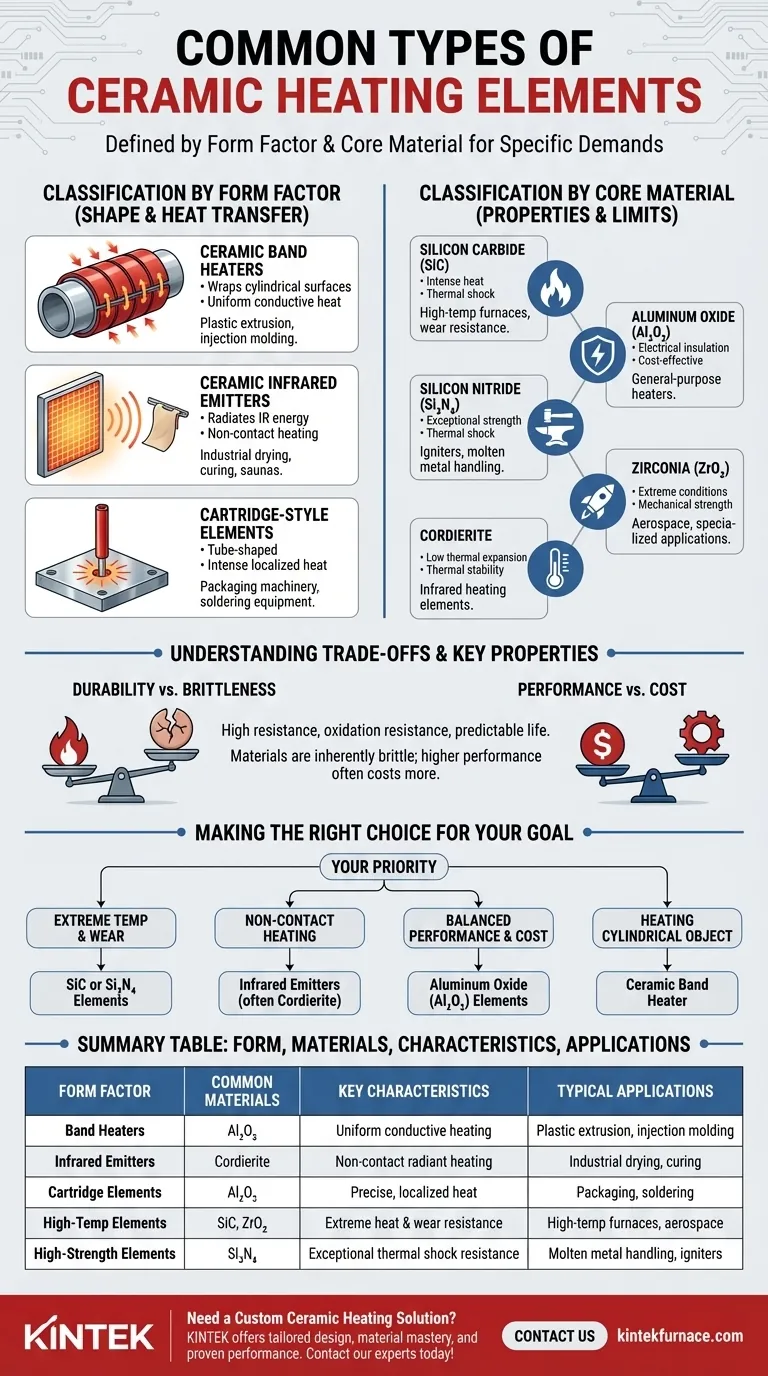
In short, the common types of ceramic heating elements are defined by both their physical form and their core material. The most frequent forms include band heaters, infrared emitters, and cartridge-style elements, which are constructed from materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC), Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), and Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) to meet specific performance demands.
Understanding the "type" of a ceramic heater requires looking at two distinct aspects: its physical shape (form factor), which determines how it delivers heat, and its core ceramic material, which dictates its temperature limits, durability, and efficiency.

Deconstructing Ceramic Heater Types
Ceramic heaters are not a single category but a family of components engineered for different tasks. The best way to understand them is to classify them first by their physical construction and then by the advanced material at their core.
Classification 1: By Form Factor
The shape of a heater is designed for a specific application and method of heat transfer.
Ceramic Band Heaters
These heaters are designed to wrap around cylindrical surfaces, providing uniform conductive heat. They are common in industrial processes like plastic extrusion and injection molding, where they heat barrels and nozzles.
Ceramic Infrared Emitters
These elements are built to generate and radiate heat in the form of infrared energy. This allows for non-contact heating, making them ideal for industrial drying, curing processes, space heating, and even saunas.
Cartridge-Style Elements
These are tube-shaped heaters inserted into holes drilled in metal parts, like dies or platens. They provide intense, localized heat and are valued for their precise temperature control in applications like packaging machinery and soldering equipment.
Classification 2: By Core Material
The choice of ceramic material is what gives the heater its fundamental performance characteristics.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Known for its ability to handle intense heat and thermal shock, SiC is used in high-temperature furnaces and applications requiring excellent wear resistance.
Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃)
Often called Alumina, this is a workhorse material valued for its excellent electrical insulation and high heat resistance. It provides a reliable and cost-effective solution for a wide range of general-purpose heaters.
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
This material offers exceptional strength and resistance to thermal shock. It is often used for robust igniters and in demanding applications like molten metal handling where mechanical durability is critical.
Zirconia (ZrO₂)
Zirconia is used in the most extreme conditions, offering superior mechanical strength at very high temperatures. It is a premium material for specialized industrial and aerospace applications.
Cordierite
Cordierite is prized for its very low thermal expansion, which prevents it from cracking during rapid heating and cooling cycles. This property makes it an efficient and reliable choice for infrared heating elements.
Understanding the Key Properties and Trade-offs
The effectiveness of any ceramic heater is rooted in a few essential properties, but these also come with inherent trade-offs.
Critical Performance Requirements
A successful ceramic heating element must balance several factors. It needs high electrical resistance to generate heat effectively without shorting, but not so high that it becomes an insulator.
It also requires excellent resistance to oxidation at high temperatures and a stable resistance level as temperature changes. This ensures a predictable and long service life.
The Trade-off: Durability vs. Brittleness
While materials like Silicon Nitride offer immense strength and thermal shock resistance, most ceramics are inherently more brittle than their metal-sheathed counterparts. They can be susceptible to failure from physical impact or improper mounting that induces stress.
The Trade-off: Performance vs. Cost
The highest-performing materials, such as Zirconia and Silicon Nitride, come at a significantly higher cost. For many applications, a more common material like Aluminum Oxide provides a superior balance of performance, reliability, and economic feasibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct ceramic element depends entirely on your specific priority, whether it's raw temperature, efficiency, or the shape of the object you need to heat.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature and wear resistance: Seek elements built from Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄).
- If your primary focus is non-contact heating over an area: Prioritize infrared emitters, which are often made with Cordierite for its thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is balanced performance and cost-effectiveness: Elements using Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) are the most common and versatile choice.
- If your primary focus is heating a cylindrical object: Your choice is defined by form factor, making a ceramic band heater the correct solution.
Ultimately, aligning the material's properties and the heater's form factor with your application's demands is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Form Factor | Common Materials | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Band Heaters | Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) | Uniform conductive heating | Plastic extrusion, injection molding |
| Ceramic Infrared Emitters | Cordierite | Non-contact radiant heating | Industrial drying, curing, space heating |
| Cartridge-Style Elements | Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) | Precise, localized heat | Packaging machinery, soldering equipment |
| High-Temperature Elements | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Extreme heat & wear resistance | High-temperature furnaces, aerospace |
| High-Strength Elements | Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | Exceptional thermal shock resistance | Molten metal handling, igniters |
Need a Custom Ceramic Heating Solution?
Struggling to find the perfect ceramic heating element for your unique requirements? KINTEK can help. Leveraging our exceptional R&D capabilities and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories and industrial facilities with advanced high-temperature heating solutions.
Our expertise includes:
- Tailored Element Design: We customize form factors and materials to precisely match your application's thermal and mechanical demands.
- Material Science Mastery: From cost-effective Alumina to high-performance Silicon Carbide and Silicon Nitride, we select the ideal ceramic for durability and efficiency.
- Proven Performance: Our elements deliver reliable heat transfer, whether you need conductive band heating, radiant infrared, or precise cartridge heating.
Let's engineer the optimal heating solution for your process. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















