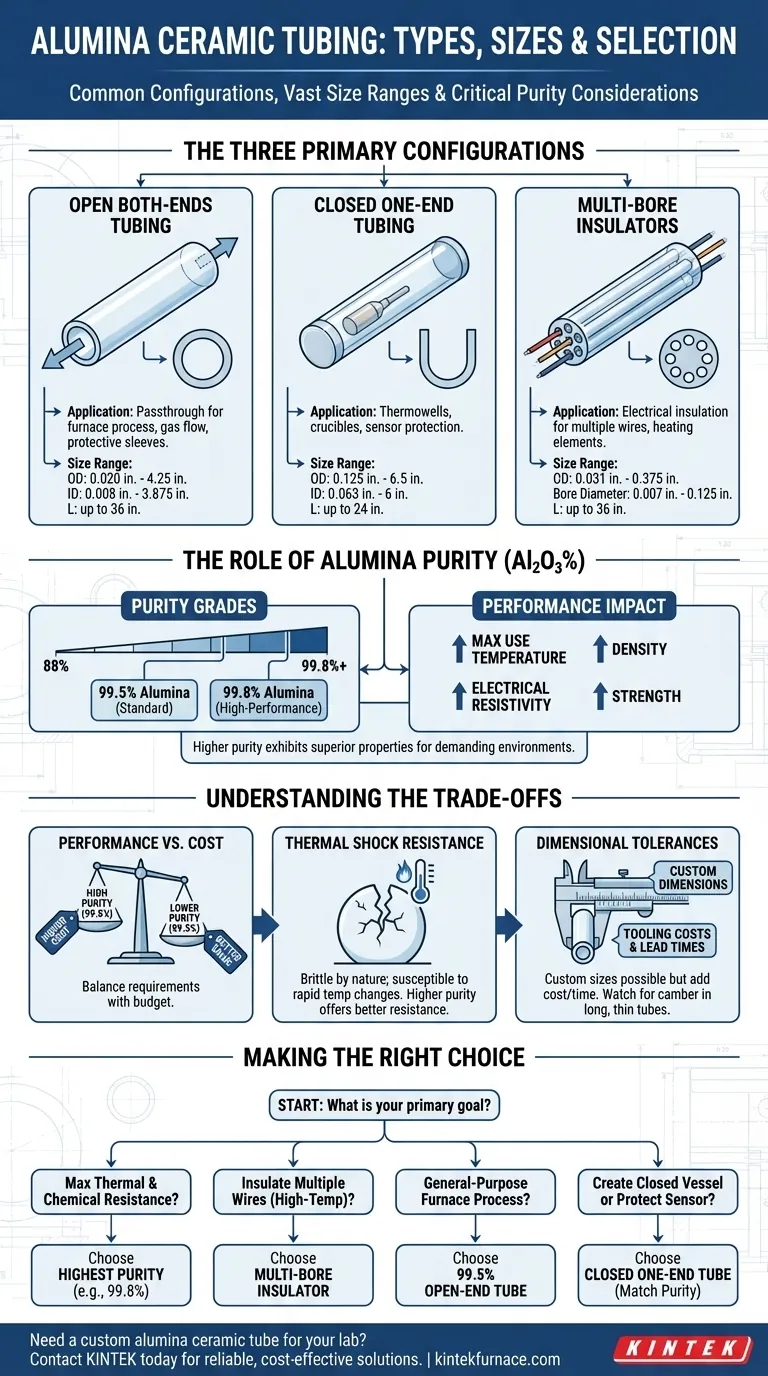
In short, alumina ceramic tubing is commonly available in three main configurations: open both-ends, closed one-end, and multi-bore insulators. These tubes are manufactured in a vast range of sizes, from miniature insulators with diameters as small as 0.020 inches to large furnace tubes over 6 inches in diameter and up to 36 inches long.
Choosing the correct alumina tubing goes beyond just its physical dimensions. The critical decision involves matching the tube's configuration and, more importantly, its material purity to the specific thermal, electrical, and mechanical demands of your application.
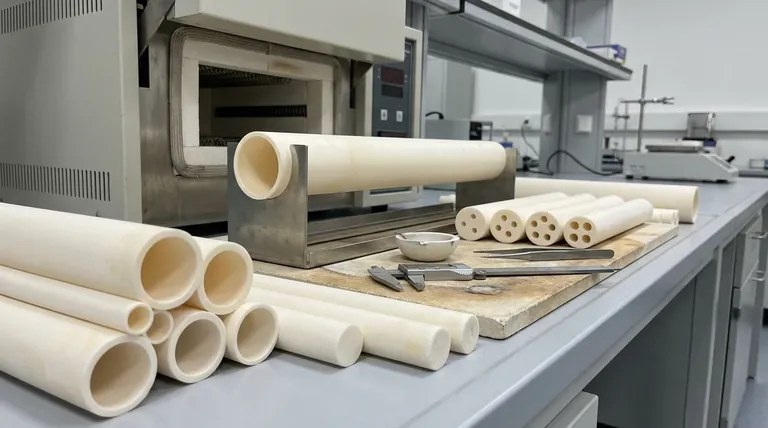

The Three Primary Tube Configurations
Understanding the purpose of each tube type is the first step in proper selection. Each geometry is designed to solve a distinct engineering problem.
Open Both-Ends Tubing
This is the most common configuration, used for applications requiring a passthrough. This includes process tubes in furnaces, protective sleeves for rods, or channels for gas flow.
Standard sizes for open-end tubes range from 0.020 in. OD x 0.008 in. ID x 6 in. L up to 4.25 in. OD x 3.875 in. ID x 36 in. L.
Closed One-End Tubing
These tubes are designed to contain a substance or protect a sensor from a harsh environment. They are frequently used as thermowells to shield thermocouples or as single-ended crucibles.
Typical sizes for closed-end tubes range from 0.125 in. OD x 0.063 in. ID x 3 in. L up to 6.5 in. OD x 6 in. ID x 24 in. L.
Multi-Bore Insulators
These tubes feature two or more parallel holes (bores) running their entire length. Their sole purpose is to feed through and electrically insulate multiple wires, such as those for heating elements or thermocouple leads.
Common sizes for multi-bore tubes range from 0.031 in. OD x 0.007 in. Bore Diameter x 12 in. L up to 0.375 in. OD x 0.125 in. Bore Diameter x 36 in. L.
Beyond Geometry: The Critical Role of Alumina Purity
While size and shape define the tube's function, its purity defines its performance limits. Alumina purity refers to the percentage of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) in the ceramic material.
What Purity Means for Performance
Higher purity grades, which contain fewer binding agents and impurities, exhibit superior properties. The two most common high-purity grades are 99.5% and 99.8%.
As purity increases, so do key characteristics like maximum use temperature, density, electrical resistivity, and strength.
Standard High-Purity Grades
While grades can range from 88% to over 99.8%, most high-performance applications use 99.5% or 99.8% alumina.
The 99.8% grade offers measurably higher density, flexural strength, and compressive strength, making it the choice for the most demanding environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the ideal tube requires balancing performance requirements with practical limitations.
Performance vs. Cost
The most significant trade-off is cost. Higher purity alumina requires more refined raw materials and more controlled firing processes, making 99.8% alumina noticeably more expensive than 99.5%.
For applications that do not push the absolute thermal or mechanical limits, the 99.5% grade often provides the best value.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Alumina is an exceptionally strong ceramic, but it is also brittle. It can be susceptible to fracturing from thermal shock—very rapid changes in temperature.
Higher purity grades generally offer better resistance to thermal shock, but care must always be taken when designing heating and cooling cycles.
Dimensional Tolerances
While a wide range of standard sizes is available, custom dimensions can be manufactured. However, this often involves significant tooling costs and lead times.
Be aware that long, thin tubes may have slight deviations in straightness (camber) due to the high-temperature manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal and chemical resistance: Choose the highest purity grade available, typically 99.8% alumina.
- If you need to insulate multiple wires in a high-temperature zone: A multi-bore insulator is the purpose-built and most effective solution.
- If you are building a general-purpose furnace process tube: A 99.5% purity open-end tube likely offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If you need to create a closed-end vessel or protect a sensor: A closed one-end tube in a purity grade that matches your temperature requirement is the correct choice.
By aligning the tube's configuration and purity with your specific operational demands, you ensure both reliability and cost-effectiveness for your project.
Summary Table:
| Configuration | Common Size Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Open Both-Ends | OD: 0.020 in. - 4.25 in., ID: 0.008 in. - 3.875 in., L: up to 36 in. | Furnace process tubes, gas flow channels, protective sleeves |
| Closed One-End | OD: 0.125 in. - 6.5 in., ID: 0.063 in. - 6 in., L: up to 24 in. | Thermowells, crucibles, sensor protection |
| Multi-Bore Insulators | OD: 0.031 in. - 0.375 in., Bore Diameter: 0.007 in. - 0.125 in., L: up to 36 in. | Electrical insulation for multiple wires in high-temperature zones |
| Purity Grades | 99.5% and 99.8% Alumina | Higher purity for better temperature resistance, strength, and electrical resistivity |
Need a custom alumina ceramic tube for your lab? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can deliver reliable, cost-effective tubing tailored to your specific thermal, electrical, and mechanical demands!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?



















