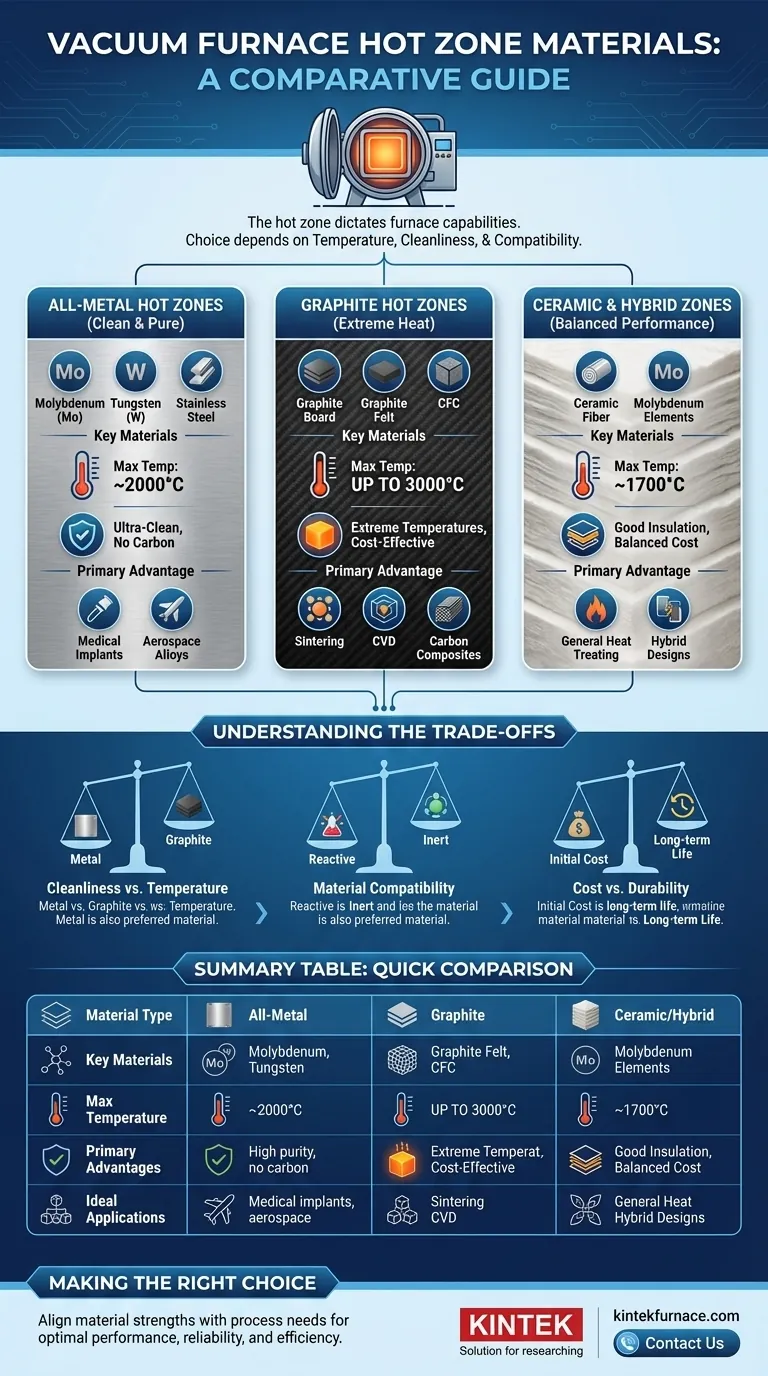
At the heart of any vacuum furnace is the hot zone, and the materials used in its construction dictate the furnace's ultimate capabilities and applications. The most common designs fall into three primary categories: all-metal, all-graphite, and ceramic fiber constructions. Each offers a unique profile of temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and durability, making the material choice a critical engineering decision.
The decision between a metallic, graphite, or ceramic hot zone is a fundamental engineering trade-off. Your choice hinges on three critical factors: the maximum required processing temperature, the necessary level of environmental cleanliness, and the chemical compatibility with the workload.
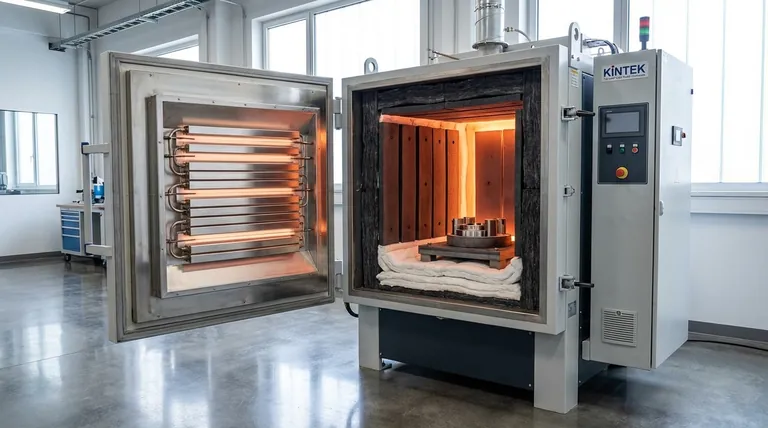

Understanding All-Metal Hot Zones
All-metal hot zones are the standard for applications demanding exceptional purity and cleanliness. They are constructed entirely from metallic elements, from the heating elements to the radiation shields and support structure.
Key Materials
The most common material for high-performance metallic hot zones is molybdenum (Mo) due to its high melting point and strength at temperature. Tungsten (W) is used for even higher temperatures, while stainless steel and nickel-based alloys are suitable for lower-temperature applications.
Primary Advantage: Cleanliness and Purity
Metallic hot zones create an "ultra-clean" environment. They do not produce dust or fibers and are ideal for processing materials that are sensitive to contamination, such as titanium alloys, medical implants, and aerospace components.
Operating Environment
These hot zones excel in high-vacuum environments and are mandatory when carbon contamination is unacceptable. The reflective metal shields provide excellent thermal insulation by minimizing heat loss through radiation.
Exploring Graphite Hot Zones
Graphite hot zones are valued for their ability to reach extreme temperatures and their relative cost-effectiveness. They are built using various forms of high-purity carbon.
Key Materials
Construction typically involves rigid graphite board, soft graphite felt for thermal insulation, and durable carbon-carbon composite (CFC) for structural components and heating elements. These layers work together to contain heat effectively.
Primary Advantage: Extreme Temperatures
Graphite sublimates rather than melts and can be used to construct furnaces capable of operating at temperatures up to 3,000°C (5,432°F). This makes it the go-to material for processes like sintering, carbon composite production, and certain chemical vapor deposition (CVD) applications.
Operating Environment
While excellent for high heat, graphite can produce fine carbon dust, which may not be suitable for all applications. It is the dominant choice for high-temperature sintering, brazing, and heat-treating where microscopic carbon particulate is not a concern.
The Role of Ceramic and Hybrid Zones
Ceramic materials are primarily used for their exceptional insulating properties and are often combined with other materials to create a cost-effective, high-performance furnace.
Ceramic Fiber Insulation
Alumina or other ceramic fibers are formed into boards and blankets that offer excellent heat retention for temperatures typically up to 1700°C (3092°F). They are lightweight and provide efficient thermal insulation.
Hybrid Designs
Many furnaces utilize a hybrid approach to balance cost and performance. A common configuration might use robust molybdenum heating elements within a chamber insulated by layers of ceramic fiber board, creating a clean, efficient, and durable hot zone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a hot zone material is never about finding a "best" option, but the right option for your process. The decision always involves balancing competing factors.
Cleanliness vs. Temperature
This is the most fundamental trade-off. All-metal hot zones offer the highest purity but are generally limited to temperatures below that of graphite. Graphite hot zones provide superior temperature capability but introduce the risk of carbon contamination.
Material Compatibility
Graphite is reactive and can form carbides when in contact with certain metals at high temperatures. If you are processing refractory metals or alloys where carbide formation is detrimental, a metallic hot zone is essential.
Cost and Durability
Graphite components can be more brittle and may have a shorter service life than their metallic counterparts, especially when subject to mechanical stress. While often cheaper initially, the long-term operational cost, including replacement parts and maintenance, must be considered. Molybdenum structures offer exceptional durability and a long lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your process and materials.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity and cleanliness (e.g., medical implants, aerospace alloys): An all-metal hot zone, typically featuring molybdenum, is the standard for preventing contamination.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures (above 2000°C) for processes like sintering or CVD: A graphite hot zone is the most effective and common solution.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating with a balance of performance and cost: A hybrid design using metallic heating elements with ceramic fiber insulation often provides the best value.
By aligning the material's core strengths with your process requirements, you ensure optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency from your vacuum furnace.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Materials | Max Temperature | Primary Advantages | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All-Metal | Molybdenum, Tungsten, Stainless Steel | Up to ~2000°C | High purity, no carbon contamination | Medical implants, aerospace alloys |
| Graphite | Graphite board, Graphite felt, CFC | Up to 3000°C | Extreme temperatures, cost-effective | Sintering, CVD, carbon composites |
| Ceramic/Hybrid | Ceramic fiber, Molybdenum elements | Up to 1700°C | Good insulation, balanced cost-performance | General heat treating, hybrid designs |
Struggling to select the right hot zone material for your vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Whether you need ultra-clean all-metal zones for sensitive materials or extreme-temperature graphite setups, we ensure optimal performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance



















