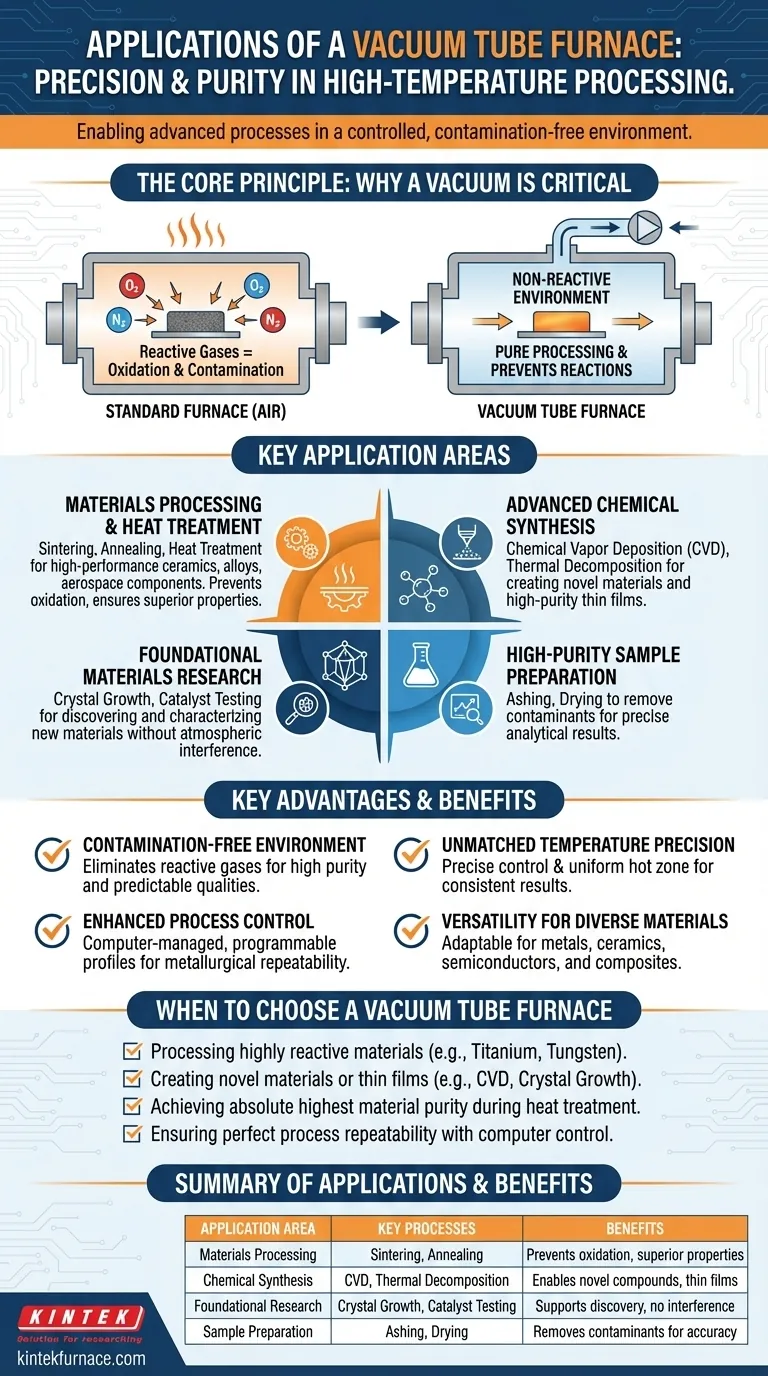
In short, a vacuum tube furnace is used for high-temperature processes that require an extremely pure, controlled environment free of air and other reactive gases. Its primary applications fall into four main categories: advanced materials processing, chemical synthesis, foundational research, and high-purity sample preparation.
The core value of a vacuum tube furnace is its ability to create a chemically non-reactive environment. By removing air, it prevents oxidation and contamination, enabling the precise thermal processing of sensitive materials and the synthesis of novel compounds that would be impossible under normal atmospheric conditions.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum is Critical
A standard furnace heats materials in the presence of air, which is composed of roughly 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. At high temperatures, these gases can aggressively react with a sample.
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
The primary function of the vacuum is to remove reactive gases. This prevents oxidation, nitridation, and other unwanted chemical changes that can degrade the quality and purity of the material being processed.
This makes the furnace essential for working with highly reactive or refractory metals, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and titanium, which would be compromised if heated in air.
Achieving Ultimate Purity
By creating a vacuum, you establish a highly pure processing environment. This ensures that the final material's properties are a direct result of the intended process, not a byproduct of contamination from the atmosphere.
Key Application Areas in Detail
The unique environment created by a vacuum tube furnace makes it indispensable across several scientific and industrial domains.
Materials Processing and Heat Treatment
This is one of the most common uses. Processes like sintering (fusing powder into a solid mass), annealing (altering a material's microstructure to make it more workable), and general heat treatment are performed in a vacuum to achieve superior material properties.
This is especially critical for producing high-performance ceramics, metal alloys, and components for the semiconductor and aerospace industries.
Advanced Chemical Synthesis
These furnaces are crucial for creating new materials. In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), precursor gases are introduced into the hot tube where they react and deposit a high-purity thin film onto a substrate.
Other processes, like thermal decomposition, use the controlled heat and vacuum to break down compounds into their constituent elements or to synthesize new ones.
Foundational Materials Research
In a research and development setting, vacuum tube furnaces are workhorses for discovering and characterizing new materials. They are used for crystal growth, where precise temperature control and a pure environment are necessary to form perfect single crystals.
They are also used for testing the performance of materials like catalysts at high temperatures without interference from atmospheric gases.
High-Purity Sample Preparation
For many advanced analytical techniques, the sample must be impeccably clean. A vacuum tube furnace can be used for ashing or drying samples to remove organic compounds or moisture without introducing contaminants.
This ensures that subsequent analysis reflects the true nature of the sample itself.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The decision to use a vacuum tube furnace is driven by a need for process control that other furnaces cannot provide.
Contamination-Free Environment
The vacuum eliminates oxygen and other reactive gases. This is the single most important advantage, ensuring that materials emerge from the furnace with high purity and stable, predictable qualities.
Unmatched Temperature Precision and Uniformity
Modern vacuum tube furnaces offer extremely precise temperature control and a uniform hot zone along the length of the tube. This ensures that the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions, leading to consistent and repeatable results.
Enhanced Process Control
The process is managed by a computer, which can execute complex heating, dwelling, and cooling profiles automatically. This ability to program the process ensures metallurgical repeatability, whether for a single research experiment or a scaled manufacturing run.
Versatility for Diverse Materials
The same furnace can be used for a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, semiconductors, and composites, simply by adjusting the temperature and pressure profiles.
When to Choose a Vacuum Tube Furnace
Use this guide to determine if a vacuum tube furnace is the correct tool for your objective.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive materials: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for preventing the oxidation of metals like titanium, tungsten, or certain alloys.
- If your primary focus is creating novel materials or thin films: The controlled environment is essential for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and controlled crystal growth.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest material purity: A vacuum is the only way to eliminate atmospheric contamination during high-temperature heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is ensuring perfect process repeatability: The computer-controlled temperature and atmosphere profiles of a vacuum furnace deliver unmatched consistency.
A vacuum tube furnace is an indispensable tool for anyone pushing the boundaries of materials science and engineering.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Processing | Sintering, Annealing, Heat Treatment | Prevents oxidation, ensures high purity and superior material properties |
| Chemical Synthesis | CVD, Thermal Decomposition | Enables creation of novel compounds and thin films in controlled environments |
| Foundational Research | Crystal Growth, Catalyst Testing | Supports discovery and characterization without atmospheric interference |
| Sample Preparation | Ashing, Drying | Removes contaminants for accurate analytical results |
Ready to elevate your materials processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in research, manufacturing, or sample preparation, our furnaces deliver contamination-free environments, precise temperature control, and unmatched repeatability. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace essential for CVD graphene? Master Growth Control & Purity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis
- What is the significance of porcelain furnaces in academic and scientific research? Unlock Innovation with Precise High-Temperature Control
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing



















