In short, vacuum induction smelting technology delivers unparalleled control over material purity and composition. This process uses induction heating within a vacuum to melt metals, which prevents contamination from atmospheric gases, removes existing impurities, and allows for the precise addition of alloying elements. The result is exceptionally clean, high-performance metals and alloys that are essential for advanced applications.
The true value of vacuum induction smelting is not just in melting metal, but in refining it. By creating a controlled environment free of oxygen and other contaminants, this technology enables the production of next-generation materials with properties unattainable through conventional methods.
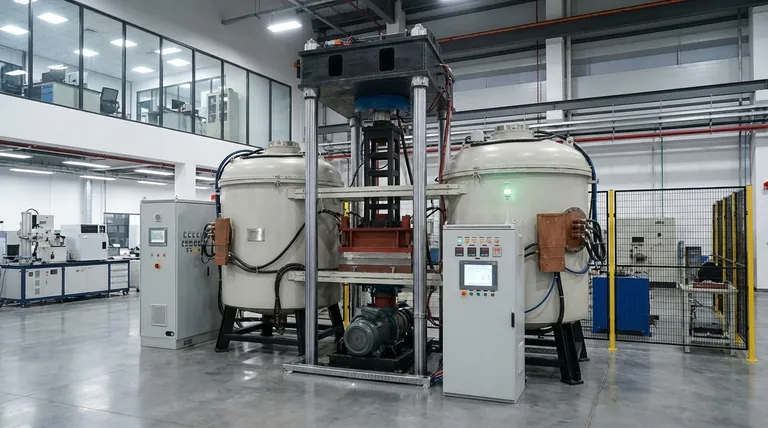

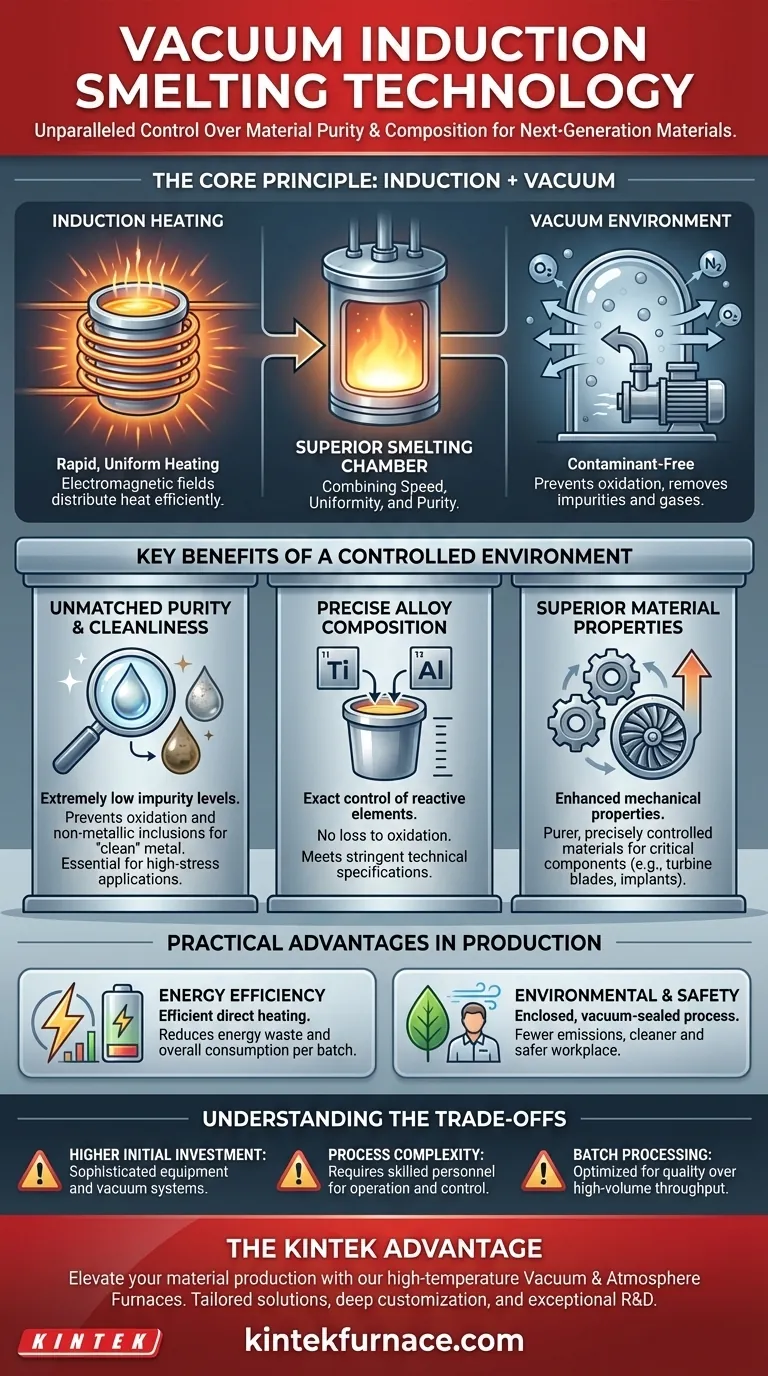
The Core Principle: How It Achieves Superior Results
Vacuum induction smelting combines two key principles—induction heating and a vacuum environment—to achieve its unique advantages. Understanding how they work together is crucial to appreciating its impact.
Induction Heating for Speed and Uniformity
Induction technology uses electromagnetic fields to rapidly and directly heat the metal. This method is exceptionally efficient and ensures the heat is distributed uniformly throughout the melt, which is critical for consistent quality and the effective removal of impurities.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
Placing the induction process inside a vacuum chamber is the game-changing element. Removing air (and thus oxygen and nitrogen) prevents the formation of oxides and nitrides, which are common impurities that degrade metal quality. The low-pressure environment also helps vaporize and extract dissolved gases and other volatile elements from the molten metal.
Key Benefits of a Controlled Environment
The combination of vacuum and induction heating directly translates into superior materials and a more efficient production process.
Unmatched Purity and Cleanliness
The primary benefit is the ability to produce materials with extremely low levels of impurities. By preventing oxidation and actively removing gases and non-metallic inclusions, the process yields a "clean" metal. This is essential for high-stress applications where even microscopic impurities can lead to material failure.
Precise Alloy Composition
In a vacuum, reactive and sensitive alloying elements like titanium or aluminum can be added without being lost to oxidation. This allows for the exact control of an alloy's final chemical composition, ensuring the material meets stringent technical specifications for strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance.
Superior Material Properties
Because the final product is purer and its composition is precisely controlled, its mechanical properties are significantly enhanced. This is why vacuum-smelted materials are required for components like jet engine turbine blades, medical implants, and high-purity electronic components.
Practical Advantages in Production
Beyond material quality, the technology offers significant operational benefits compared to traditional air-melting furnaces.
Energy Efficiency
Intermediate-frequency induction systems are highly efficient at converting electricity into heat directly within the metal, minimizing energy waste. This rapid heating cycle also reduces overall energy consumption per batch.
Environmental and Safety Improvements
The enclosed, vacuum-sealed process contains fumes and heat, leading to a cleaner and safer work environment. It produces far fewer harmful emissions compared to conventional smelting, aligning with modern environmental standards and improving working conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum induction technology is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
The sophisticated equipment required for vacuum induction smelting, including robust vacuum pumps and advanced control systems, represents a significant capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces.
Process Complexity
Operating a vacuum induction furnace requires a higher level of technical expertise. Managing vacuum levels, temperature profiles, and alloy additions demands skilled personnel to ensure consistent and successful results.
Batch Processing Throughput
This technology is typically a batch process, which may have a lower throughput than some continuous-casting methods. It is optimized for high-value, high-quality production rather than high-volume commodity metal production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum induction smelting hinges entirely on your final material requirements and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is producing high-volume, standard-grade metals: This technology is likely unnecessary, as more cost-effective conventional methods will suffice.
- If your primary focus is creating mission-critical components with maximum purity and performance: Vacuum induction smelting is the definitive standard for achieving the required material integrity.
- If your primary focus is developing novel alloys with reactive elements: The controlled vacuum environment is the only way to reliably achieve the precise composition you need.
Ultimately, vacuum induction smelting empowers engineers and scientists to create advanced materials that were previously impossible to manufacture.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Purity | Prevents contamination, removes impurities for clean metals |
| Precise Alloy Control | Allows exact addition of reactive elements in vacuum |
| Superior Material Properties | Enhances strength, corrosion resistance for critical uses |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses induction heating to minimize waste and reduce costs |
| Environmental Safety | Enclosed process cuts emissions, improves work conditions |
| High Initial Investment | Requires significant capital for advanced equipment |
| Process Complexity | Demands skilled operators for consistent results |
| Batch Processing | Optimized for quality over high-volume production |
Ready to elevate your material production with advanced smelting solutions? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace technologies, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for precise control and purity. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and material performance! Get in touch now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- What role does Vacuum Hot Press technology play in the automotive industry? Boost EV Batteries, Safety, and Efficiency
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials



















