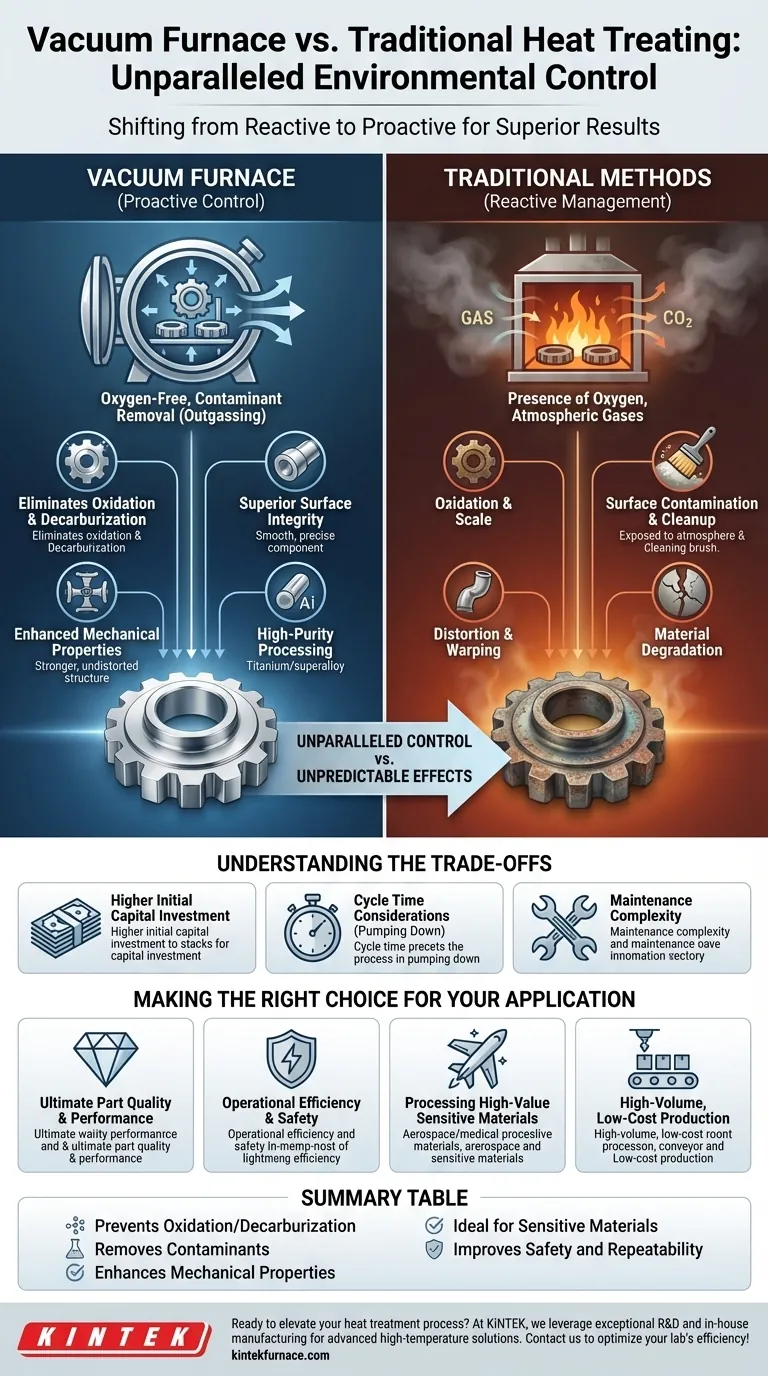
From a technical standpoint, the benefits of using a vacuum furnace for heat treating stem from one core principle: unparalleled environmental control. By removing atmospheric gases like oxygen, a vacuum furnace prevents negative surface reactions, resulting in cleaner parts with superior mechanical properties, enhanced process repeatability, and significant safety and environmental advantages over traditional atmosphere-based methods.
The fundamental advantage of vacuum heat treating is not a single feature, but the shift from a reactive process (managing unpredictable atmospheric effects) to a proactive one. By creating a near-perfectly controlled environment, you gain the power to precisely dictate the final properties of the material itself.

The Foundation: How a Vacuum Environment Changes Everything
A vacuum furnace operates by pumping nearly all the air and other gases out of a sealed chamber before heating the parts inside. This seemingly simple change has profound consequences for the entire heat treatment process.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
In a traditional furnace, the presence of oxygen, even in controlled atmospheres, inevitably leads to oxidation at high temperatures. This creates scale, discoloration, and a rough surface finish that often requires costly secondary cleaning operations.
A vacuum environment is, by definition, oxygen-free. This completely prevents oxidation and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel), ensuring parts emerge from the furnace with a bright, clean, and unaltered surface.
Removing Contaminants and Volatiles
The vacuum actively pulls contaminants off the part's surface. This includes residual oils, greases, and even gases trapped within the material itself, a process known as outgassing.
This purification effect is impossible in an atmospheric furnace, where such contaminants would simply burn off and potentially redeposit on the material, compromising its quality.
The Impact on Product Quality and Performance
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace translates directly into measurable improvements in the final component. This is the primary driver for its adoption in high-stakes industries like aerospace, medical, and high-performance tooling.
Superior Surface Integrity
Because there is no oxidation or scale, the part's surface and dimensional tolerances are preserved exactly as they were pre-treatment. This is critical for high-precision components where even microns of material loss are unacceptable.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
The combination of perfectly uniform radiant heating and controlled cooling (quenching) in a vacuum minimizes thermal stress. This results in significantly less distortion and warping compared to traditional methods.
Furthermore, this precise control leads to improved and more consistent material properties like hardness, ductility, wear resistance, and increased fatigue life.
Unlocking High-Purity Processing
For reactive metals like titanium or advanced superalloys, any interaction with oxygen or nitrogen at high temperatures can be catastrophic to their mechanical properties.
Vacuum furnaces provide the only environment pure enough to process these sensitive, high-value materials without contamination, ensuring they meet stringent compositional and performance requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnace technology is not a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging its specific limitations.
Higher Initial Capital Investment
Vacuum furnaces, with their sealed chambers, vacuum pumps, and sophisticated control systems, represent a significantly higher upfront cost compared to conventional atmosphere furnaces.
Cycle Time Considerations
The process of pumping the chamber down to the required vacuum level adds time to the beginning of every cycle. For certain high-volume, low-margin parts, a continuous belt-style atmosphere furnace may offer higher throughput.
Maintenance Complexity
The vacuum system itself—including pumps, seals, valves, and instrumentation—requires specialized knowledge for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. This can represent a steeper learning curve for maintenance teams accustomed to simpler furnace types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heat treatment technology depends entirely on the goals and constraints of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate part quality and performance: The superior surface finish, minimal distortion, and enhanced mechanical properties from a vacuum furnace are essential for critical components.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and safety: A vacuum furnace eliminates the cost, logistics, and significant safety hazards associated with storing and handling flammable atmospheric gases.
- If your primary focus is processing high-value or sensitive materials: The inert, contamination-free environment of a vacuum furnace is the only viable choice for heat-treating reactive metals and high-purity alloys.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production of simple parts: Carefully evaluate cycle times and investment costs; a traditional atmosphere furnace may remain the more cost-effective option for non-critical components.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is an investment in process control, enabling you to deliver unparalleled quality and consistency in your final product.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation/Decarburization | Eliminates surface scale and carbon loss for bright, clean parts without secondary cleaning. |
| Removes Contaminants | Vacuum outgassing purifies surfaces by removing oils and gases, improving material purity. |
| Enhances Mechanical Properties | Uniform heating and controlled cooling reduce distortion, increase hardness, and boost fatigue life. |
| Ideal for Sensitive Materials | Essential for processing reactive metals like titanium and superalloys without contamination. |
| Improves Safety and Repeatability | No flammable gases needed, offering consistent results and reduced environmental risks. |
Ready to elevate your heat treatment process with precision and reliability?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or tooling industries, our vacuum furnaces ensure superior surface integrity, minimal distortion, and enhanced performance for high-value materials. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory's efficiency and deliver unmatched quality in your heat treatment applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















