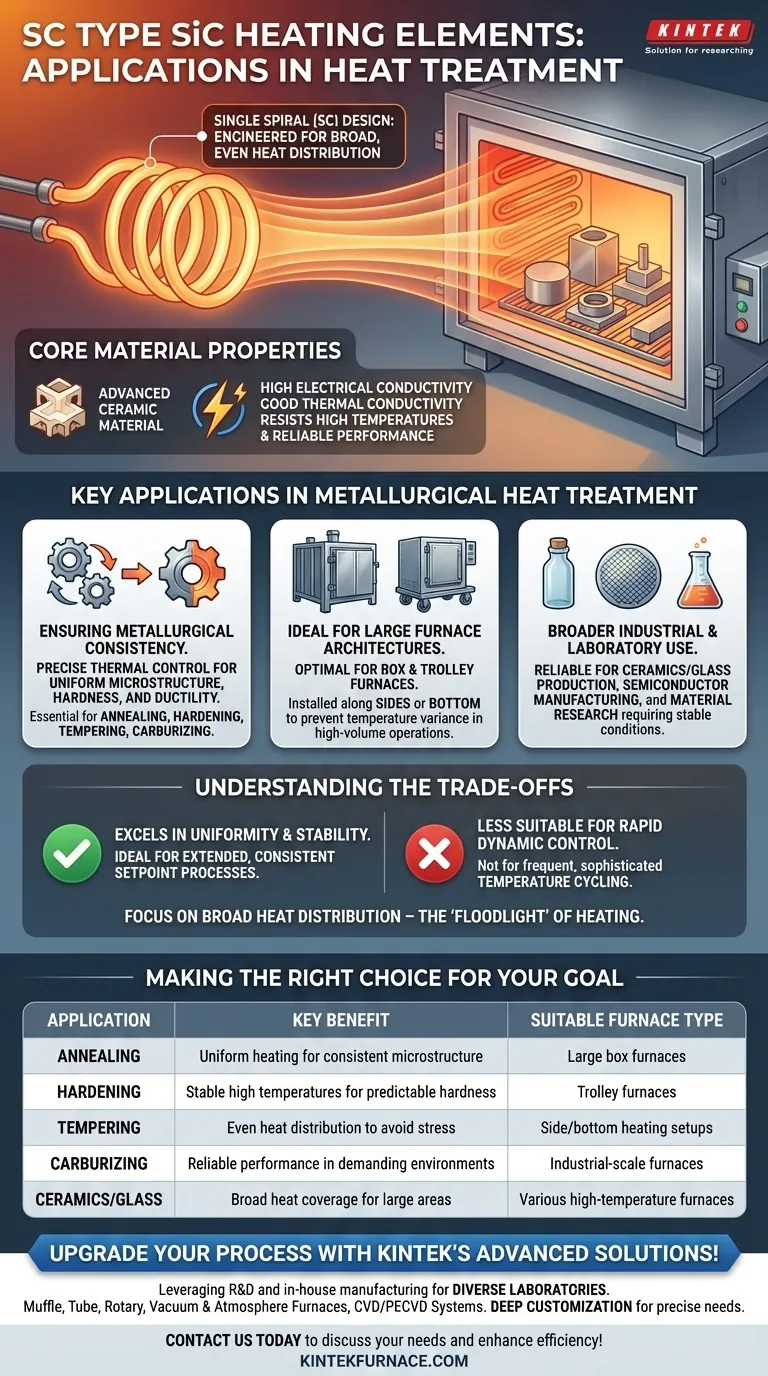
In the field of metallurgical heat treatment, SC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are fundamental components used in furnaces for processes such as annealing, hardening, tempering, and carburizing. Their defining application is to provide the highly uniform and stable high-temperature environment required to achieve consistent and predictable properties in treated metals.
The critical challenge in heat treatment is achieving uniform temperature across the entire workload. The Single Spiral (SC) design of these elements is specifically engineered to deliver broad, even heat distribution, making them the standard choice for large-scale furnaces where temperature consistency is non-negotiable.

What Defines an SC Type Heating Element?
To understand its applications, we must first understand its design. The SC Type element is not just a material but a specific configuration optimized for a distinct purpose.
The Single Spiral (SC) Configuration
The "SC" designation refers to the element's Single Spiral construction. This design is fundamental to its performance, creating a large, consistent radiating surface.
This physical form is engineered to convert electrical energy into radiant heat with high efficiency and distribute it evenly over a wide area, minimizing hot spots.
Core Material Properties
SC Type elements are advanced ceramic materials with high electrical conductivity and good thermal conductivity. This combination allows them to heat up efficiently while resisting the high temperatures they generate.
Their ceramic nature provides the necessary structure and resistance to operate reliably for extended periods in demanding furnace environments.
Key Applications in Heat Treatment Furnaces
The unique characteristics of the SC Type element make it ideal for specific, critical applications where thermal stability is paramount.
Ensuring Metallurgical Consistency
The primary goal of processes like annealing and hardening is to alter a material's microstructure in a controlled way. This requires uniform heating and cooling.
SC elements provide this precise thermal control, ensuring that every part of a component or batch receives the same thermal treatment. This directly translates to consistent hardness, ductility, and strength in the final product.
Ideal for Large Furnace Architectures
These elements are exceptionally well-suited for large box furnaces and trolley furnaces. They are often installed along the sides or at the bottom of the heating chamber.
This placement leverages their ability to radiate heat evenly across large surfaces, which is crucial for preventing temperature variance in high-volume industrial operations.
Broader Industrial and Laboratory Use
While essential in metallurgy, the reliability of SC elements makes them valuable in other high-temperature fields.
They are used in the production of ceramics and glass, semiconductor manufacturing, and even in laboratory settings for material research, where stable and repeatable heating conditions are essential for valid experimental work.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single component is perfect for every scenario. The strengths of the SC Type element also define its ideal use case and distinguish it from other designs.
Uniformity Over Dynamic Control
The SC Type excels at providing stable, uniform heat. It is designed for processes that run at a consistent setpoint for extended durations.
For high-end applications requiring rapid, sophisticated, and automated temperature adjustments, other configurations like the SCR Type are often favored. The SC element's strength is its steadiness, not its agility.
Focus on Broad Heat Distribution
The single spiral design is optimized for area heating. In applications requiring highly concentrated or targeted heat in a very small zone, other element geometries might be more suitable.
The SC Type is a "floodlight," not a "spotlight." Its purpose is to heat the entire chamber evenly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating element depends entirely on your specific process requirements and furnace design.
- If your primary focus is achieving consistent metallurgical properties across large batches: The uniform, stable heating of SC Type elements makes them the ideal and most reliable choice.
- If your process requires frequent and rapid temperature cycling in a highly automated environment: You should evaluate more advanced configurations designed for sophisticated thermal management, such as SCR types.
- If you are operating standard box or trolley furnaces for processes like annealing or tempering: SC Type elements are the industry standard due to their suitability for side and bottom heating configurations that ensure chamber uniformity.
Ultimately, understanding the design principle of your heating element is the first step toward mastering your heat treatment process.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Suitable Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Uniform heating for consistent microstructure | Large box furnaces |
| Hardening | Stable high temperatures for predictable hardness | Trolley furnaces |
| Tempering | Even heat distribution to avoid stress | Side/bottom heating setups |
| Carburizing | Reliable performance in demanding environments | Industrial-scale furnaces |
| Ceramics/Glass Production | Broad heat coverage for large areas | Various high-temperature furnaces |
Upgrade your heat treatment process with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, such as achieving uniform heating in large-scale operations. Contact us today to discuss how our SC Type SiC heating elements and other products can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















