At their core, vacuum furnaces provide a decisive advantage in tool and die manufacturing by enabling absolute control over the heat treatment environment. This control directly translates into tools with superior hardness, enhanced wear resistance, and exceptional longevity. By eliminating atmospheric variables, these furnaces ensure that the final product meets the most demanding specifications for precision and performance.
The fundamental value of a vacuum furnace is not just the heat it provides, but the atmosphere it removes. By creating a controlled vacuum, you eliminate unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, resulting in metallurgically cleaner, stronger, and more consistent tools.
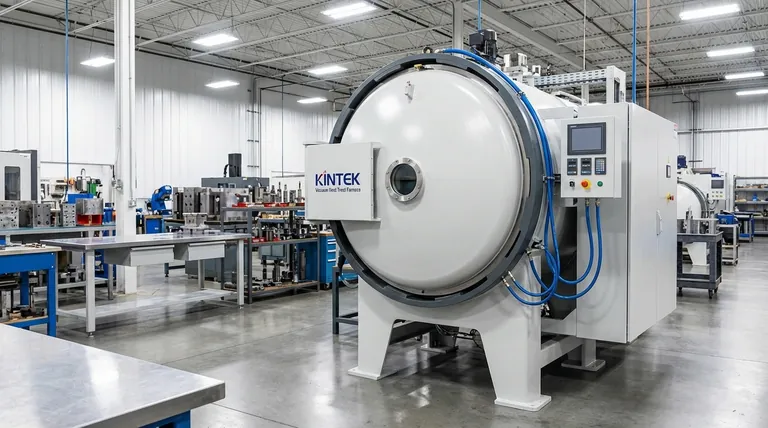

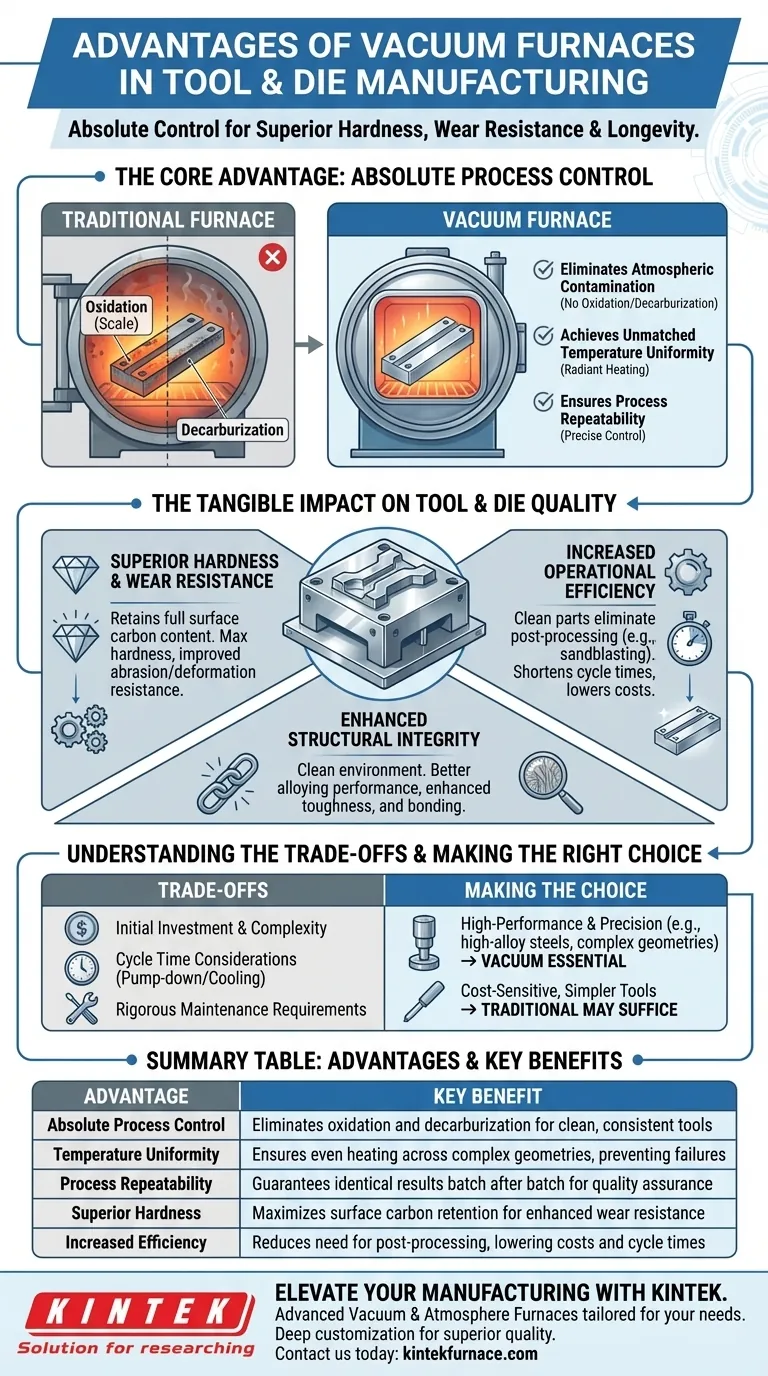
The Core Advantage: Absolute Process Control
The primary benefit of a vacuum furnace is its ability to create a perfectly controlled environment, free from the reactive gases present in a standard atmosphere. This control is the foundation for all other advantages.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
In a conventional furnace, oxygen reacts with the hot metal surface, causing oxidation (scale) and decarburization (loss of surface carbon). This degrades the tool's surface integrity and hardness.
A vacuum furnace removes nearly all atmospheric gases. This prevents these harmful reactions, resulting in a bright, clean surface that requires little to no post-processing.
Achieving Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
A vacuum is an excellent insulator. In a vacuum furnace, heat is transferred primarily through radiation, which promotes exceptionally uniform heating across the entire workpiece, including complex geometries.
This uniformity ensures that every part of the tool or die achieves the desired metallurgical structure, preventing soft spots or internal stresses that can lead to premature failure.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
With precise control over vacuum levels, temperature ramp rates, and cooling cycles, vacuum furnaces offer unparalleled repeatability. The process is defined by programmable logic, not by atmospheric fluctuations.
This guarantees that a part processed today will have the exact same properties as a part processed months from now, a critical factor for quality control in high-volume production.
The Tangible Impact on Tool & Die Quality
This level of process control has a direct and measurable impact on the final product, creating tools that are fundamentally better.
Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
By preventing decarburization, the tool's surface retains its full carbon content, allowing it to achieve maximum hardness during quenching.
This results in a finished tool with significantly improved resistance to wear, abrasion, and deformation, extending its operational life under demanding conditions.
Enhanced Structural Integrity
The clean, controlled environment ensures that the alloying elements within the tool steel perform exactly as intended without reacting with outside contaminants.
This leads to enhanced material integrity, better bonding in processes like vacuum brazing, and a final product with superior mechanical properties and toughness.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Because parts emerge from a vacuum furnace clean and bright, the need for costly and time-consuming secondary operations like sandblasting, grinding, or chemical cleaning is drastically reduced or eliminated.
This shortens the overall production cycle and lowers labor costs, contributing directly to a more efficient and profitable operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnace technology is not without its considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging its specific demands.
Initial Investment and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to traditional atmospheric furnaces. They are complex systems that require specialized knowledge for operation and programming.
Cycle Time Considerations
Achieving a high vacuum takes time (pump-down), and the controlled cooling (quenching) process can also be longer than in some atmospheric methods. This can impact overall throughput for certain applications.
Maintenance Requirements
The integrity of the system depends on pristine seals, powerful pumps, and accurate sensors. These components demand a rigorous and consistent maintenance schedule to ensure reliable performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to use a vacuum furnace should be driven by the material requirements and the desired quality of your final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and precision: A vacuum furnace is essential for high-alloy tool steels (like H13, D2), complex geometries, and applications where a pristine surface finish is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive production of simpler tools: A traditional atmospheric furnace may be sufficient for lower-alloy steels where some surface finishing is acceptable and the highest level of metallurgical purity is not required.
Ultimately, investing in vacuum furnace technology empowers you to produce tools and dies that meet the highest possible standard of quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Absolute Process Control | Eliminates oxidation and decarburization for clean, consistent tools |
| Temperature Uniformity | Ensures even heating across complex geometries, preventing failures |
| Process Repeatability | Guarantees identical results batch after batch for quality assurance |
| Superior Hardness | Maximizes surface carbon retention for enhanced wear resistance |
| Increased Efficiency | Reduces need for post-processing, lowering costs and cycle times |
Ready to elevate your tool and die manufacturing with advanced vacuum furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for diverse laboratories. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering superior hardness, wear resistance, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your production quality and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density



















