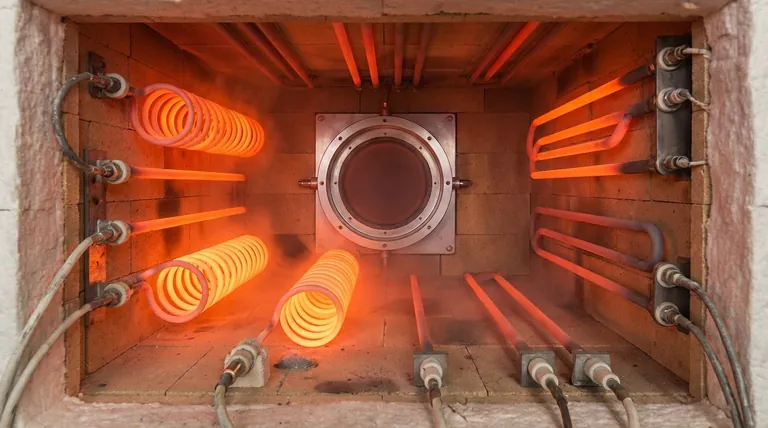
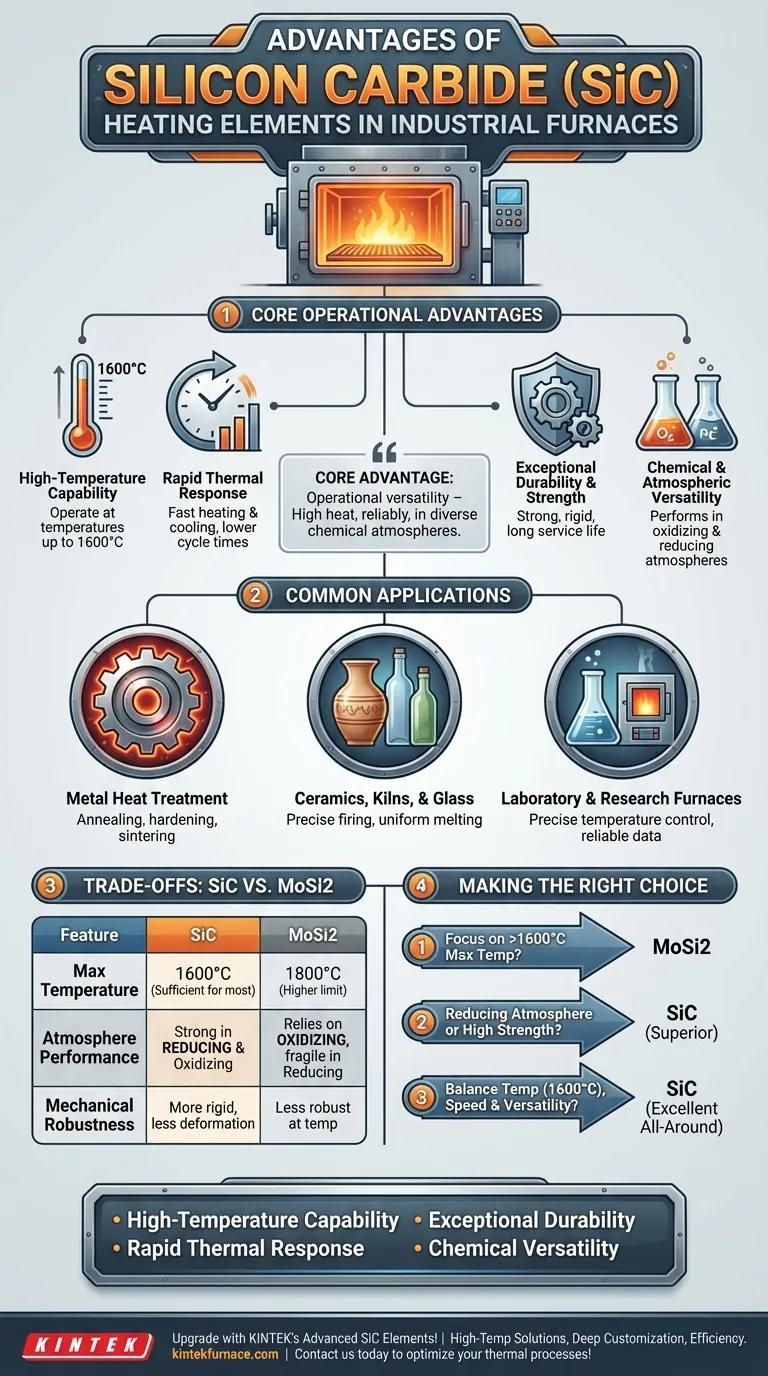
For industrial heating applications, the choice of element is a critical decision that impacts efficiency, reliability, and operating cost. Silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are a leading choice, prized for their ability to operate at very high temperatures (up to 1600°C), heat up and cool down rapidly, resist chemical attack, and provide a long, reliable service life. This combination of attributes makes them a versatile and robust solution for many demanding thermal processes.
The core advantage of silicon carbide is its operational versatility. It delivers not just high heat, but does so reliably and efficiently across a wider range of chemical atmospheres than many alternatives, making it a uniquely durable and adaptable choice for complex industrial environments.

The Core Operational Advantages of SiC
Silicon carbide’s material properties translate directly into tangible benefits for industrial furnaces. These advantages address the primary challenges of high-temperature processing: speed, consistency, and durability.
High-Temperature Capability
SiC elements can consistently operate at temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). This makes them suitable for a vast range of high-heat processes, including the sintering of ceramics, heat treatment of metal alloys, and glass manufacturing.
Their ability to sustain these temperatures without rapid degradation is fundamental to their value in modern furnaces.
Rapid Thermal Response
These elements are known for their ability to reach a target temperature quickly. This rapid heating and cooling capability reduces process cycle times, increases throughput, and lowers energy consumption per cycle.
By minimizing the time a furnace spends ramping up to temperature, SiC elements directly contribute to lower operational costs and improved industrial sustainability.
Exceptional Durability and Strength
Silicon carbide is an inherently strong and rigid material that maintains its mechanical integrity even at extreme temperatures. This high-temperature strength ensures a long and predictable service life.
Longer-lasting elements mean less frequent replacement, reduced maintenance downtime, and more consistent furnace operation.
Chemical and Atmospheric Versatility
A key differentiator for SiC is its excellent performance in both oxidizing and reducing atmospheres. It is highly resistant to chemical reactions that can degrade other types of heating elements.
This makes SiC an ideal choice for chemical processing and for heat treatments where the process atmosphere is a critical variable.
Common Applications Where SiC Excels
The unique properties of SiC make it a preferred technology in several key industries that rely on precise and reliable high-temperature heating.
Metal Heat Treatment
SiC elements are widely used for processes like annealing, hardening, tempering, and sintering of various metals and alloys. Their uniform heating ensures consistent metallurgical properties in the final product.
Ceramics, Kilns, and Glass
In the manufacturing of ceramics, pottery, and glass, precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution are non-negotiable. SiC elements provide the stability required for consistent firing and melting.
Laboratory and Research Furnaces
For research and testing applications, process repeatability is paramount. SiC heaters offer the precise temperature control and uniform heating zones necessary for obtaining reliable experimental data.
Understanding the Trade-offs: SiC vs. MoSi2
To fully appreciate the advantages of silicon carbide, it is useful to compare it to Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), another common high-temperature heating element. The choice between them hinges on specific process requirements.
The Temperature Ceiling
The primary advantage decisões elements is their higher maximum operating temperature, which can reach up to 1800°C. If a process absolutely requires temperatures above 1600°C, MoSi2 is the clear choice.
However, for the vast majority of industrial applications fatores de 1600°C, SiC provides more than sufficient thermal capability.
Performance in Different Atmospheres
This is a critical trade-off. SiC elements are significantly stronger and more durable in reducing atmospheres. MoSi2 elements, conversely, rely on an oxidizing atmosphere to form a protective silica layer and can be damaged in reducing environments.
Therefore, the chemical environment मशीन your furnace is a deciding factor.
Mechanical Robustness
At operating temperature, SiC is a more rigid and mechanically robust material. It is less prone to deformation under its own weight, which can be a factor in certain furnace designs and orientations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your thermal application. There is no single "best" element, only the right element for the job.
- If your primary focus is the absolute maximum operating temperature (above 1600°C): MoSi2 elements are designed for these ultra-high thermal ranges and are the appropriate choice.
- If your process involves a reducing atmosphere or requires high mechanical strength at temperature: SiC elements are the superior and more reliable option due to their inherent durability in these conditions.
- If your goal is balancing high-temperature performance (up to 1600°C) with rapid cycling and atmospheric versatility: SiC provides an excellent, cost-effective, and robust all-around solution for a wide range of industrial processes.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element requires a clear-eyed assessment of your specific temperature, atmosphere, and operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Capability | Operates up to 1600°C, ideal for sintering, heat treatment, and glass manufacturing |
| Rapid Thermal Response | Quick heating and cooling reduces cycle times and energy costs |
| Exceptional Durability | Long service life with high mechanical strength at extreme temperatures |
| Chemical Versatility | Performs well in oxidizing and reducing atmospheres, resistant to degradation |
Upgrade your industrial furnace with KINTEK's advanced silicon carbide heating elements! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















