In short, modern muffle furnaces are vastly superior to older models due to significant advancements in control, efficiency, and sample integrity. They leverage programmable digital controllers for unmatched temperature uniformity, utilize advanced insulation and heating elements to drastically reduce energy consumption, and ensure complete isolation of the sample from contaminants.
The primary advantage is the shift from a simple, manually-operated "hot box" to a precise, automated, and highly efficient scientific instrument. This transformation delivers more reliable and repeatable results while lowering operational costs.
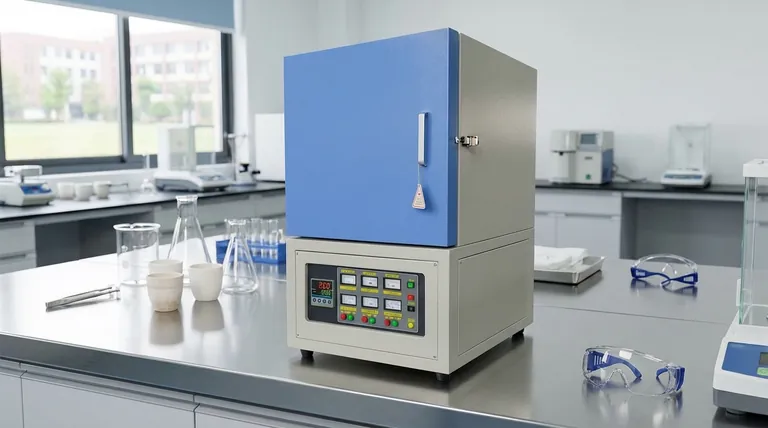

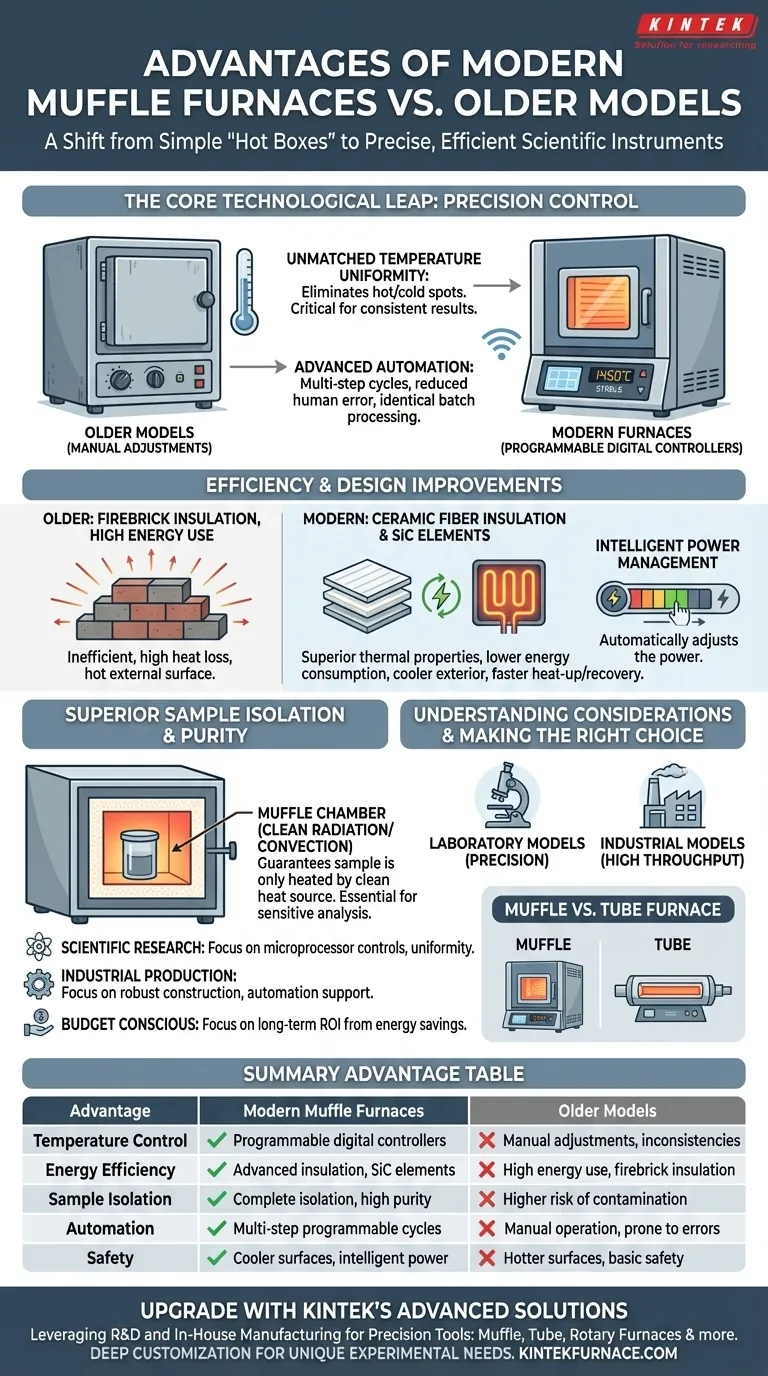
The Core Technological Leap: From Brute Force to Precision Control
Older furnaces were effective at getting hot, but modern designs excel at getting hot intelligently. This leap is driven by key technological upgrades that give users unprecedented control over the heating process.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
Modern furnaces use programmable digital controllers or microprocessor-controlled thermoregulators. These systems constantly monitor and adjust power to the heating elements.
This ensures a highly stable and uniform temperature throughout the entire chamber, eliminating the hot and cold spots common in older models. For applications like materials research or sample ashing, this uniformity is critical for achieving consistent and repeatable outcomes.
Superior Sample Isolation
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle"—an inner chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements and any potential contaminants from combustion.
Modern designs perfect this concept by using advanced materials and construction. This guarantees that the sample is only heated by clean radiation or convection, which is essential for sensitive analytical processes where sample purity is paramount.
Advanced Automation and Programmability
Unlike older, manually adjusted furnaces, modern units allow users to program complex, multi-step heating and cooling cycles.
You can set a specific ramp rate, a hold time at a target temperature, and a controlled cooling phase. This automation reduces the chance of human error, frees up operator time, and ensures every batch is processed identically.
Efficiency and Design Improvements
Modern furnaces are not just more precise; they are also significantly more efficient and compact, addressing both operational budgets and limited lab space.
Advanced Insulation Materials
Modern furnaces replace heavy, inefficient firebrick with lightweight ceramic fiber insulation. This material has superior thermal properties, drastically reducing heat loss.
The result is a furnace that consumes less energy to maintain its target temperature and has a cooler external surface, improving lab safety.
High-Efficiency Heating Elements
Many modern units employ silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements. These components provide stable, reliable heating while consuming less energy than the elements found in older equipment.
They also contribute to faster heat-up and temperature recovery times, increasing overall throughput.
Intelligent Power Management
Newer furnaces often include energy-saving modes and intelligent functions. The controller can automatically reduce power output once the set temperature is reached, maintaining stability with minimal energy draw.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While modern furnaces are superior, choosing the right one requires understanding the different types and their intended applications.
Laboratory vs. Industrial Models
Laboratory furnaces are designed for precision. They typically have smaller capacities but feature highly accurate temperature controls for scientific experiments, such as sintering or binder burnout.
Industrial furnaces, like those from Nabertherm or Thermolyne, are built for durability and high throughput in production environments like metal treatment or glass manufacturing.
Customization vs. Standard Models
For most applications, a standard, off-the-shelf furnace is more than sufficient. However, for unique research or specialized production processes, custom-built furnaces can be designed to meet exact requirements for size, temperature range, and other features.
Muffle Furnace vs. Tube Furnace
It's also important to know when a muffle furnace is the right tool. Compared to tube furnaces, muffle furnaces generally offer larger internal capacity and higher maximum temperatures at a similar price point, making them ideal for processing larger samples or batches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your primary goal. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable scientific research: Prioritize models with microprocessor-based controls and documented temperature uniformity specifications.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: Look for robust construction, high-efficiency heating elements, and features that support process automation.
- If your primary focus is upgrading older equipment on a budget: Emphasize the long-term ROI from energy savings and reduced manual oversight offered by even entry-level modern furnaces.
Investing in a modern muffle furnace elevates your thermal processing from a rough approximation to a controlled, reliable, and efficient scientific procedure.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Modern Muffle Furnaces | Older Models |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Programmable digital controllers for uniform heating | Manual adjustments with inconsistencies |
| Energy Efficiency | Advanced insulation and SiC elements reduce consumption | High energy use with firebrick insulation |
| Sample Isolation | Complete isolation from contaminants for purity | Higher risk of contamination |
| Automation | Multi-step programmable cycles for repeatability | Manual operation prone to errors |
| Safety | Cooler external surfaces and intelligent power management | Hotter surfaces and basic safety features |
Upgrade your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precision tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering enhanced efficiency, reliability, and cost savings. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















