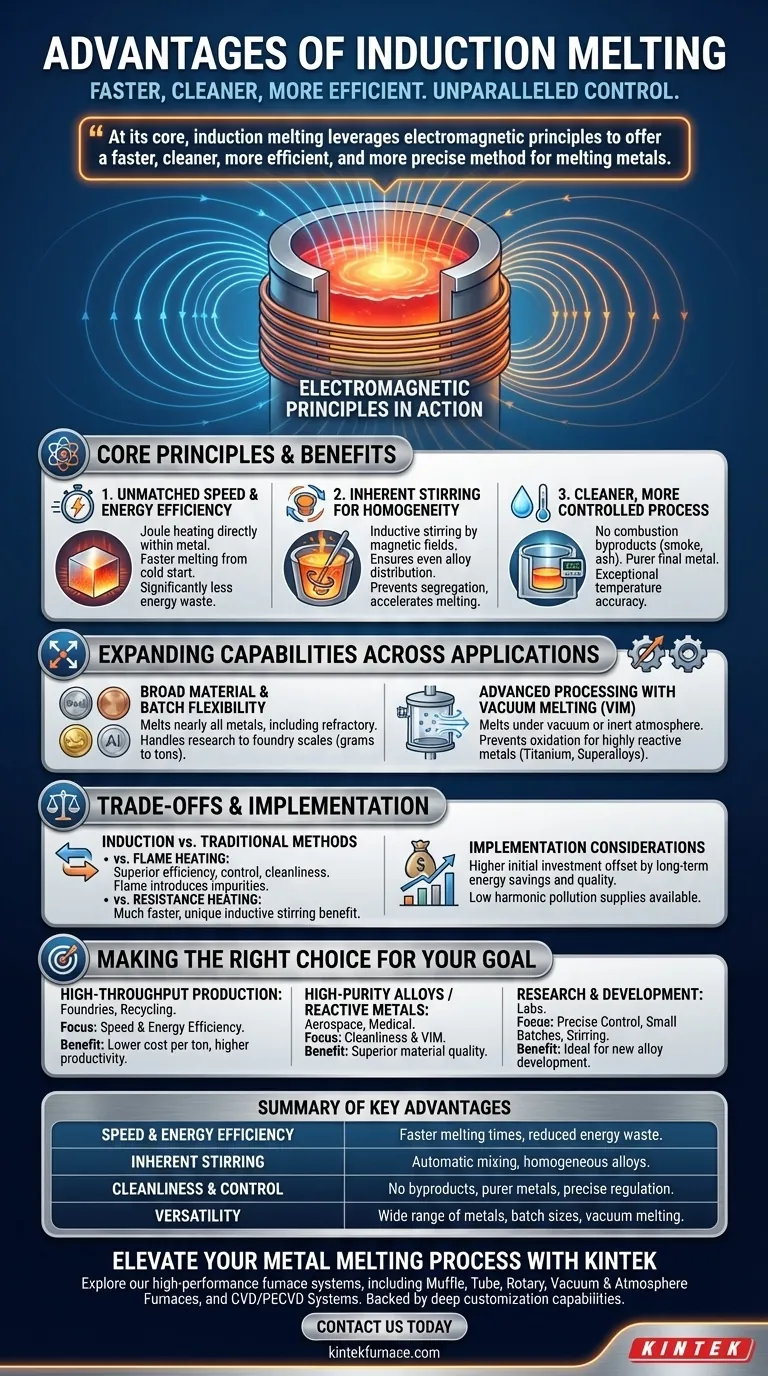
At its core, induction melting leverages electromagnetic principles to offer a faster, cleaner, more efficient, and more precise method for melting metals compared to traditional fuel-fired or resistance furnaces. The process provides unparalleled control over the molten material, resulting in higher quality output and greater operational flexibility.
The fundamental advantage of induction melting isn't just its speed, but its ability to heat and mix the metal simultaneously and without contamination. This unique combination of properties translates directly into superior metallurgical quality and process efficiency.
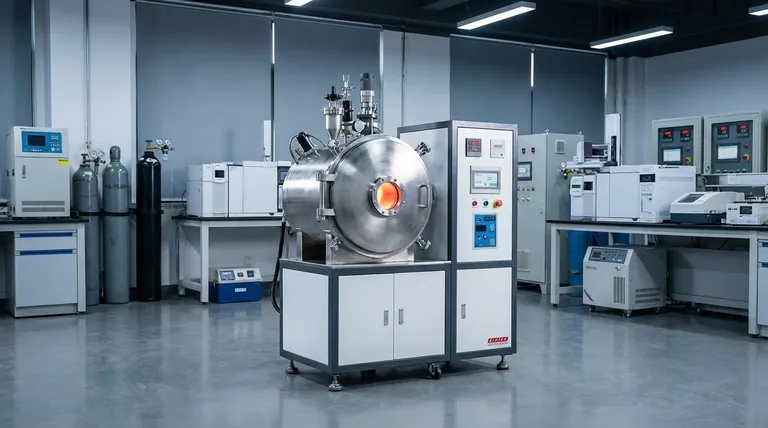

The Core Principles Driving the Advantages
Induction melting works by using a powerful alternating magnetic field to induce an electric current directly within the metal charge. This internal current flow is what generates the heat, leading to a fundamentally different and more advantageous melting process.
Unmatched Speed and Energy Efficiency
The heating process, known as Joule heating, occurs inside the metal itself. This is fundamentally more efficient than external heating methods (like a flame) where heat must first transfer through the crucible wall to the charge.
This direct energy transfer results in significantly faster melting times from a cold start. It also means less energy is wasted heating the surrounding environment, making induction furnaces highly energy-efficient.
Inherent Stirring for Homogeneity
The same magnetic fields that generate heat also create powerful stirring forces within the molten metal bath. This phenomenon, known as inductive stirring, is an automatic and invaluable benefit.
This continuous mixing action ensures that alloying elements are distributed evenly, preventing segregation and resulting in a completely homogeneous final product. It also helps move superheated metal from the edges toward the cooler center, further accelerating the melt.
A Cleaner, More Controlled Process
Because heat is generated without any combustion, there are no byproducts like smoke, ash, or flue gases to contaminate the melt. This results in a much cleaner melting environment and a purer final metal.
This cleanliness, combined with precise power control, allows for exceptional temperature accuracy. This level of control is critical for producing sensitive alloys and meeting tight metallurgical specifications.
Expanding Capabilities Across Applications
The versatility of induction melting makes it the preferred choice for a wide range of industrial and research applications, from large-scale foundries to high-tech laboratories.
Broad Material and Batch Flexibility
Induction furnaces can efficiently melt nearly all metals, including steel, iron, copper, aluminum, and precious metals. The technology is also highly effective for refractory materials that have extremely high melting points.
Furthermore, the systems can be designed to handle a vast range of charge sizes, from a few grams in a research lab to many tons in a large foundry, without a significant loss in efficiency.
Advanced Processing with Vacuum Melting (VIM)
For highly reactive metals like titanium or superalloys used in aerospace, even minimal contact with air can be detrimental. Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) addresses this by placing the entire induction coil and crucible assembly inside a vacuum chamber.
Since the magnetic field can easily penetrate the non-conductive walls of the chamber, the metal can be melted under a complete vacuum or a controlled inert atmosphere. This prevents oxidation and removes dissolved gases, enabling the production of the highest purity materials possible.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While induction melting offers clear advantages, it's important to understand it in the context of other methods and its own implementation requirements.
Against Traditional Furnace Methods
Compared to flame heating, induction is vastly superior in terms of efficiency, control, and cleanliness. Flame furnaces introduce impurities from combustion and suffer from poor heat transfer.
Compared to resistance heating, induction is much faster and offers the unique benefit of inductive stirring. While both are electric methods, induction's direct heating mechanism gives it a significant performance edge.
Implementation Considerations
The primary consideration for adopting induction technology is the initial capital investment in the power supply, furnace, and cooling systems. However, this is often offset by long-term savings from higher energy efficiency, reduced material loss, and improved product quality.
Modern induction power supplies are also designed to produce very low harmonic pollution, ensuring they integrate cleanly into a facility's electrical grid, but this is a critical specification to verify during procurement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting technology depends entirely on your operational priorities and the materials you are processing.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production (foundries, recycling): The key advantages are speed and energy efficiency, which translate directly to a lower cost per ton and higher productivity.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys or reactive metals (aerospace, medical): The cleanliness of the process and the capabilities of Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) are the most critical factors for achieving superior material quality.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The precise temperature control, ability to handle small batches, and inherent stirring make it ideal for developing new alloys and studying material properties.
Ultimately, adopting induction melting is a strategic move toward greater process control, material quality, and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Speed and Energy Efficiency | Faster melting times and reduced energy waste through direct internal heating. |
| Inherent Stirring | Automatic mixing ensures homogeneous alloys and prevents segregation. |
| Cleanliness and Control | No combustion byproducts, enabling purer metals and precise temperature regulation. |
| Versatility | Suitable for a wide range of metals, batch sizes, and applications, including vacuum melting for reactive materials. |
Ready to elevate your metal melting process with advanced induction solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories and industries with high-performance furnace systems. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency, quality, and control—let's achieve your goals together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















