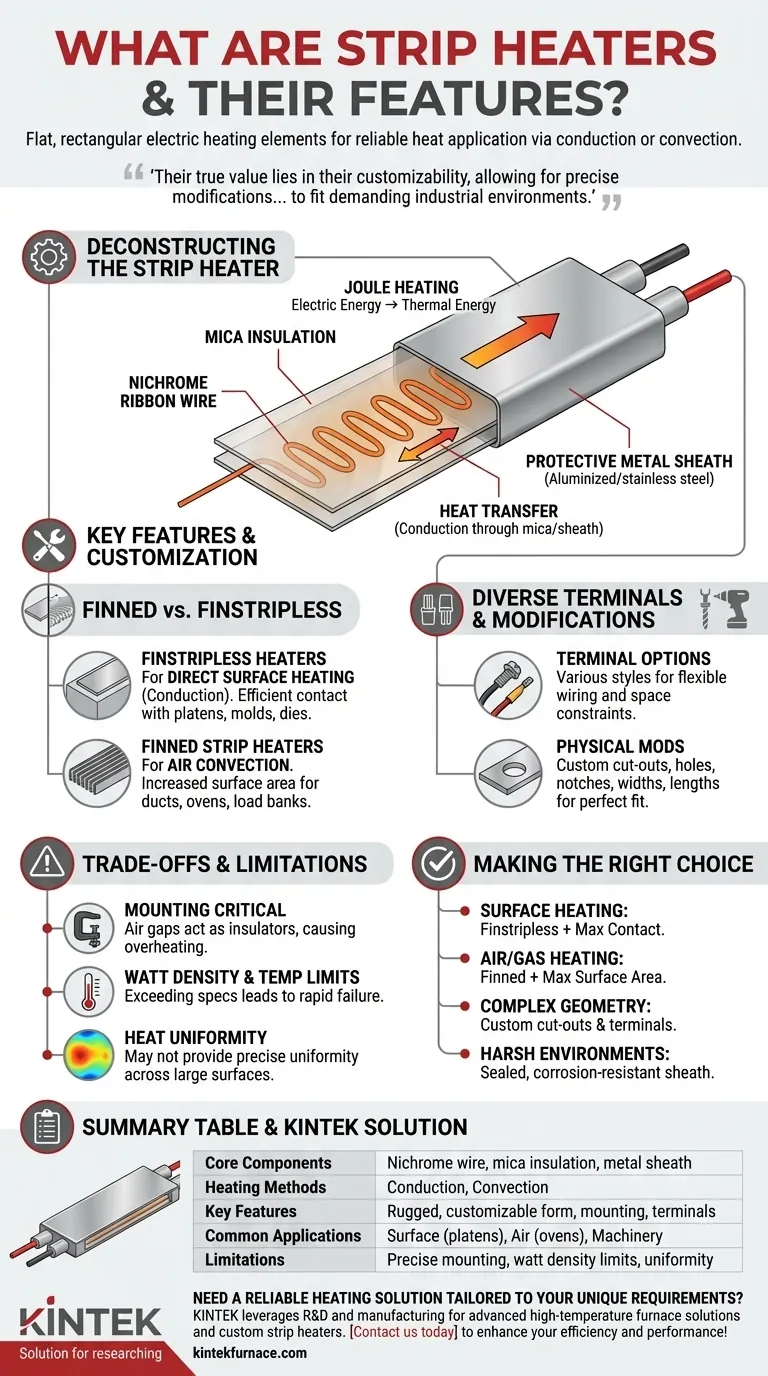
At their core, strip heaters are flat, rectangular electric heating elements designed for reliable and versatile heat application. They consist of a resistance wire element, typically wrapped in or sandwiched between layers of mica insulation, and enclosed within a protective metal sheath. This simple construction allows them to provide localized heat through either direct contact (conduction) or by heating the surrounding air (convection).
While their flat design seems basic, strip heaters offer a uniquely rugged and adaptable solution for surface and air heating. Their true value lies in their customizability, allowing for precise modifications in form, mounting, and electrical termination to fit demanding industrial environments.

Deconstructing the Strip Heater: Core Components
The effectiveness of a strip heater comes from the synergy of its three main components. Understanding each part is key to understanding its function.
The Heating Element and Insulation
The heart of the heater is a nickel-chromium (nichrome) ribbon wire. This alloy is chosen for its high electrical resistance and ability to withstand repeated heating cycles without degrading.
This wire is carefully wound and electrically insulated with mica sheets. Mica is a critical material because it is an excellent electrical insulator but a good thermal conductor, allowing heat to pass through efficiently while preventing short circuits.
The Protective Sheath
An outer metal sheath, typically made of aluminized or stainless steel, encases the mica and wire assembly. This sheath serves two purposes: it protects the internal components from moisture, contamination, and physical damage, and it provides a durable, flat surface to transfer heat to its target.
The Principle of Operation
Strip heaters work on the simple principle of Joule heating, where electrical energy is converted into thermal energy as current passes through the resistance wire. This heat is then conducted through the mica and sheath to the outside environment. They can be clamped directly to a surface for conductive heating or outfitted with fins to transfer heat to the air via convection.
Key Features and Customization Options
The true power of strip heaters lies in their adaptability. They are not a one-size-fits-all component but a platform that can be tailored to a specific task.
Finned vs. Finstripless
The most significant variation is the presence of fins.
- Finstripless heaters are designed for surface heating. They rely on direct, tight contact to conduct heat efficiently into platens, molds, dies, or tanks.
- Finned strip heaters have fins attached to the sheath to dramatically increase the surface area. This makes them ideal for convection air heating in ducts, ovens, and load bank resistors.
Diverse Terminal Configurations
Strip heaters can be manufactured with various electrical terminal styles to accommodate different wiring needs and space constraints. Options range from simple screw terminals to insulated lead wires, allowing for flexible and safe installation in tight or complex machinery.
Physical Modifications for a Perfect Fit
To integrate into complex assemblies, strip heaters can be manufactured with custom cut-outs, holes, or notches. This allows them to fit around bolts, sensors, or other obstructions without compromising the heating function. They can also be made in different widths and lengths to match a specific application footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly versatile, strip heaters have practical limitations that are crucial to consider for successful implementation.
Mounting is Critical for Performance
For surface heating applications, performance is entirely dependent on the quality of the mounting. Any air gaps between the heater and the target surface will act as an insulator, trapping heat, reducing efficiency, and potentially causing the heater to overheat and fail prematurely.
Watt Density and Temperature Limits
Every strip heater has a maximum watt density (watts per square inch) and temperature rating. Attempting to run a heater beyond these specifications, especially without a proper heat sink, will lead to rapid failure. The application must be able to absorb the heat as fast as the heater produces it.
Heat Uniformity
While excellent for many applications, a standard strip heater may not provide the precise temperature uniformity across a large surface that an etched foil or silicone rubber heater can. For applications requiring extremely tight thermal control, another heater type may be more suitable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct strip heater configuration is essential for performance, efficiency, and longevity.
- If your primary focus is direct surface heating: Choose a finstripless heater and prioritize a mounting system that ensures maximum surface contact for efficient conduction.
- If your primary focus is heating air or gases: Select a finned strip heater to maximize the surface area for effective convection.
- If your application has complex geometry: Work with a manufacturer to specify custom cut-outs, holes, and a terminal configuration that fits your physical constraints.
- If you operate in a harsh or moist environment: Ensure you select a model with a sealed, corrosion-resistant sheath (like stainless steel) and appropriate moisture-resistant terminals.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of a strip heater is defined by how well its configuration is matched to the specific heating task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Components | Resistance wire (nichrome), mica insulation, metal sheath (e.g., aluminized or stainless steel) |
| Heating Methods | Conduction (direct surface contact), Convection (air heating with fins) |
| Key Features | Rugged design, high customizability in form, mounting, and terminals |
| Common Applications | Surface heating for platens/molds, air heating in ovens/ducts, industrial machinery |
| Limitations | Requires precise mounting, has watt density and temperature limits, may lack uniform heat distribution |
Need a reliable heating solution tailored to your unique requirements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom strip heaters. Our product line—featuring Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed to meet the diverse needs of laboratories and industrial settings. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental and operational demands. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance














