In short, rotary kilns are the industrial workhorses for high-temperature material processing. Their most common and large-scale application is in the manufacturing of cement, but they are essential across a wide range of industries, including metallurgy for metal extraction, chemical processing, and increasingly, in environmental sectors for waste management and resource recovery.
The true value of a rotary kiln lies not in a single application, but in its ability to enable a few fundamental thermal processes—like calcination, pyrolysis, and reduction. By mastering these processes, the kiln transforms low-value bulk materials into the high-value foundational products of our modern economy.
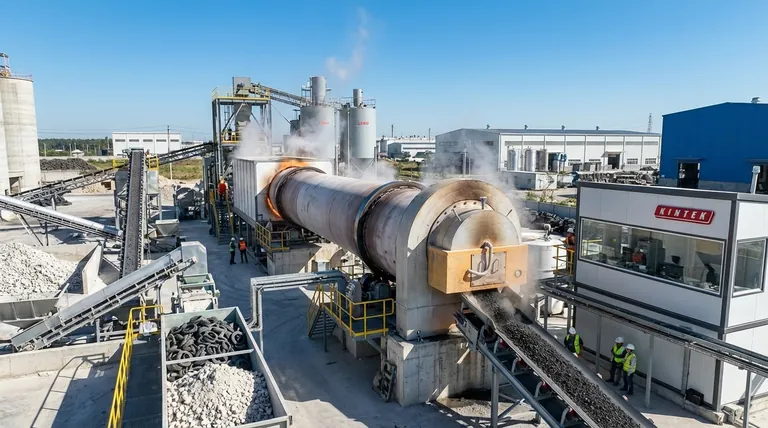

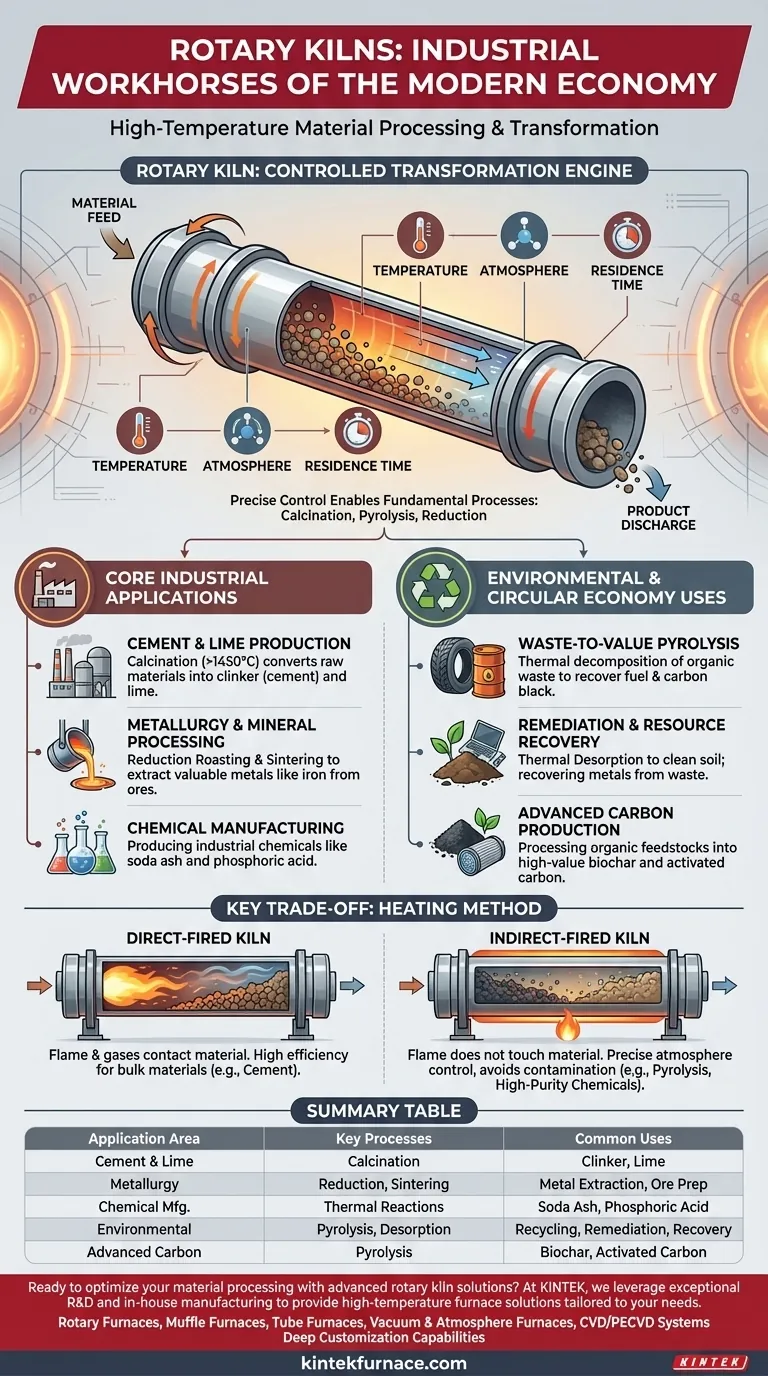
The Principle: A Controlled Transformation Engine
A rotary kiln is, at its core, a simple machine: a long, rotating, and slightly inclined cylinder that is heated to extreme temperatures. Material fed into the higher end slowly tumbles toward the lower end, ensuring every particle is uniformly processed.
Why This Design Is So Versatile
The kiln's power comes from its precise control over the three critical variables of thermal processing: temperature, atmosphere, and residence time.
By adjusting the rotation speed, the incline, the fuel source, and the gas flow, operators can create the perfect environment to induce specific chemical reactions or physical changes in a material.
Core Industrial Applications
For decades, rotary kilns have been the backbone of heavy industry, enabling massive-scale production of essential commodities.
Cement and Lime Production
This is the most well-known application. Raw materials like limestone are heated to over 1450°C in a process called calcination, which chemically converts them into "clinker," the primary component of cement. The same principle is used to produce lime.
Metallurgy and Mineral Processing
In the metals industry, kilns are used for processes like reduction roasting and sintering. They heat mineral ores in a controlled atmosphere to either remove impurities or prepare the ore for smelting, making it easier to extract valuable metals like iron.
Chemical Manufacturing
Rotary kilns are used to produce a variety of industrial chemicals. For example, they can be used to produce soda ash or to create phosphoric acid from low-grade phosphate rock—a process that consumes less energy and avoids the need for sulfuric acid.
The Rise of Environmental and Circular Economy Uses
More recently, the versatility of the rotary kiln has been applied to critical environmental challenges, turning waste streams into valuable resources.
Waste-to-Value Pyrolysis
Using an oxygen-starved environment, a kiln can perform pyrolysis. This process thermally decomposes organic materials without burning them. It's used to recover carbon black and fuel from scrap tires or to convert mixed plastics into synthetic crude oil.
Remediation and Resource Recovery
Kilns use thermal desorption to heat contaminated soils, vaporizing and removing pollutants. They are also used to recover valuable metals and components from industrial waste and electronic scrap.
Advanced Carbon Production
Organic feedstocks like wood or agricultural waste can be processed in a kiln to produce high-value carbon products. This includes biochar for agriculture and activated carbon for filtration and purification applications.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Heating Method
The specific application dictates a critical design choice: how the kiln is heated. This decision balances efficiency against material purity.
Direct-Fired Kilns
In these kilns, a flame and hot combustion gases pass directly over the material. This is highly efficient and ideal for robust, bulk materials where direct contact with the flame is not an issue, such as in cement and lime production.
Indirect-Fired Kilns
Here, the cylinder is heated from the outside, and the flame never touches the material. This prevents contamination and allows for precise atmospheric control. It is essential for processes like pyrolysis or when producing high-purity chemicals or catalysts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal use of a rotary kiln depends entirely on the transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is large-scale mineral calcination: Direct-fired kilns are the standard, providing the brute-force thermal efficiency needed for cement and lime.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-value or pyrolysis: An indirect-fired kiln is required to maintain an oxygen-free atmosphere and prevent the combustion of valuable output materials.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity or sensitive materials: Indirect heating is non-negotiable to avoid contamination from combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation: The choice depends on the contaminant, but thermal desorption in either direct or indirect kilns is a proven solution.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln’s enduring relevance is rooted in its fundamental ability to apply controlled heat, transforming raw materials into foundational products.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Cement & Lime Production | Calcination | Manufacturing clinker for cement, producing lime |
| Metallurgy & Mineral Processing | Reduction Roasting, Sintering | Extracting metals like iron, preparing ores |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Various Thermal Reactions | Producing soda ash, phosphoric acid, and other chemicals |
| Environmental & Waste Management | Pyrolysis, Thermal Desorption | Recycling tires, plastics, remediating soils, recovering metals |
| Advanced Carbon Production | Pyrolysis | Creating biochar, activated carbon for filtration |
Ready to optimize your material processing with advanced rotary kiln solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in cement production, metallurgy, chemical processing, or environmental management, we can help you achieve superior efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results



















