The primary advantages of Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) are its ability to deposit high-quality films at low temperatures and its significantly faster deposition rates compared to conventional methods. This unique combination allows for the creation of durable, uniform coatings on a wide variety of materials, including those that cannot withstand high heat.
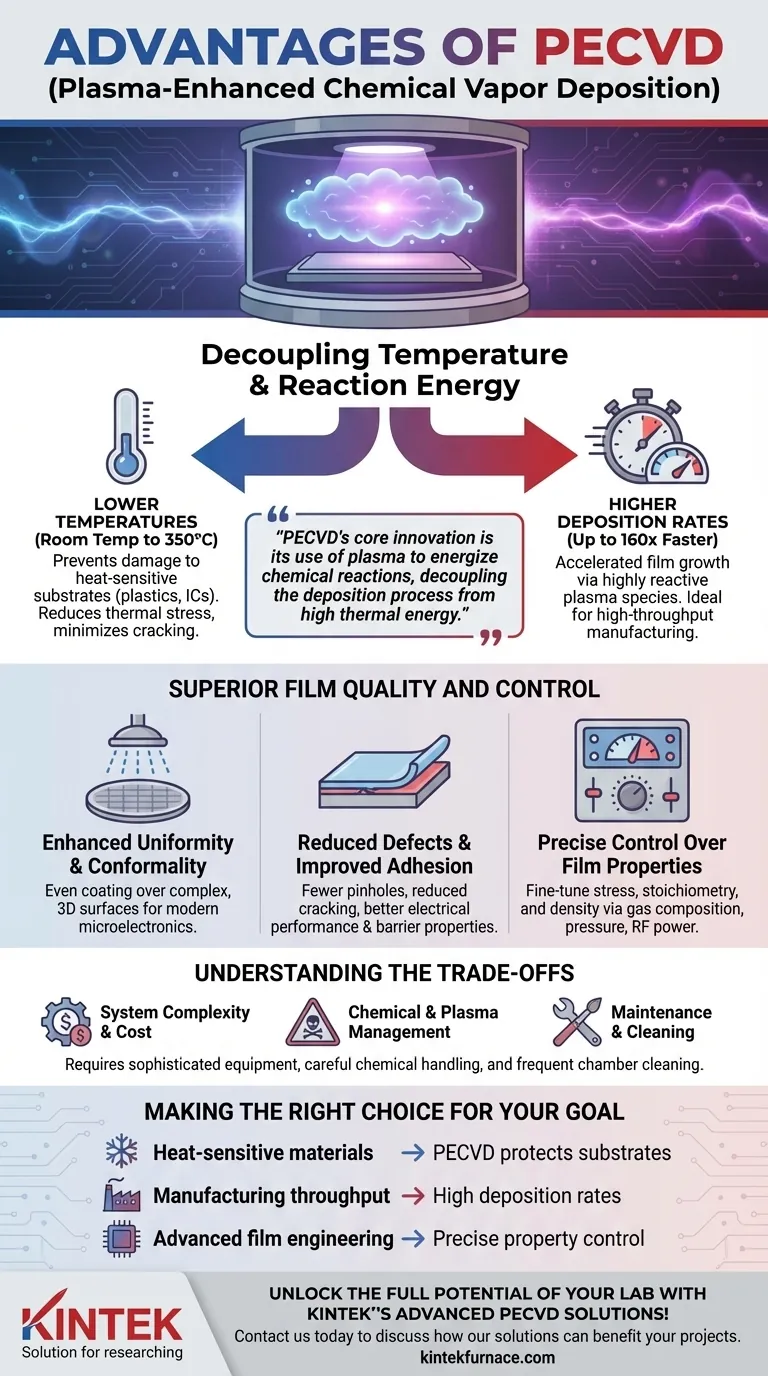
PECVD's core innovation is its use of plasma to energize chemical reactions, decoupling the deposition process from high thermal energy. This fundamental shift allows you to create high-quality, dense, and uniform films on heat-sensitive substrates at speeds that would be impossible with traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).

The Core Advantage: Decoupling Temperature and Reaction Energy
The defining benefit of PECVD stems from its ability to generate the required reaction energy from plasma rather than solely from heat. This has two profound consequences for the manufacturing process.
Operating at Lower Temperatures
Conventional CVD often requires very high temperatures (600-800°C or higher) to drive the chemical reactions needed to form a film. PECVD operates at much lower temperatures, typically between room temperature and 350°C.
This low-temperature operation is critical because it prevents damage to thermally sensitive substrates like plastics, polymers, and complex integrated circuits. It also dramatically reduces thermal stress between the deposited film and the substrate, which minimizes the risk of cracking and improves adhesion.
Achieving High Deposition Rates
The plasma creates a highly reactive environment filled with ions, radicals, and other excited species. These species accelerate the necessary chemical reactions, leading to significantly faster film growth.
For example, the deposition rate for silicon nitride can be up to 160 times faster with PECVD than with low-pressure CVD. This drastic increase in speed is a major advantage for high-throughput manufacturing environments.
Superior Film Quality and Control
Beyond speed and temperature, PECVD provides a higher degree of control over the final film, resulting in superior quality and performance.
Enhanced Uniformity and Conformality
PECVD is known for depositing films with excellent uniformity across the entire substrate. The gas is often introduced through a "showerhead" inlet, ensuring even distribution of precursor chemicals within the plasma.
This process also yields excellent conformality, meaning it can evenly coat complex, non-flat surfaces and three-dimensional geometries. This ability to cover intricate topographies is essential for modern microelectronics and MEMS devices.
Reduced Defects and Improved Adhesion
The lower process temperature and controlled reaction environment lead to films with fewer defects. The resulting layers have fewer pinholes and a reduced tendency to crack, leading to better electrical performance and barrier properties.
This translates to good adhesion of the film to the substrate, creating a more robust and reliable final product. The films often exhibit high solvent and corrosion resistance due to their dense, well-bonded structure.
Precise Control Over Film Properties
PECVD allows for fine-tuning of the final film's characteristics. By adjusting process parameters such as gas composition, pressure, and the frequency of the RF power source, you can precisely control properties like film stress, stoichiometry, and density.
For instance, mixing high and low-frequency plasma sources is a common technique used to deliberately engineer the stress in the deposited film, which is critical for optical and electronic applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
System Complexity and Cost
PECVD systems are sophisticated instruments. They involve vacuum chambers, complex gas handling systems, high-frequency RF power generators, and intricate control software. This complexity generally leads to a higher initial equipment cost compared to simpler methods like thermal evaporation or sputtering.
Chemical and Plasma Management
The process uses precursor chemicals that can be hazardous and requires careful handling and exhaust management. While the plasma is the source of PECVD's advantages, it can also cause plasma-induced damage to extremely sensitive device layers if the process is not meticulously controlled.
Maintenance and Cleaning
While some sources note that chamber cleaning is relatively easy, it is a necessary and frequent part of the operational cycle. Byproducts from the chemical reactions deposit on the chamber walls and must be periodically removed to ensure process repeatability and prevent contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PECVD depends entirely on the specific requirements of your substrate, your desired film properties, and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is working with heat-sensitive materials: PECVD is the clear choice, as its low operating temperature protects substrates like polymers or fully fabricated semiconductor devices.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing throughput: The high deposition rates offered by PECVD provide a significant advantage for high-volume production lines.
- If your primary focus is advanced film engineering: The precise control over film stress, composition, and conformality makes PECVD essential for creating high-performance electronic and optical components.
Ultimately, PECVD empowers engineers and scientists to create advanced thin films where traditional methods would fail due to thermal constraints or insufficient quality control.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Operation | Prevents damage to heat-sensitive substrates like plastics and ICs |
| High Deposition Rates | Up to 160x faster than CVD methods for increased throughput |
| Superior Film Quality | Excellent uniformity, conformality, and reduced defects |
| Precise Control | Tunable film stress, stoichiometry, and density for specific applications |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced PECVD solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental goals, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods



















