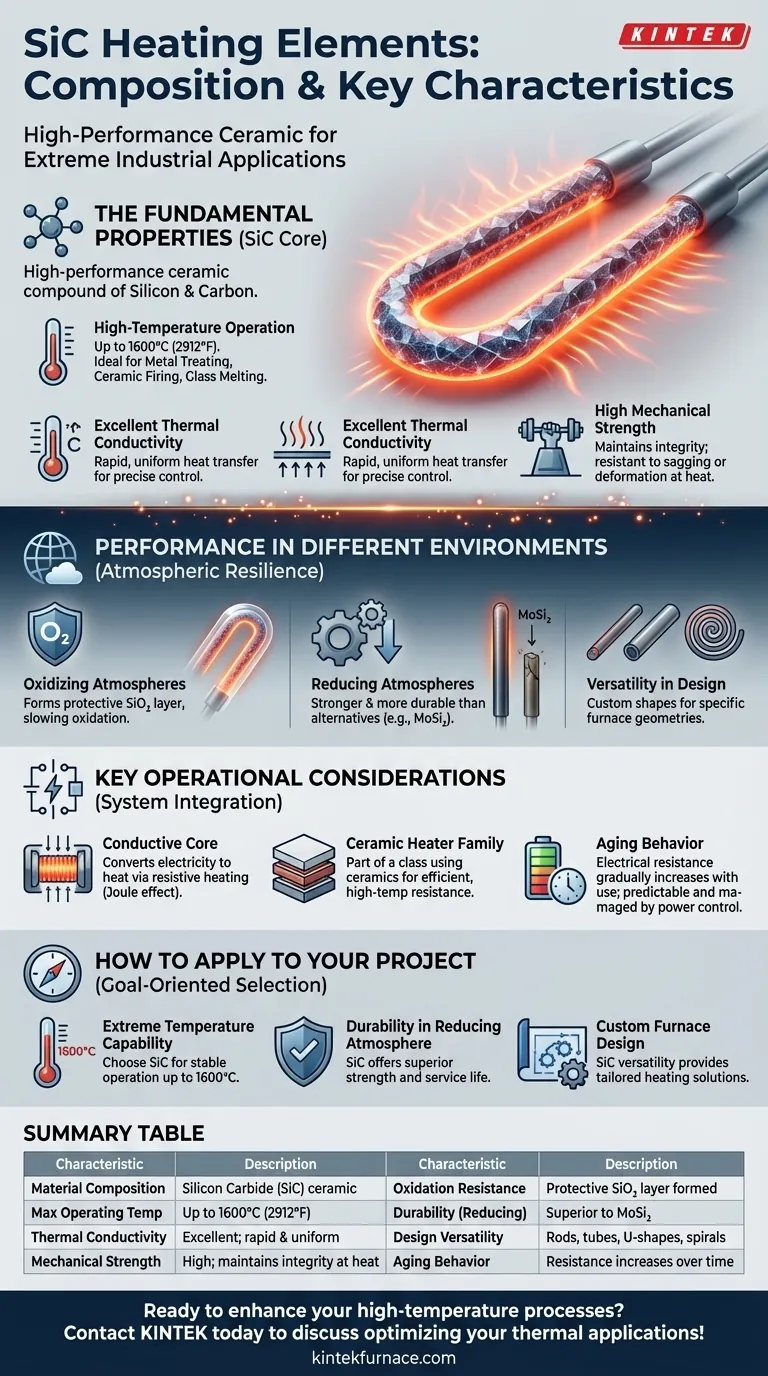
At their core, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are high-performance components made from a man-made ceramic called silicon carbide. They are engineered specifically for reliability in high-temperature industrial applications, valued for their exceptional durability, thermal efficiency, and resistance to harsh operating conditions.
Silicon Carbide's true value lies not just in its ability to get hot, but in its capacity to perform reliably and efficiently under extreme thermal and atmospheric stress where lesser materials would fail.
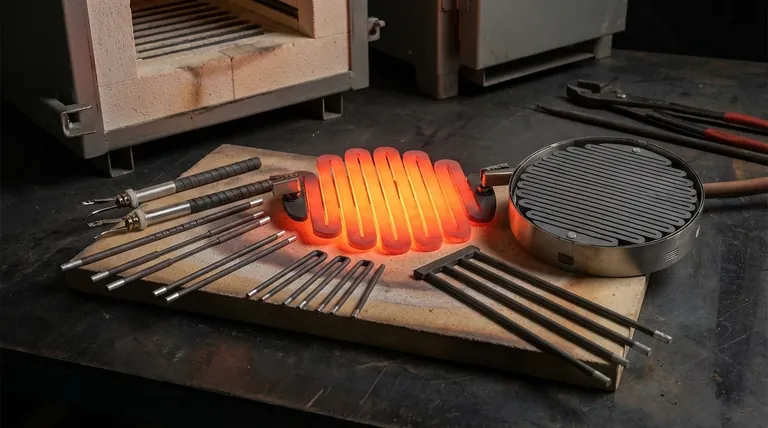

The Fundamental Properties of Silicon Carbide (SiC)
To understand why SiC elements are chosen for demanding applications, we must look at the inherent properties of the material itself.
### Material Composition
SiC heating elements are composed of silicon carbide, a compound of silicon and carbon. This ceramic material possesses an exceptional combination of thermal and mechanical stability.
### High-Temperature Operation
The standout characteristic of SiC is its ability to operate at very high temperatures, often up to 1600°C (2912°F). This makes it suitable for processes like metal heat treating, ceramic firing, and glass melting.
### Excellent Thermal Conductivity
SiC transfers heat very efficiently. This property ensures that energy is converted to useful heat rapidly and uniformly, which is critical for precise temperature control in industrial furnaces and kilns.
### High Mechanical Strength
Even at extreme temperatures, SiC elements maintain high physical strength. This structural integrity ensures a long service life and resistance to sagging or deformation under their own weight.
Performance in Different Operating Environments
An element's interaction with its surrounding atmosphere is just as important as its temperature rating. SiC exhibits distinct advantages in this area.
### Natural Resistance to Oxidation
In the presence of oxygen, a SiC element forms a thin, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) on its surface. This layer acts as a barrier, slowing further oxidation and contributing to the element's longevity in standard oxidizing atmospheres.
### Superiority in Reducing Atmospheres
Compared to other common high-temperature elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂), SiC elements are noted to be stronger and more durable in reducing atmospheres (environments with low oxygen content).
### Versatility in Design
SiC can be manufactured in a wide variety of shapes and sizes, including rods, tubes, U-shapes, and spirals. This allows engineers to design heating systems that are highly customized for specific furnace geometries and process requirements.
Key Operational Considerations
While robust, SiC elements are part of a larger system. Understanding their role and limitations is key to successful implementation.
### SiC as the Conductive Core
A heating element is more than just the hot material. It is a system comprising an insulating framework, electrical connectors, and the conductive core. In this system, the SiC component serves as the electrically conductive core that converts electricity into heat through resistive heating (Joule effect).
### The Ceramic Heater Family
SiC is a type of ceramic heating element. This class of heaters is defined by its use of ceramic materials to achieve efficient heat transfer and high-temperature resistance, making them indispensable in both industrial processes and consumer appliances.
### Aging and Resistance
A critical characteristic of SiC elements is that their electrical resistance gradually increases with use over time, a phenomenon known as aging. This is a predictable behavior that must be managed by the power control system to ensure consistent temperature output throughout the element's lifespan.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of heating element must be directly tied to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature capability: SiC is a premier choice for applications requiring stable operation up to 1600°C.
- If your primary focus is durability in a reducing atmosphere: SiC offers superior mechanical strength and a longer service life compared to alternatives like MoSi₂.
- If your primary focus is custom furnace design: The availability of SiC in diverse shapes and sizes provides the flexibility needed for tailored heating solutions.
Ultimately, selecting Silicon Carbide is choosing a reliable foundation for your most demanding thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Made of silicon carbide, a ceramic compound of silicon and carbon |
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1600°C (2912°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent, ensuring rapid and uniform heat transfer |
| Mechanical Strength | High, maintaining integrity at extreme temperatures |
| Oxidation Resistance | Forms protective SiO₂ layer in oxidizing atmospheres |
| Durability in Reducing Atmospheres | Superior to alternatives like MoSi₂ |
| Design Versatility | Available in rods, tubes, U-shapes, and spirals for customization |
| Aging Behavior | Electrical resistance increases predictably over time |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable SiC heating solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your thermal applications for superior performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















