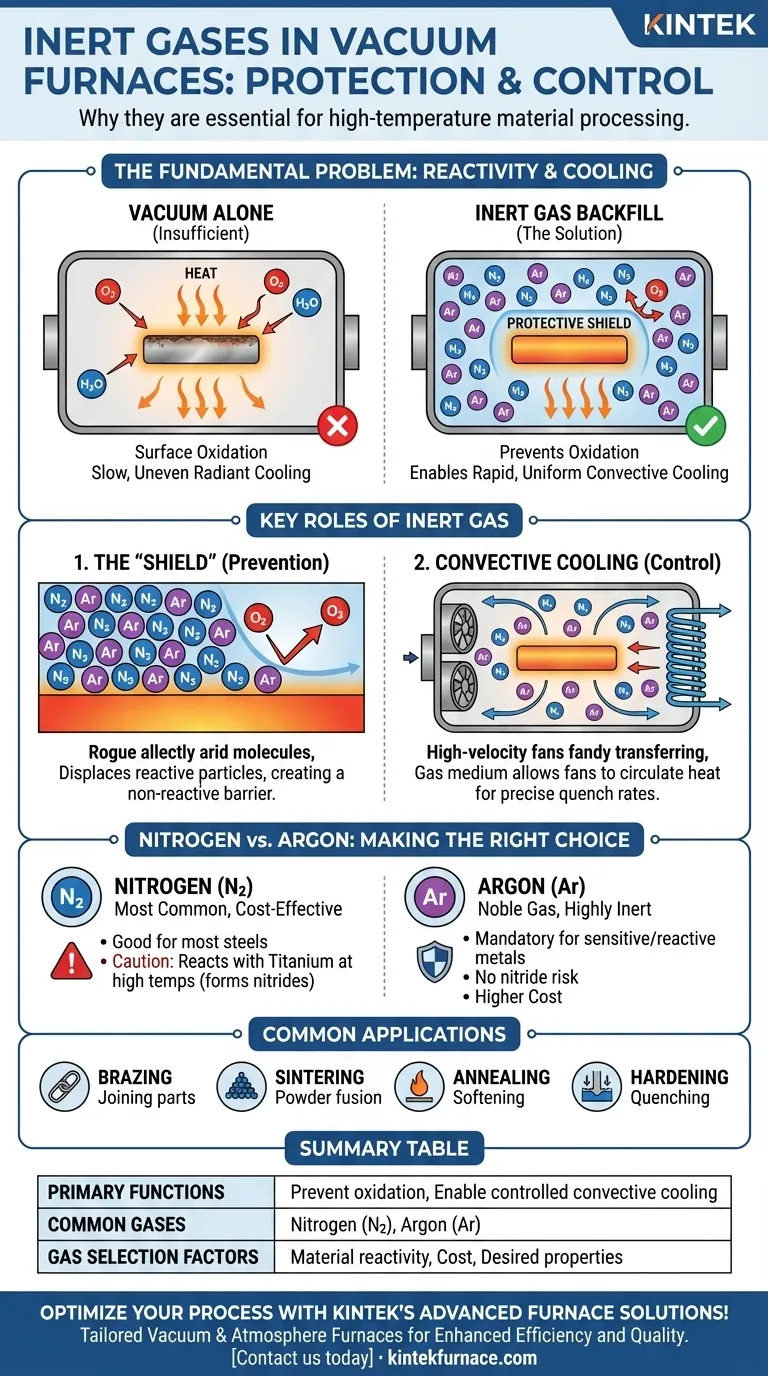
In essence, inert gases are protective blankets for materials at a molecular level. They are elements, most commonly nitrogen and argon, that are chemically non-reactive and will not combust or react with other materials. In vacuum furnaces, they are used for two primary reasons: to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation at high temperatures and to provide a medium for controlling the rate of cooling after the heating cycle is complete.
While a vacuum is excellent at removing reactive air molecules, it is also an excellent insulator. Inert gases solve this by creating a non-reactive atmosphere that not only shields the material but also enables rapid and uniform cooling through convection, a process impossible in a pure vacuum.

The Fundamental Problem: Reactivity at High Temperatures
The core challenge in any high-temperature thermal process, such as brazing or annealing, is that heat acts as a catalyst. It dramatically accelerates chemical reactions between a material and its surrounding environment.
Why a Vacuum Isn't Always Enough
A vacuum furnace works by pumping out the air, which removes the vast majority of reactive particles like oxygen. This is the first and most critical step in creating a clean processing environment.
However, even a "high vacuum" is not a perfect void. Trace amounts of oxygen and water vapor always remain. For many sensitive materials, these few remaining particles are enough to cause detrimental surface oxidation when heated to extreme temperatures.
The Role of Inert Gas as a "Shield"
Introducing an inert gas after achieving a vacuum displaces these remaining reactive particles. By backfilling the chamber with a gas like argon or nitrogen, you create a slight positive pressure of a completely non-reactive substance.
This inert atmosphere acts as a physical barrier, effectively shielding the hot material from any stray oxygen molecules and preventing degradation. It ensures the material's surface chemistry remains pristine throughout the process.
Beyond Protection: Controlling the Cooling Process
A material's final properties are determined not only by how it is heated but also by how it is cooled. This is where inert gases play their second, equally critical, role.
The Insulating Effect of a Vacuum
Heat transfer occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. In the near-perfect vacuum of a furnace chamber, conduction and convection are almost entirely eliminated.
Heat can only escape the workpiece through radiation, which can be slow and uneven. This lack of control over the cooling rate (or "quench") is often unacceptable for achieving specific metallurgical properties like hardness and grain structure.
How Inert Gas Enables Convective Cooling
By introducing an inert gas, you provide a medium for convection. High-velocity fans within the furnace can now circulate the gas, efficiently transferring heat away from the workpiece.
This forced convection allows for rapid, uniform cooling at a precisely controlled rate. This "gas quenching" is fundamental to modern heat treatment and is only possible because of the inert gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of inert gas is not arbitrary; it involves a calculated decision based on the material being processed and the desired outcome.
Nitrogen vs. Argon: Reactivity and Cost
Nitrogen (N2) is the most common inert gas used in heat treatment. It is highly effective for most applications involving steels and is significantly less expensive than argon.
However, nitrogen is not perfectly inert under all conditions. At very high temperatures, it can react with certain reactive metals like titanium and some stainless steels to form nitrides, altering the material's properties.
Argon (Ar) is a noble gas and is chemically inert under all known furnace conditions. It is the mandatory choice when processing highly sensitive or reactive materials, where the risk of nitride formation is unacceptable. Its primary downside is its higher cost.
Common Furnace Applications
The controlled atmosphere provided by inert gases is essential for numerous industrial processes:
- Brazing: Joining components with a filler metal without oxidizing the base materials.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered metals into a solid mass without impurities.
- Annealing: Softening a metal to improve its ductility by relieving internal stresses in a clean environment.
- Hardening: Achieving specific hardness through controlled heating and rapid gas quenching.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace atmosphere—be it a high vacuum or a specific inert gas backfill—is crucial for meeting your material specifications.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective processing of common steels: Nitrogen backfilling is the standard for preventing oxidation and enabling controlled gas quenching.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium or specific superalloys: Argon is essential to prevent the formation of unwanted nitrides, justifying its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity with very slow, gentle cooling: A high vacuum without a gas backfill may be sufficient, relying solely on radiant heat transfer.
By understanding the distinct roles of vacuum and inert gas, you gain precise control over your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Functions | Prevent oxidation; Enable controlled cooling via convection |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective), Argon (highly inert) |
| Key Applications | Brazing, Sintering, Annealing, Hardening |
| Gas Selection Factors | Material reactivity, Cost, Desired metallurgical properties |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering enhanced efficiency and material quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















