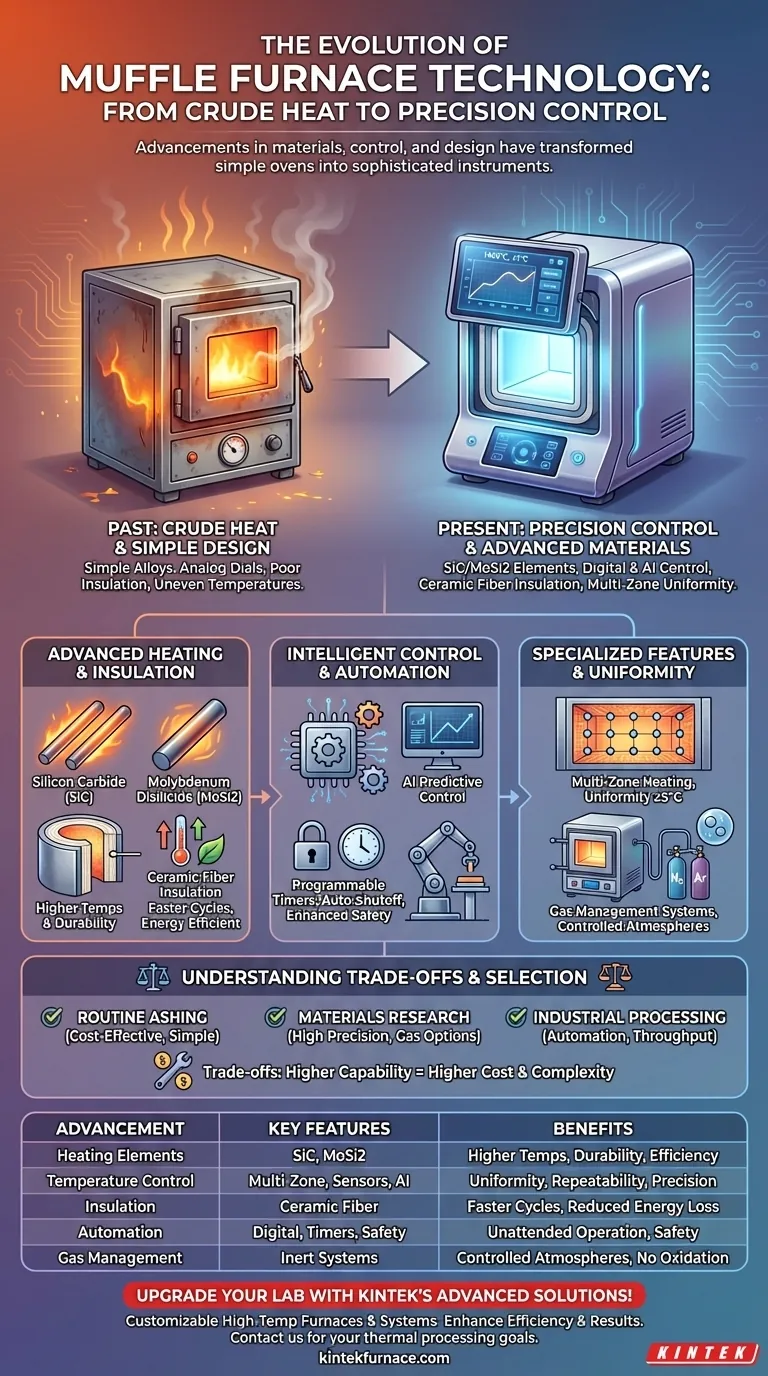
In recent years, muffle furnace technology has evolved far beyond the simple high-temperature ovens of the past. Key advancements now center on superior heating element materials, precise digital control and automation, and a significant focus on energy efficiency and customizable design. These improvements have transformed them into sophisticated instruments essential for modern laboratory and industrial applications.
The core advancement in muffle furnaces is the shift from providing crude, high heat to delivering precisely controlled, uniform, and repeatable thermal processing. This is achieved through a combination of advanced materials, intelligent control systems, and application-specific designs.

The Core Evolution: From Crude Heat to Precision Control
Modern muffle furnaces are defined by their ability to achieve and maintain exact thermal conditions. This precision is not the result of a single change, but an evolution across several key components.
Advanced Heating Elements: The Engine of Efficiency
The heart of any furnace is its heating element. Older designs often used simpler metallic alloys, but modern furnaces leverage superior materials.
Silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are now common in advanced models. Their high melting points and excellent thermal conductivity allow for greater durability, higher operating temperatures, and better energy efficiency.
Unprecedented Temperature Uniformity
For processes like materials research or sample ashing, having the entire chamber at the exact same temperature is critical.
Early furnaces often suffered from hot and cold spots. Today’s models incorporate multi-zone heating and advanced sensor placement (like K-type or J-type thermocouples) to ensure temperature uniformity with accuracies often within ±5°C.
Superior Insulation and Chamber Design
Efficiency and speed are directly linked to insulation. Modern furnaces use advanced, lightweight ceramic fiber insulation.
This improvement leads to faster heat-up and cool-down times, which increases throughput. It also significantly reduces energy consumption by preventing heat loss, making the furnace cooler to the touch and safer to operate.
Intelligence and Automation: The Modern Brain
The most visible advancements are in the control systems that govern the furnace's operation. These systems provide a level of precision and safety that was previously unattainable.
Advanced Digital Control
Simple analog dials have been replaced by sophisticated digital controllers, often with 7-segment LED or full graphical displays.
These controllers allow operators to program complex heating profiles with multiple ramps and soaks. Some forward-looking designs are even integrating AI for predictive control, which anticipates thermal changes to prevent temperature overshoot and maintain tighter stability.
Automation for Repeatability and Safety
Automation is key to reducing human error and improving lab efficiency. Modern furnaces feature programmable timers (often up to 999 hours) that allow for unattended operation.
Crucially, this automation is tied to enhanced safety features. Automatic shut-offs, door interlocks, and over-temperature protection are now standard, protecting both the operator and the samples.
Sophisticated Gas Management Systems
Many modern applications require processing materials in a specific atmosphere to prevent oxidation or encourage a certain reaction.
Advanced furnaces can be equipped with gas management systems. These allow for the introduction of inert gases like nitrogen or argon, creating a controlled environment isolated from contaminants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While modern advancements offer significant benefits, it's crucial to understand the associated trade-offs to make an informed decision.
Cost vs. Capability
High-performance features come at a price. Furnaces with molybdenum disilicide elements, multi-zone control, and advanced gas management systems carry a higher initial investment than basic models.
Complexity and Maintenance
A furnace with a highly programmable controller and multiple subsystems is inherently more complex. This may require more operator training and specialized maintenance for components like advanced sensors or control boards.
Application-Specific Limitations
No single furnace is perfect for every task. A furnace designed for high-temperature materials science (e.g., 1400°C+) may be inefficient or oversized for simple, lower-temperature ashing procedures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right muffle furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is routine ashing or basic heat-treating: A standard, reliable furnace with a simple digital controller and a temperature range up to 1200°C is often the most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research: Prioritize a furnace with exceptional temperature uniformity, a high-precision controller, and options for controlled gas atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial processing: Look for robust automation, rapid heat-up/cool-down cycles, and an energy-efficient design to minimize long-term operating costs.
By understanding these technological advancements, you can select an instrument that serves not just as a source of heat, but as a precise tool for achieving your scientific or industrial objectives.
Summary Table:
| Advancement | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Silicon carbide (SiC), molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) | Higher temperatures, durability, energy efficiency |
| Temperature Control | Multi-zone heating, precise sensors | Uniformity within ±5°C, repeatable results |
| Insulation | Lightweight ceramic fiber | Faster heat-up/cool-down, reduced energy loss |
| Automation | Programmable controllers, timers, safety features | Unattended operation, error reduction, enhanced safety |
| Gas Management | Inert gas systems | Controlled atmospheres, prevention of oxidation |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced muffle furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your thermal processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















