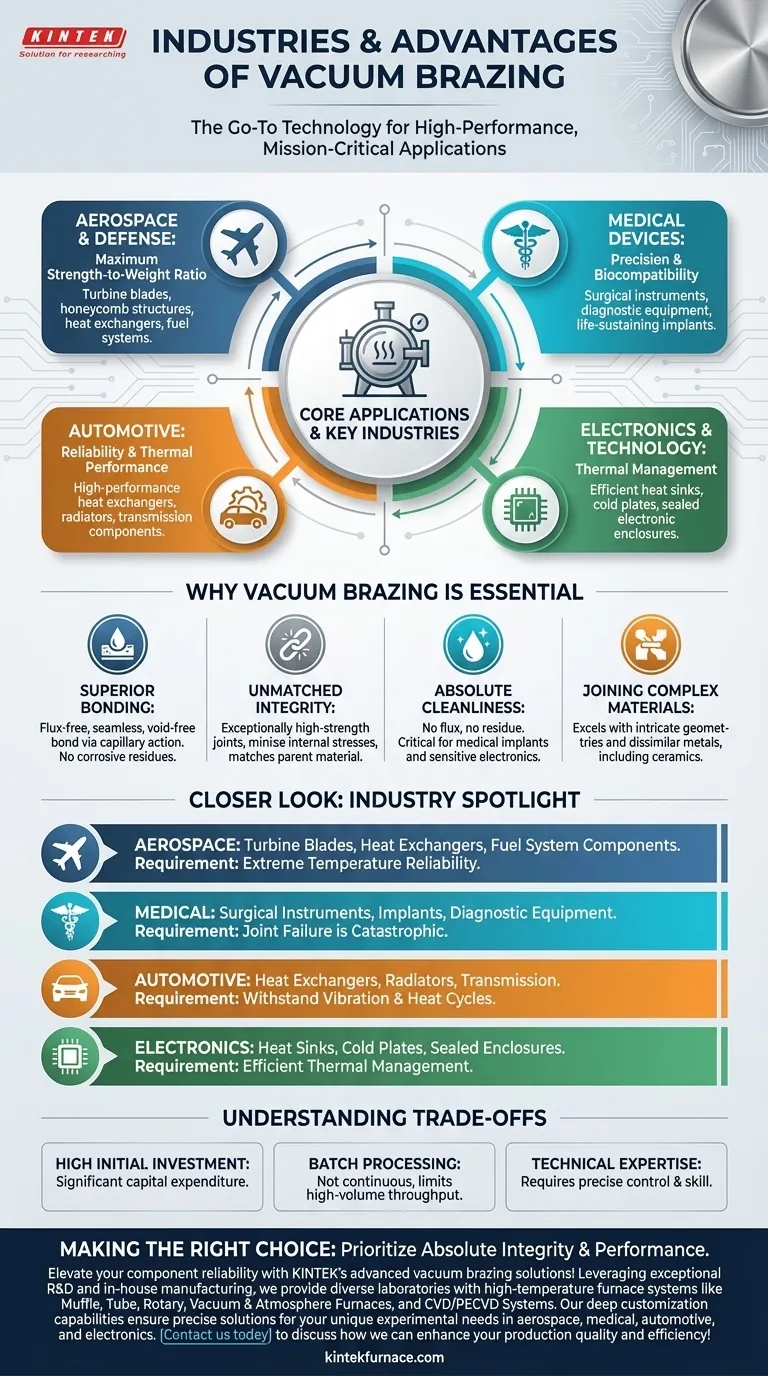
At its core, vacuum brazing is the go-to joining technology for the world's most demanding industries. It is most commonly used in aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics manufacturing. These sectors rely on the process to create components where failure is not an option, leveraging its ability to produce exceptionally strong, clean, and complex assemblies.
The widespread adoption of vacuum brazing is not accidental. It is a direct result of its unique ability to create flux-free, metallurgically superior joints in a highly controlled environment, making it indispensable for high-performance and mission-critical applications.

Why Vacuum Brazing is Essential for Critical Applications
The choice to use vacuum brazing stems from a need for ultimate reliability. The process involves heating components with a filler metal in a vacuum furnace, which fundamentally changes the quality of the resulting bond.
The Principle of Superior Bonding
A vacuum environment prevents oxidation during the heating cycle. This allows the molten filler metal to wet and flow into the joints purely through capillary action, creating a strong, seamless, and void-free bond without the need for corrosive chemical fluxes.
Unmatched Joint Integrity
The slow, uniform heating and cooling cycles within a vacuum furnace minimize internal stresses on the components. This results in exceptionally high-strength joints that often match or exceed the strength of the parent materials themselves.
Absolute Cleanliness and Purity
Because no flux is used, the finished part is incredibly clean, with no residue to remove or trap. This is a non-negotiable requirement for medical implants, where biocompatibility is critical, and for sensitive electronics, where contaminants could cause failure.
Joining Complex and Dissimilar Materials
Vacuum brazing excels at joining intricate geometries and dissimilar materials that are difficult or impossible to weld. This includes bonding metals like stainless steel, titanium, and nickel alloys to each other or even to ceramics.
A Closer Look at Key Industries
The theoretical benefits of vacuum brazing translate into tangible advantages for specific industrial applications.
Aerospace and Defense
This sector demands a maximum strength-to-weight ratio and reliability in extreme temperatures. Vacuum brazing is used to create lightweight yet robust assemblies like turbine blades, honeycomb structures, heat exchangers, and fuel system components.
Medical Devices
Precision, cleanliness, and biocompatibility are paramount. The process is vital for manufacturing surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and life-sustaining implants where joint failure could have catastrophic consequences.
Automotive
Reliability and thermal performance are key drivers in the automotive industry. Vacuum brazing is essential for producing high-performance heat exchangers, radiators, fuel injectors, and critical transmission components that must withstand constant vibration and heat cycles.
Electronics and Technology
As electronics become smaller and more powerful, thermal management is a primary challenge. Vacuum brazing is used to create highly efficient heat sinks, cold plates, and sealed electronic enclosures that protect sensitive components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not the solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
High Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital expenditure. The cost of the equipment and its installation makes it best suited for high-value components where the benefits justify the investment.
Batch Processing Limitations
Unlike continuous welding or soldering lines, vacuum brazing is a batch process. Loading, pumping down the vacuum, running the heat cycle, and cooling can take several hours, which can limit high-volume throughput.
Technical Expertise Required
Operating a vacuum furnace and designing a successful brazing cycle requires a high degree of technical skill. Success depends on precise control over temperature, vacuum levels, and material selection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right joining process depends entirely on your project's primary requirements.
- If your primary focus is ultimate strength and reliability for mission-critical parts: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice, especially for complex geometries in aerospace or medical applications.
- If your primary focus is thermal performance and purity for sensitive devices: The clean, void-free joints from vacuum brazing are ideal for electronics and high-purity systems.
- If your primary focus is mass production of reliable, complex assemblies: Vacuum brazing offers a significant quality advantage for automotive components like heat exchangers, justifying its use over cheaper alternatives.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum brazing is a decision to prioritize the absolute integrity and performance of the final component.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, heat exchangers, fuel systems |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, implants, diagnostic equipment |
| Automotive | Heat exchangers, radiators, transmission components |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, cold plates, sealed enclosures |
Elevate your component reliability with KINTEK's advanced vacuum brazing solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs in aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your production quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















