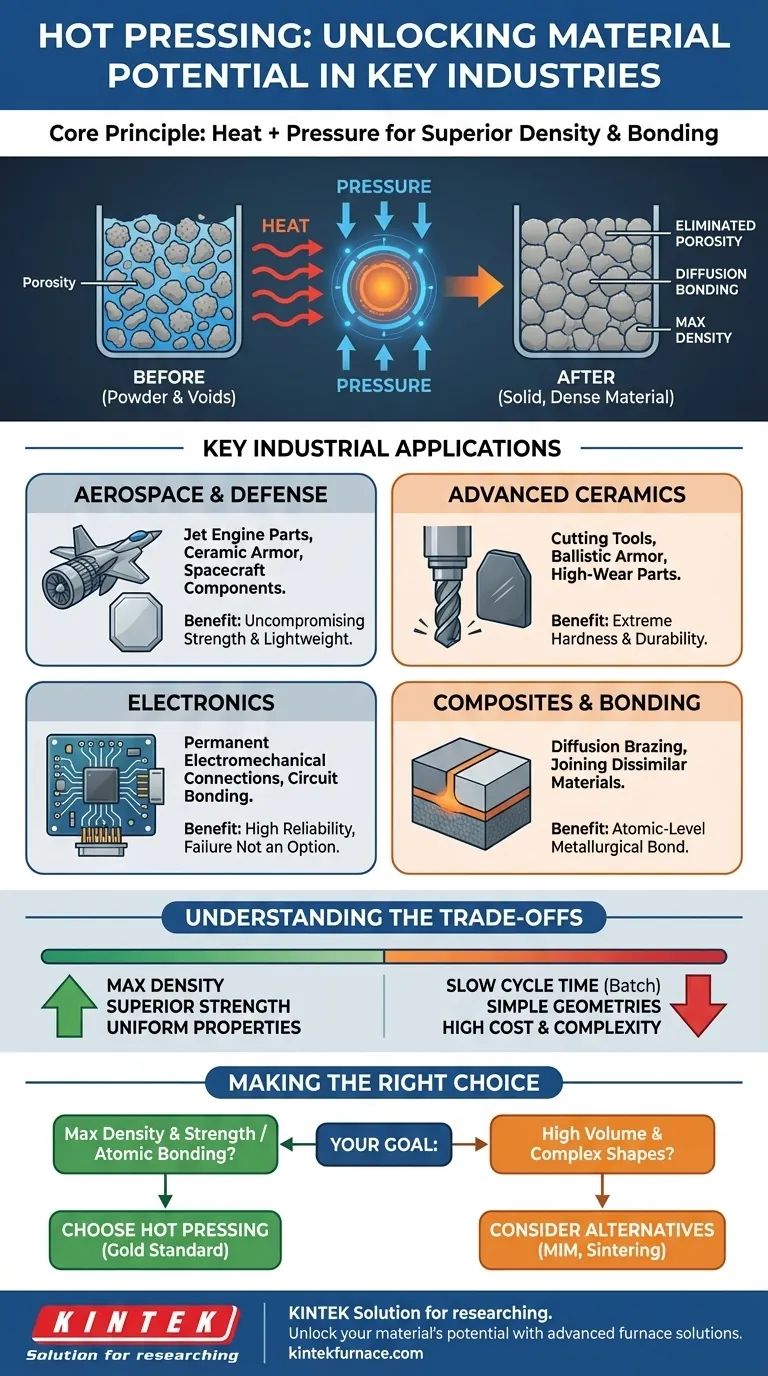
At its core, hot pressing is a critical manufacturing process used in industries where material performance cannot be compromised. It is most commonly employed in the aerospace, advanced ceramics, electronics, and defense sectors for producing components with exceptional strength and density.
Hot pressing is chosen not merely to shape a part, but to fundamentally alter its microstructure. By applying simultaneous heat and pressure, it eliminates internal voids and fuses material powders into a solid, high-density state, achieving properties unattainable through other methods.

How Hot Pressing Unlocks Material Potential
To understand why specific industries rely on hot pressing, you must first understand the unique changes it imparts on a material at the microscopic level.
The Core Principle: Heat and Pressure
Hot pressing involves placing a material—often in powder form—into a die and subjecting it to high temperatures and significant mechanical pressure at the same time. This combination is the key to its effectiveness.
Eliminating Porosity for Maximum Density
The primary function of the pressure is to squeeze out the empty spaces, or porosity, between the initial material particles. This consolidation process pushes the material toward its theoretical maximum density, which is directly linked to improved mechanical strength and reliability.
Promoting Diffusion and Bonding
Simultaneously, the high temperature energizes the atoms within the material. This energy allows them to move and diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles, creating strong, permanent metallurgical bonds. The result is a single, monolithic piece with uniform properties.
Key Industrial Applications
The ability to create dense, defect-free materials makes hot pressing indispensable for high-stakes applications.
Aerospace and Defense: For Uncompromising Strength
These industries demand materials that are both lightweight and incredibly strong. Hot pressing is used to manufacture components like advanced ceramic armor for vehicles and personnel, as well as high-performance parts for jet engines and spacecraft that must withstand extreme conditions.
Advanced Ceramics: Creating Super-Hard Materials
Hot pressing is essential for creating non-oxide ceramics like boron carbide or silicon nitride. These materials are used for industrial cutting tools, high-wear components, and ballistic armor plates, where extreme hardness and durability are the primary requirements.
Composites and Bonding: Fusing Dissimilar Materials
The process is also used to create composite materials or to join different materials together. A key example is diffusion brazing, where a hot press furnace facilitates a bond between two parts at an atomic level, creating a joint that is as strong as the parent materials themselves.
Electronics: For Permanent and Reliable Connections
In specialized electronics, hot pressing is used to create permanent electromechanical connections. This can involve bonding flexible circuits to rigid boards or creating other high-reliability interconnects where failure is not an option.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its benefits, hot pressing is not a universal solution. It comes with specific limitations that make it unsuitable for many common manufacturing scenarios.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Hot pressing is a batch process that is inherently slow. The heating, pressing, and cooling cycles can take several hours, making it poorly suited for high-volume production where speed is a priority.
Geometric Limitations
The process is generally limited to producing parts with relatively simple geometries, such as discs, blocks, or plates. Creating highly complex, three-dimensional shapes is difficult and often requires extensive post-process machining, which adds cost.
Cost and Complexity
Hot press furnaces and the high-strength dies required are expensive capital equipment. The process demands precise control over temperature and pressure gradients, adding to operational complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting hot pressing depends entirely on whether the final material properties justify the cost and complexity of the process.
- If your primary focus is creating materials with maximum density and mechanical strength: Hot pressing is the gold standard for eliminating porosity and achieving peak performance in advanced ceramics and composites.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials with a robust metallurgical bond: Hot pressing enables diffusion bonding and brazing, creating joints that are often superior to conventional welding or fastening.
- If your primary focus is producing complex parts in high volume: You should investigate alternative methods like metal injection molding (MIM) or conventional sintering, which offer higher throughput for intricate shapes.
Ultimately, you choose hot pressing when the integrity of the material itself is the most critical factor for success.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Jet engine parts, ceramic armor, spacecraft components |
| Advanced Ceramics | Cutting tools, ballistic armor, high-wear parts |
| Electronics | Permanent electromechanical connections, circuit bonding |
| Composites & Bonding | Diffusion brazing, joining dissimilar materials |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether you're in aerospace, ceramics, electronics, or defense, our expertise in hot pressing can help you achieve maximum density, strength, and reliability. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your high-stakes applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What role does a high-pressure press play in the preparation of zinc sample pellets? Optimize Carbothermic Reduction
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?



















