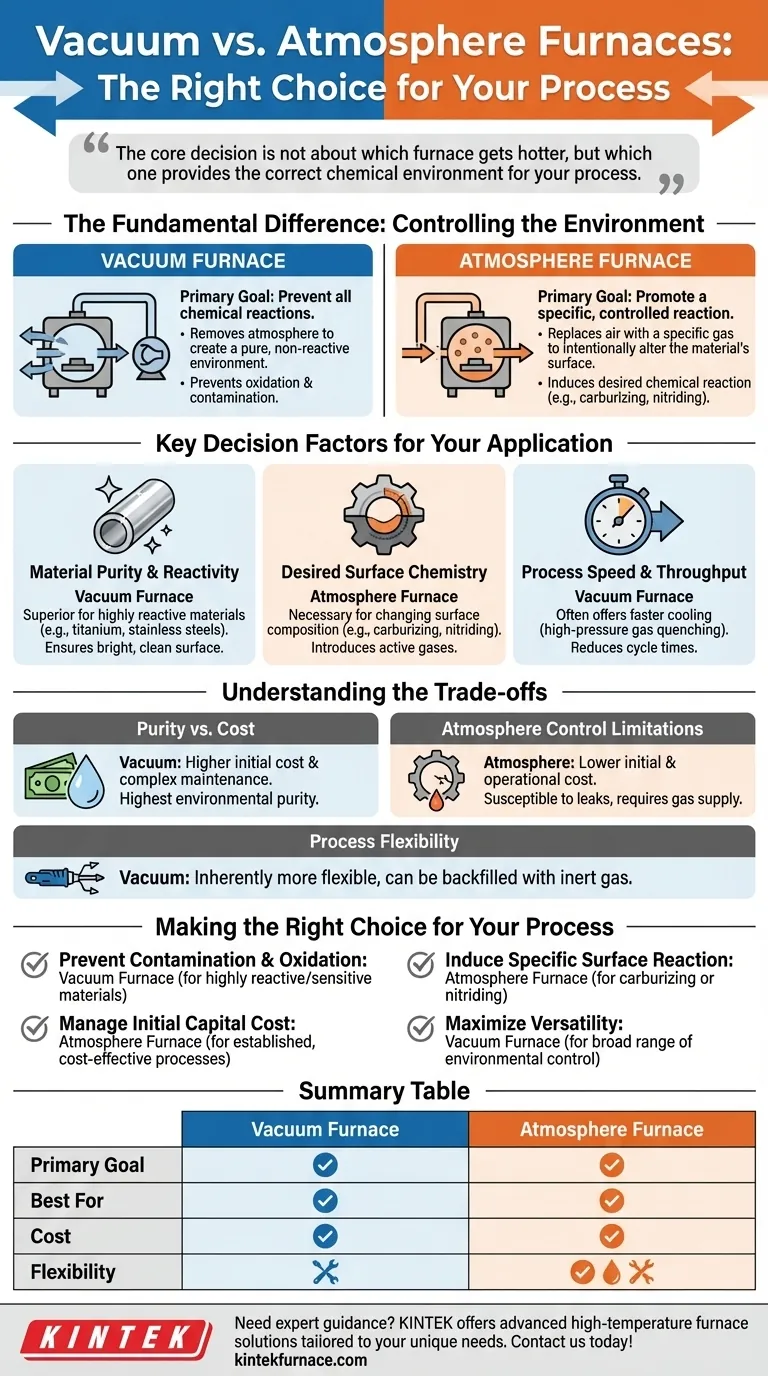
Choosing between a vacuum furnace and an atmosphere furnace comes down to one primary factor: whether your goal is to prevent all chemical reactions or to promote a specific, controlled reaction. A vacuum furnace removes the atmosphere to create a pure, non-reactive environment, while an atmosphere furnace replaces the air with a specific gas to intentionally alter the material's surface.
The core decision is not about which furnace gets hotter, but which one provides the correct chemical environment for your process. A vacuum furnace is for achieving purity by removing reactive elements, whereas an atmosphere furnace is for achieving specific properties by adding them.
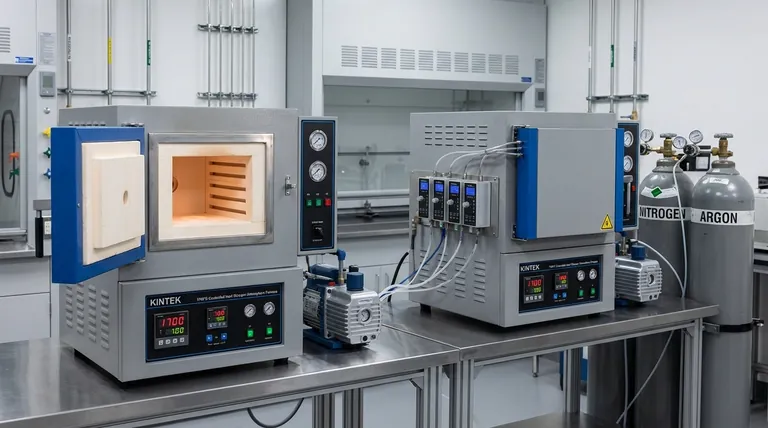

The Fundamental Difference: Controlling the Environment
The choice between these two furnaces is fundamentally about how you intend to control the chemistry inside the chamber at high temperatures.
How a Vacuum Furnace Works
A vacuum furnace operates by pumping out nearly all the air and other gases from a sealed chamber before heating begins.
The primary goal is to create an environment that is as close to empty as possible. This prevents oxidation and contamination from atmospheric gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, which can be highly reactive with materials at elevated temperatures.
How an Atmosphere Furnace Works
An atmosphere furnace works by first purging the ambient air from its chamber and then backfilling it with a carefully controlled gas or mixture of gases.
The goal is to create a specific, artificial atmosphere. This environment is used to induce a desired chemical reaction on the surface of the part, such as carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen). It can also be used with inert gases like argon to simply prevent oxidation in a more cost-effective way than a full vacuum.
Key Decision Factors for Your Application
Your specific process requirements will dictate which technology is the appropriate choice.
Material Purity and Reactivity
If you are heat-treating materials that are highly sensitive to oxygen or other impurities, a vacuum furnace is superior. This includes materials like titanium, refractory metals, and certain stainless steels.
The near-total removal of atmospheric gases ensures the material's surface remains bright, clean, and uncontaminated throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Desired Surface Chemistry
If your process requires changing the chemical composition of the material's surface, you must use an atmosphere furnace.
Processes like carburizing, nitriding, and carbonitriding depend on the introduction of active gases (like methane or ammonia) to diffuse elements into the steel's surface to increase hardness and wear resistance. This is impossible in a vacuum.
Process Speed and Throughput
Vacuum furnaces, particularly those equipped with high-pressure gas quenching, can often offer faster cooling rates than traditional atmosphere furnaces that rely on oil or slow gas cooling.
This rapid, controlled cooling can reduce cycle times and, in some cases, minimize part distortion, leading to higher overall throughput.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is universally "better." Each comes with a distinct set of compromises related to cost, purity, and flexibility.
The Purity vs. Cost Equation
Vacuum furnaces provide the highest level of environmental purity, but this comes at a price. They typically have a higher initial capital cost and more complex maintenance requirements due to pumps, seals, and control systems.
Atmosphere furnaces are generally less expensive to purchase and operate for standard processes, making them a cost-effective choice when absolute purity is not the primary concern.
Atmosphere Control Limitations
While a vacuum furnace offers the purest environment, achieving a perfect vacuum is impossible. Trace amounts of gas will always remain.
Conversely, atmosphere furnaces are susceptible to leaks that can introduce oxygen or moisture, potentially compromising the process. Maintaining the integrity of the chamber and gas supply is critical for consistent results.
Process Flexibility
A vacuum furnace is inherently more flexible. It can be operated at various vacuum levels or backfilled with an inert gas to act as a high-purity atmosphere furnace.
A standard atmosphere furnace, however, cannot pull a high vacuum. This makes the vacuum furnace a more versatile tool, especially for research and development or job shops that handle a wide variety of materials and processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific outcome you need to achieve for your material.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination and oxidation: A vacuum furnace is the definitive choice for processing highly reactive or sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is inducing a specific surface reaction: An atmosphere furnace is necessary to introduce the active gases required for processes like carburizing or nitriding.
- If your primary focus is managing initial capital cost for established processes: A dedicated atmosphere furnace is often the more economical solution when a specific, well-defined gas environment is required.
- If your primary focus is maximizing versatility for varied applications: A vacuum furnace with inert gas backfilling capabilities offers the broadest range of environmental control.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one that provides precise and repeatable control over the chemical environment your material requires to achieve its final properties.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Vacuum Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prevent chemical reactions by removing atmosphere | Promote specific reactions with controlled gases |
| Best For | Highly reactive materials (e.g., titanium, stainless steels) | Surface treatments (e.g., carburizing, nitriding) |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance costs | Lower initial and operational costs |
| Flexibility | High (can backfill with inert gases) | Limited to specific gas environments |
Need expert guidance to select the perfect furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you require purity, specific surface chemistry, or cost-effective performance, we can help you achieve precise and repeatable results. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance



















