The quality and consistency of a thin film created through Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are not accidental; they are the direct result of meticulous control. The flow of precursor gases into the reaction chamber is governed by a critical component known as a Mass Flow Controller (MFC), which precisely regulates the rate and composition of the gas mixture to ensure the desired outcome.
The core principle of gas control in CVD is not just about using a single component, but about designing an entire gas delivery system. While the Mass Flow Controller is the heart of this system, its performance depends on the integrity of the entire gas path, from the source cylinder to the reaction chamber.
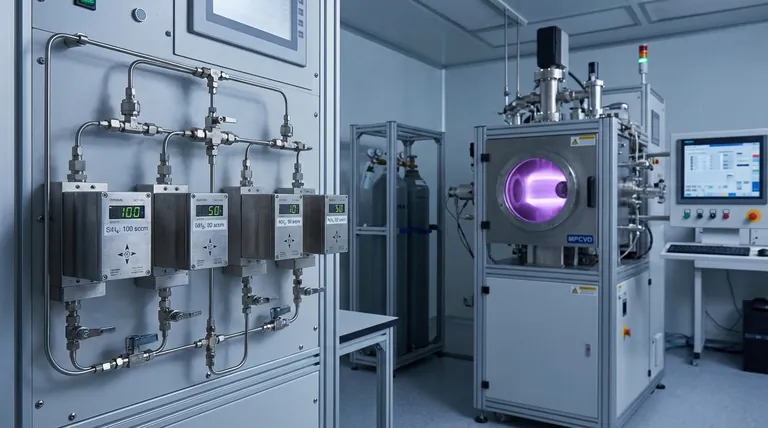

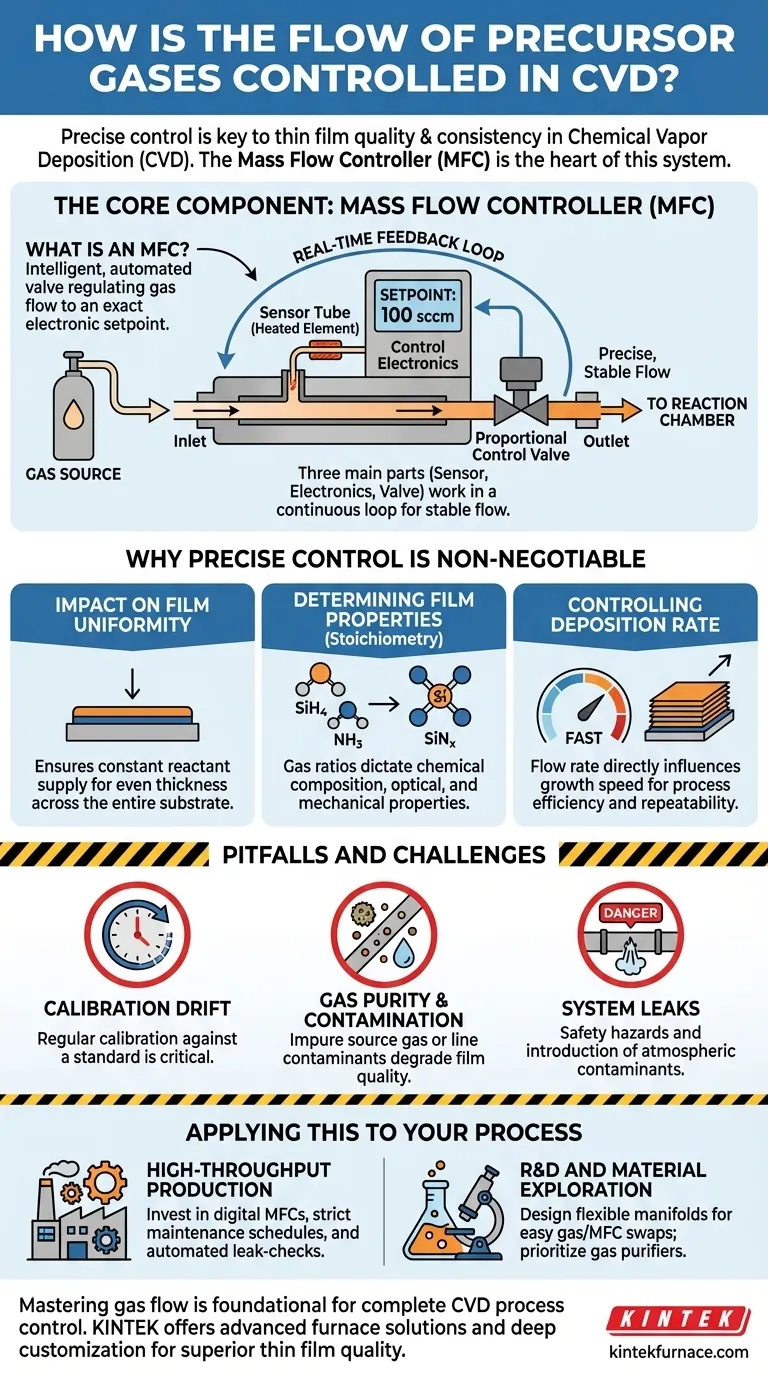
The Core Component: The Mass Flow Controller (MFC)
What is a Mass Flow Controller?
An MFC is a self-contained device designed to measure and control the flow of a specific gas at a specified rate. Think of it as an intelligent, automated valve.
You provide it with an electronic setpoint (e.g., "100 standard cubic centimeters per minute"), and the MFC automatically adjusts its internal valve to maintain that exact flow rate, regardless of fluctuations in upstream or downstream pressure.
How an MFC Works
At its core, an MFC consists of three main parts: a sensor, control electronics, and a proportional control valve.
- A small portion of the gas is diverted through a tiny sensor tube with a heated element.
- The gas flow cools the element, and the amount of cooling is directly proportional to the mass of gas flowing through it.
- The control electronics compare this measured flow rate to the user's setpoint and send a signal to the control valve, telling it to open or close slightly to correct any deviation.
This continuous feedback loop happens in real-time, ensuring the gas flow remains exceptionally stable.
Why Precise Control is Non-Negotiable
The rigorous control provided by MFCs is essential because the gas flow directly dictates the final properties of the thin film.
Impact on Film Uniformity
To grow a film of even thickness across an entire substrate, every part of that substrate must be exposed to the same concentration of precursor gases.
MFCs ensure a constant and stable supply of reactants, which is the first and most critical requirement for achieving uniform deposition.
Determining Film Properties
The chemical composition, or stoichiometry, of the final film is determined by the ratio of different precursor gases.
For example, when depositing silicon nitride (SiNx), the ratio of silane (SiH4) to ammonia (NH3) gas will determine the final Si:N ratio in the film. This, in turn, dictates its optical and mechanical properties.
Controlling Deposition Rate
The rate at which the film grows is directly influenced by the amount of precursor gas delivered to the chamber.
Higher flow rates generally lead to faster deposition, a key parameter for process efficiency. MFCs allow operators to precisely tune this rate for repeatable results batch after batch.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Challenges
Even with high-quality MFCs, achieving perfect gas delivery requires attention to the entire system. Ignoring these factors can undermine the precision of the controller.
MFC Calibration Drift
Like any precision instrument, MFCs can drift over time. Regular calibration against a known standard is critical to ensure the device's reported flow rate matches the actual flow rate.
Gas Purity and Contamination
The MFC can only control the gas it is given. If the source gas is contaminated or if the gas lines themselves introduce impurities (like moisture or oxygen), these contaminants will be delivered to the chamber and incorporated into the film, degrading its quality.
System Leaks
A small leak anywhere in the gas delivery system can have a major impact. An inward leak can introduce atmospheric contaminants, while an outward leak of a toxic or pyrophoric gas poses a significant safety hazard.
Applying This to Your Process
Your approach to designing and maintaining a gas delivery system depends on your ultimate goal.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: Invest in high-quality MFCs with digital control interfaces, implement a strict preventative maintenance and calibration schedule, and use automated leak-checking procedures.
- If your primary focus is R&D and material exploration: Design a flexible gas manifold system that allows different gases and MFCs to be swapped easily, and prioritize gas purifiers on each line to ensure material purity during experimentation.
Ultimately, mastering the flow of precursor gases is the foundational step toward achieving complete control over the CVD process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Component | Mass Flow Controller (MFC) for precise gas regulation |
| How MFC Works | Uses sensor, control electronics, and valve for real-time flow adjustment |
| Importance | Ensures film uniformity, stoichiometry, and deposition rate control |
| Challenges | Calibration drift, gas purity, and system leaks |
| Applications | High-throughput production and flexible R&D setups |
Achieve unparalleled precision in your CVD processes with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior thin film quality and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can elevate your research and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of MPCVD in diamond synthesis? Achieve High-Purity, Scalable Diamond Production
- Why is MPCVD considered a cornerstone of modern materials science and engineering? Unlock High-Purity Materials for Innovation
- How does MPCVD achieve high growth rates for diamond synthesis? Unlock Rapid, High-Quality Diamond Growth
- In which industries is the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system commonly used? Unlock High-Purity Material Synthesis
- How does MPCVD compare to other CVD methods like HFCVD and plasma torch? Uncover Superior Film Purity and Uniformity



















